Перейти к содержанию
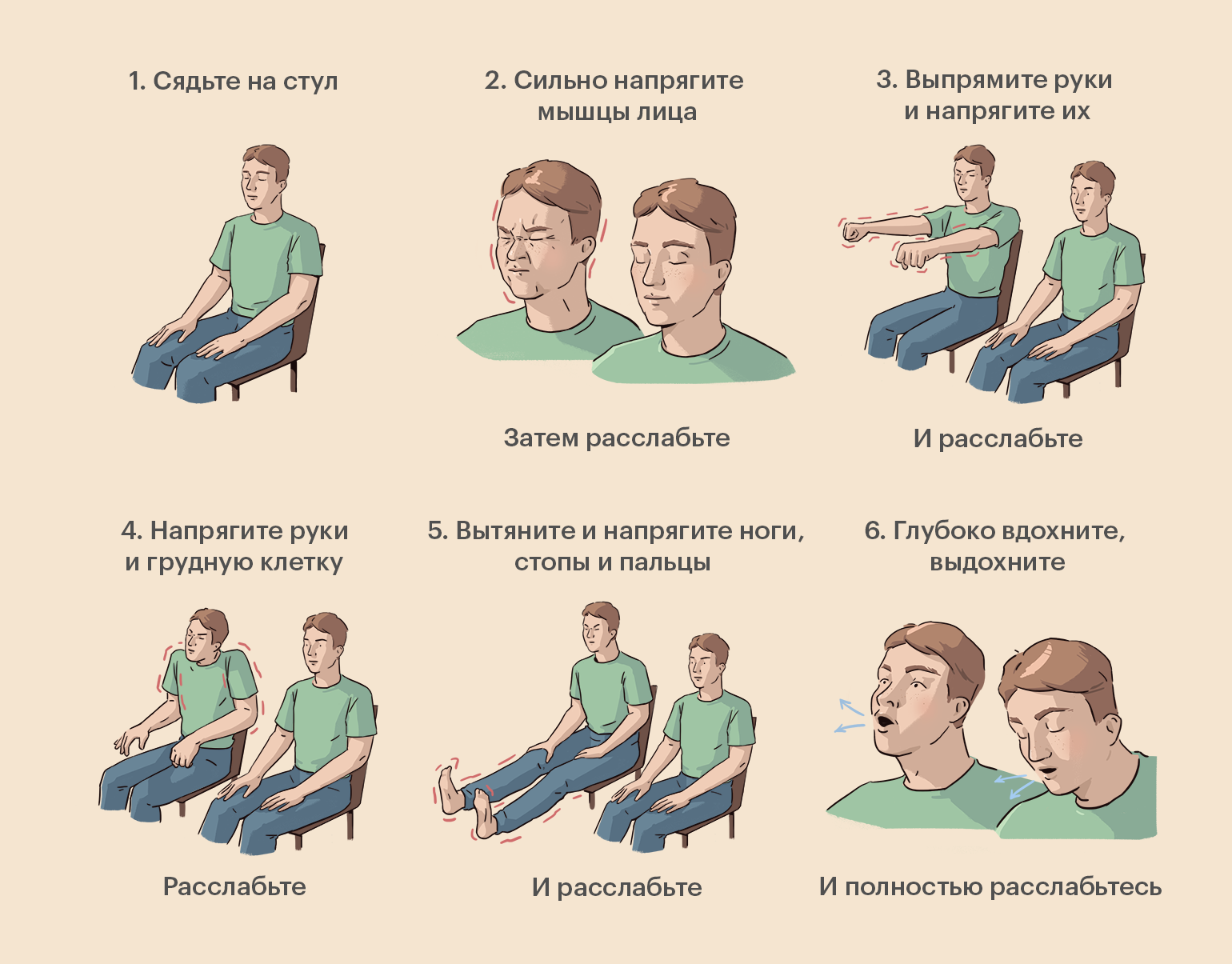
Катастрофический сценарий
Любое стрессовое переживание трансформируется в нашей психике в агрессию. Тревога делает нас раздражительными, крикливыми — мы срываемся даже на близких людей. Тревожные состояния важно проговаривать, и не обязательно со специалистом, можно с подругой, с супругом.
Когда наша тревога связана с какой-то конкретной ситуацией, из которой мы никак не можем найти выход, может помочь упражнение «Катастрофический сценарий», о котором сегодня мы хотим вам рассказать.
Оператор: Роман Тонконогов
Монтаж: Дмитрий Кононов

Наталья Барложецкая
Детский и семейный психолог, более 25 лет работает психологом в одной из московских школ. Специализация – педагог-психолог в социально-коррекционной сфере. Автор книг и статей в области педагогической, детской и возрастной психологии. Ведущая телевизионных программ для детей и родителей. Преподаватель ряда московских вузов.
Нашли ошибку в тексте? Выделите её мышкой! И нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Техника Декатастрофизации Мышления
Катастрофизирующее мышление — это систематическое преувеличение опасности проблемы и вероятности наихудшего будущего.
Примеры катастрофических мыслей:
- Если мы расстанемся, то я навсегда останусь одна!
- Я не справлюсь с работой и меня точно уволят!
- Это беспокойство сведёт меня с ума!
- Мне не поставят зачёт!
- Он целый день не отвечает на звонки, вдруг попал в аварию!?
- Если я скажу что-то не то, то люди обсмеют меня!
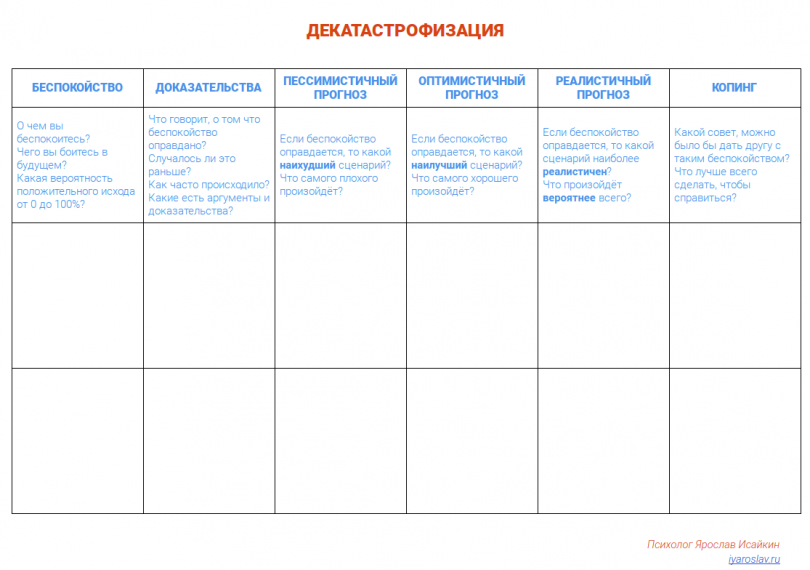
Помочь переучиться не раздувать из мухи слона может помочь техника «Декатастрофизация».
Она помогает рассмотреть альтернативные сценарии развития событий, оценить реальную опасность и определить оптимальную реакцию
Полную версию техники вы можете увидеть в шапке этой записи. Она состоит из 6 шагов.
Скачать PDF Декатастрофизации
3-шаговая техника декатастрофизации
Полная версия шаблона достаточно объёмна, но с практикой можно сократить до 3 пунктов:
- Заметьте, какие картинки рисует ваше сознание по поводу будущего и какой интонацией вы разговариваете с собой
- Несколько раз задайтесь вопросом: «Допустим, это произойдёт. Что тогда? Что дальше?». Постарайтесь отвечать себе спокойным ровным голосом
- Задайтесь вопросом: «Что делал бы другой человек на моём месте?». Сохраняйте ровную интонацию в своём голосе
1-шаговая техника декатастрофизации
А с ещё большей практикой, можно сократить до 1 шага:
- Измените интонацию катастрофизирующего внутреннего голоса на мультяшную. Представьте мысль: «ОН МНЕ ИЗМЕНЯЕТ» голосом Микки Мауса
Но если у вас при этом возникает вопрос:
«А ЧТО ЕСЛИ Я НЕ КАТАСТРОФИЗИРУЮ И МОИ ОПАСЕНИЯ РЕАЛЬНЫ? К ЭТОМУ НЕЛЬЗЯ ОТНОСИТЬСЯ ВОТ ТАК НЕСЕРЬЁЗНО»,
то поработайте некоторое время с полной таблицей приложенной к посту.
Скачать PDF Декатастрофизации
Загрузка…
Вас может заинтересовать
#статьи
- 5 дек 2022
-
0
Когнитивно-поведенческая терапия — простыми словами
О том, что такое КПТ, а также об основах направления, его возможностях и ограничениях рассказывает когнитивно-поведенческий терапевт Ирина Волынцева.
Кадр: фильм «Иррациональный человек»
Пишет и редактирует тексты для СМИ и рассылок. Любит объяснять сложное простыми словами. Пытается разобраться, почему люди делают то, что делают.
Из статьи вы узнаете:
- что такое когнитивно-поведенческая терапия;
- кому она помогает;
- чем этот подход отличается от других популярных направлений;
- как помочь себе самостоятельно, используя техники когнитивно-поведенческой терапии.
Психолог, КПТ-терапевт, также работает в подходах схематерапии и терапии принятия и ответственности (АСТ). Член Ассоциации когнитивно-поведенческой психотерапии.
Когнитивно-поведенческая терапия (КПТ) — это психологический подход, основанный на идее, что мысли и убеждения влияют на эмоциональное состояние человека.
С точки зрения этого подхода причина негативных переживаний — не в жизненных обстоятельствах, а в их интерпретации человеком, которая часто опирается на ложные убеждения о себе, других людях и мире.
КПТ учит выявлять убеждения и ошибки мышления, которые искажают восприятие реальности, а также формировать на их месте более реалистичные и изменять поведение, опираясь на новую картину мира.
Автоматические мысли — это умозаключения, которые не основаны на рефлексии, они возникают спонтанно и на автомате.
Такие мысли — результат глубинных убеждений, то есть ключевых представлений человека о самом себе. Как правило, у людей есть как позитивные убеждения о себе («Я способный», «Я справлюсь», «Я нравлюсь людям»), так и негативные («Я должен всё делать идеально», «Со мной что-то не так», «Я непривлекателен»).
Но под воздействием стресса, сильных негативных эмоций (грусть, чувство одиночества, страх) или при ментальном расстройстве, например депрессии, именно негативные убеждения проявляются и становятся первостепенными. Так появляются мысли «Мне никогда не стать таким, как они», «Я опять облажался», «Меня уволят».
Также негативные убеждения могут сформироваться ещё в детстве и сохраняться из-за когнитивных искажений. Человек принимает их за правду неосознанно, не пытаясь выяснить, имеют ли они под собой почву.
КПТ помогает людям, которые борются:
- с тревожностью;
- с тревожными расстройствами, включая социальную тревогу, ОКР (обсессивно-компульсивное расстройство) и паническое расстройство;
- с биполярным аффективным расстройством, депрессией, фобиями и ПТСР.
Также когнитивно-поведенческая терапия помогает разрешить проблемы в межличностных отношениях, сформировать адекватную самооценку и преодолеть сложности в достижении целей.
Хотя сейчас протокол работы в рамках КПТ предназначен для решения практически любой проблемы, классическая когнитивно-поведенческая терапия второй волны не подходит клиентам в кризисной ситуации или состоянии острого горя.
Для лечения пограничного расстройства личности и ряда других личностных расстройств лучше выбрать методы третьей волны КПТ, которые изначально разрабатывали именно для таких случаев. Например, диалектически-поведенческую терапию (ДБТ) или схематерапию.
Первой волной когнитивно-поведенческой терапии считают появившийся в 1920-х бихевиоризм — направление психологии, ищущее способы изменить поведение человека.
Классической КПТ считается вторая волна, совмещающая поведенческую и когнитивную психологию. В основе её метода — поиск и изменение дезадаптивных, то есть причиняющих страдание, мыслей, а затем и коррекция поведения.
Когнитивно-поведенческая терапия третьей волны фокусируется на отношении человека к происходящему с ним: она опирается на принципы осознанности (mindfulness) и принятия.
Сократический диалог. В основе этой техники лежит представление о том, что человек уже обладает достаточными знаниями, чтобы понять суть своей проблемы. Терапевт лишь помогает ему сложить пазл, задавая вопросы. В разговоре специалист обращает внимание на те стороны проблемы, которые ускользают от клиента, но не подталкивает к какому-то конкретному ответу.
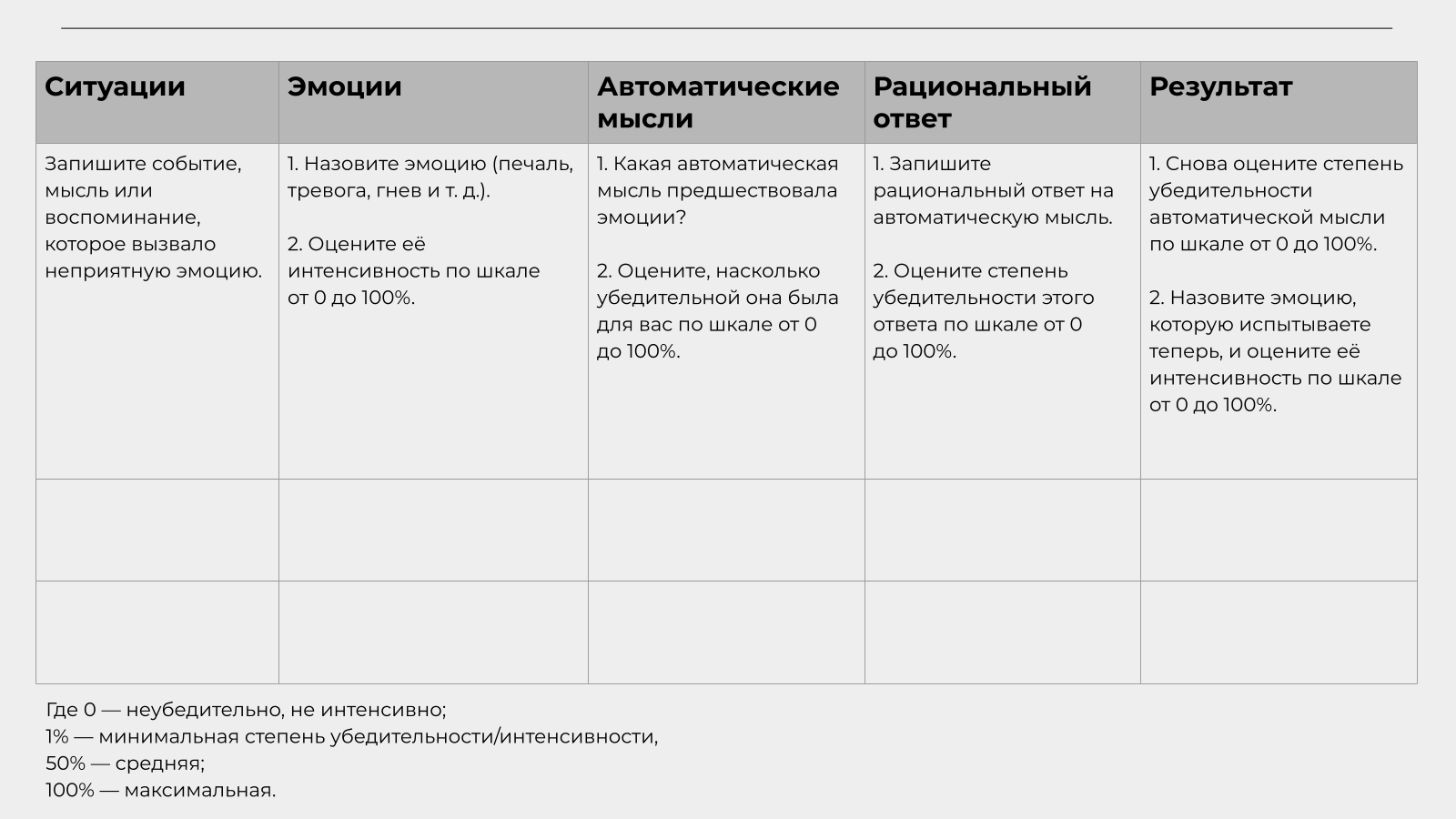
Техники, направленные на коррекцию когнитивных искажений. Самый известный пример — дневник автоматических мыслей. Терапевт предлагает клиенту, когда тот заметит изменение в своём настроении, записать произошедшую ситуацию, возникшую мысль и эмоцию, которую вызвала эта мысль. А затем определить, какое когнитивное искажение он допустил и насколько теперь убеждён в истинности этой автоматической мысли.
Поведенческие эксперименты. Чтобы проверить достоверность убеждений клиента (например, «Если я подойду на вечеринке к девушке, она посмотрит на меня как на таракана и уйдёт») или закрепить новые способы мышления и поведения, терапевт может предложить эксперимент и помочь его спланировать. Для социально тревожного человека, например, им может стать поход в людное место, где он попробует с кем-то заговорить.
Также в когнитивно-поведенческой терапии могут применять элементы осознанности, например медитации и техники прогрессивной релаксации.
Иллюстрация: Катя Павловская для Skillbox Media
Называют три основных отличия.
- Роль терапевта. В КПТ его отношения с клиентом — скорее партнёрство и наставничество, чем «врач — пациент». Терапевт и клиент совместно решают, чему посвятить сегодняшнюю сессию, как часто видеться и что делать между встречами. По мере улучшения своего состояния клиент всё активнее участвует в планировании.
- Работа со «здесь и сейчас». В классической когнитивно-поведенческой терапии второй волны не работают с проживанием эмоций по отношению к родителям и воспоминаний из детства. КПТ использует детский опыт, лишь чтобы понять источник проблемы и показать клиенту, что его актуальный способ мышления и поведения — не более чем привычка.
- Сроки терапии. Согласно исследованиям, КПТ даёт один из самых быстрых результатов.
Когнитивно-поведенческая терапия как подход придаёт большое значение письменным практикам, предоставляющим человеку пространство для рефлексии. Самая известная из них — дневник записи автоматических мыслей, о котором мы говорили выше. Вести такой дневник удобно, используя специальный бланк.
Источник: Skillbox
Техника падающей стрелы. Запишите автоматическую мысль, вызывающую у вас неприятные эмоции, например «Моё домашнее задание неидеально», и спросите себя: «И что теперь?» Проделайте то же самое со всеми последующими ответами, пока не придёте к мысли, для которой ответа на вопрос «И что теперь?» не найдётся. Так вы сможете ближе подобраться к тому, что вас беспокоит на самом деле.
Вот пример подобной цепочки рассуждений:
— Моё домашнее задание неидеально.
— И что?
— Преподаватель подумает, что я не старался.
— И что?
— Я получу незачёт.
— И что?
— Все будут считать меня неудачником.
— И что?
— Со мной никто не захочет общаться.
— И что?
— Я останусь в одиночестве и не смогу с этим справиться.
- Дэвид Бёрнс, «Терапия настроения. Клинически доказанный способ победить депрессию без таблеток». Практические упражнения, позволяющие справиться с депрессивным состоянием и тяжёлыми мыслями.
- Роберт Лихи, «Свобода от тревоги. Справься с тревогой, пока она не расправилась с тобой». Пошаговое руководство по избавлению от разных типов навязчивого беспокойства — от фобий до ПТСР.
- Недра Гловер Тавваб, «Установи границы, обрети душевный покой. Как построить здоровые отношения с окружающими». Книга о том, как методики когнитивно-поведенческой терапии помогают выстроить здоровые личные границы.
- Аарон Бек, «Узники ненависти: когнитивная основа гнева, враждебности и насилия». Книга основателя когнитивной психотерапии о том, как автоматические мысли и когнитивные искажения приводят к насилию как на уровне отдельных людей, так и на уровне государств.
- Анатейша С. Ким, Алисия М. дель Прадо, «Так можно: сохранить себя в разговорах на конфликтные темы». Руководство по разрешению конфликтов, возникающих в разговоре, с помощью методов когнитивно-поведенческой терапии.

Учись бесплатно:
вебинары по программированию, маркетингу и дизайну.
Участвовать

Школа дронов для всех
Учим программировать беспилотники и управлять ими.
Узнать больше
Catastrophizing is an illogical belief a lot of us have in trusting that something is far shoddier than it really is.
Catastrophizing usually can take place in two different kinds of methods.
One is creating a catastrophe out of a present state, and the other one is imagining making a catastrophe out of an upcoming state.
Type 1
The first of these is making a catastrophe out of a condition.
For example, if you are a shop assistant and haven’t made a sale for a moment, you may have faith that you are a complete and utter failure and you will drop your profession.
In reality, it may only be a momentary condition, and there are things that you can do to change this condition.
Alternative instance is trusting that if you make one small error at your job, you may get fired.
This sort of catastrophizing takes a present condition and gives it a truly adverse spin.
Type 2
The second kind of catastrophizing is somewhat related to the first, but it is more cerebral and more upcoming oriented.
This kind of catastrophizing happens when we look to the future and forestall all the things that are going to go wrong. We then make a reality around those opinions.
For the reasons that we trust something will go incorrect, we make it go wrong.
Falling prey to catastrophizing is like striking out in attention before you even get to the plate.
Both of these kinds of catastrophizing restrict your chances in life, effort, relations and more.
It can distress our whole viewpoint in life, and makes a self-fulfilling prediction of failure, dissatisfaction, and underachievement.
Both types may lead you to self-pity, to an irrational, negative belief about the situation, and to a sensation of impossibility about your future forecasts.
Additionally, both of these kinds of catastrophizing will describe either the company or non-appearance of other opportunities, and probably paralyse you from going additional with hard work in the direction of your goal line in life.
Causes of Catastrophizing
It’s unclear what exactly causes catastrophizing. It could be a coping method learned from family or other significant people in a person’s life.
It could be a consequence of something learned, or could be connected to brain chemistry.
Research Trusted Source connecting people who catastrophize and who also have long-lasting pain suggest they may have changes in the hypothalamus and pituitary responses, as well as augmented action in the parts of the brain that register emotions allied with pain.
People who have other circumstances such as unhappiness and anxiety, and people who are often exhausted may also be more likely to catastrophize.
While there are numerous possible reasons and donors to catastrophizing, most fall into one of various groups. These are given as follow:
Uncertainty
Uncertainty or being unclear can open an individual up to catastrophic thinking.
An example would be receiving a text message from a contact or partner that recites, “We have to talk.”
This vague note could be something optimistic or undesirable, but a person cannot know which of these it is with just the evidence they have.
So, they may start to visualise the very foulest news.
Value
Relationships and circumstances that a person grips in high value can result in a propensity to catastrophize.
When something is chiefly important to a person, the concept of loss or trouble can be harder to deal with.
An example would be smearing for a job that an individual wants.
They may start to envision the great dissatisfaction, nervousness, and unhappiness they will be involved in if they do not get the job before the group has even made any choices.
Fear
Fear, particularly illogical fear, plays a big share in catastrophizing.
If a person is frightened of going to the doctor, they could twitch to think about all the bad things a surgeon could tell them, even if they are just going for a check-up.
An individual may also practise catastrophizing connected to a medical disorder or past event in their life.
How Does Catastrophizing Affect You?
Regardless of whether you do it deliberately or not, continually catastrophizing can affect you in two different ways: genuinely and emotionally.
Emotional Effects
In his book Feeling Good, Dr. David Burns portrays catastrophizing as another name for the amplification segment of “Amplification and Minimization,” which positions at number six on his rundown of normal cognitive contortions.
Cognitive contortions are examples of erroneous and negative thinking that stay at the core of temperament issues, for example, tension and sadness.
The thought, created by analyst Aaron Beck and clarified by Burns, is that steady negative thinking prompts consistent negative feelings.
This is the place the side effects of melancholy and tension begin to kick in.
As an individual from a family that exposed them to cognitive mutilation, disastrous thinking looks somewhat like reality, and can really affect the cataclysmic mastermind’s life.
At the point when you catastrophize, your brain takes a little issue and incorporates it with a debacle of immeasurable scope.
That sort of continued thinking is staggeringly poisonous to your emotional atmosphere.
William Ralph Inge is credited with saying, “Stress is intrigue paid on inconvenience before it comes due.”
At the end of the day, investing all your energy stressing and envisioning fiascoes that may never happen denies you of the delight of the current second and acquires with enthusiasm from your future.
Physical Effects
Catastrophizing is such incredible power, that it can impact an individual’s physical wellbeing.
Pain catastrophizing is a genuine wonder that numerous people suffer consistently.
This idea design is intense to such an extent that it prompted the advancement of the catastrophizing pain scale, which basically gauges and inspects the job of catastrophizing in how individuals experience pain.
Steps to manage catastrophic thinking
Cerebral health specialists frequently use methods called cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) to support an individual’s talking about their catastrophic thinking.
These methods need the person to be conscious that they are feeling catastrophic thinking, to know their schedules, and to make an effort to stop and identify where their illogical thinking is coming from.
Following are the instructions to achieve this, which include memorising and making use of the following methods.
These can be supported to manage the conditions.
1. Admitting that unfriendly things occur
Life is filled with trials as well as good and evil days.
Just because one day is not good does not show that all days will be bad.
2. Identifying when opinions are irrational
Catastrophizing frequently follows a separate pattern. A person will start with a belief, such as “I am sad nowadays.”
They will then enlarge on the thought with fear and nervousness, such as, the pain is only going to become inferior.
When a person acquires these opinions, they are healthier prepared to grip them.
3. Saying “stop!”
To stop the boring, catastrophic opinions, an individual may have to say out brash or in their head break.
These arguments can retain the stream of opinions from on-going and support a person to change the sequence of their thinking.
4. Discerning about another consequence
Instead of discerning about an undesirable outcome, consider a positive one or even a less-unfriendly choice.
5. Offering positive confirmations
When it comes to a catastrophic thought, a creature has to trust in themselves and that they can overcome their propensity to fear the foulest.
They may wish to repeat an optimistic assertion to themselves on a daily basis.
6. Excellent self-care
Catastrophic opinions are more likely to take over when an individual is weary and stressed.
Receiving enough rest and appealing in stress-relieving methods, such as exercise, consideration, and journaling, can all support an individual sense better.
Difference between catastrophizing and anxiety
The primary distinction between anxiety and catastrophizing is that anxiety will play a helpful role in every person’s life.
As an example, anxiety is often a positive feeling, because sometimes it will ease someone to take care of themselves.
However, catastrophizing doesn’t typically have any edges.
Having these ruinous thoughts will fill a person’s mind with unnecessary emotions that take time and thought faraway from the truth of a scenario.
Whereas each anxiety and catastrophizing are often harmful, anxiety is helpful in some circumstances.
Treatment
Most people experience worry and worry for a while.
However, if someone perpetually fears the worst or hears from their friends and family that they’re thinking during this means, they’ll have to be compelled to address their ruinous thinking.
For example, if someone experiences this kind of distress due to some underlying medical condition, like depression, a doctor might inflict medicine medications to assist.
Following are the treatments methods:
Choosing Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI’s)
Fluoxetine (Prozac) and paroxetine (Paxil). These drugs upsurge the quantity of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the human mind.
They are frequently the first-line for dealing for people with unhappiness but may also be prearranged for a variability of nervousness complaints.
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
Duloxetine (Cymbalta) and venlafaxine (Effexor).
These medicines rise the quantity of serotonin as well as norepinephrine in the human brain.
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA’s)
These medications are called amitriptyline and nortriptyline (Pamelor).
Clinicians do not propose TCA’s very frequently nowadays because of their unwanted side effects.
Atypical antidepressants
These medicines do not fit into a specific group concerning how they work. Instances comprise bupropion (Wellbutrin, Aplenzin) and trazodone.
Treatment With the Help of Therapy
Since catastrophizing is carefully related with mental illnesses, it’s no astonishment that therapy can efficiently treat catastrophizing.
Cognitive-behavioural treatment, or CBT, is one of the most shared forms of talk therapy.
A 2017 study Trusted Source found that CBT was real at addressing catastrophizing in fibromyalgia patients, and that it aided them better achieve their pain.
CBT tries to address your rational and behavioural patterns.
In the case of catastrophizing, your psychoanalyst might help you know irrational thoughts and swap them with rational ones.
For example, you might be used to thinking, “I handed this statement in late. I’m a total disappointment, and I’m going to lose my job. I’ll be financially destitute.”
Through CBT, you will know that this is an illogical thought.
From time to time, a doctor may originally recommend one type of medication that may not be real in plummeting both unhappiness and catastrophizing.
In this case, the doctor may suggest other medicines also.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Frequently Asked Questions
Is catastrophizing a mental illness?
No, catastrophizing is not a mental illness on its own.
However, catastrophizing is a symptom of many different mental illnesses, such as anxiety, depression, and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD).
How do I stop myself from catastrophizing?
Take control of your situation.
Understand that what you are feeling is temporary, and is not based on facts, but is instead your mind playing tricks on you.
It may also be helpful to think about what you might tell your best friend; if they were freaking out about something, what would you say to them to help them feel better?
Then, apply that same thing you would do or say to a best friend to yourself.
Resources
- https://psychcentral.com/lib/what-is-catastrophizing/
- https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/basics/catastrophizing
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320844
Interested in why people catastrophize? Here are some links to novels about this topic on Amazon:
- https://www.amazon.com/Dont-Feed-Monkey-Mind-Anxiety/dp/B072HTXPY7/ref=sr_1_1?dchild=1&keywords=catastrophizing+and+anxiety&qid=1588099506&sr=8-1
- https://www.amazon.com/Worry-Trick-Brain-Tricks-Expecting/dp/B01HDXCV12/ref=sr_1_2?dchild=1&keywords=catastrophizing+and+anxiety&qid=1588099518&sr=8-2
- https://www.amazon.com/Generalized-Anxiety-Disorder-Workbook-Comprehensive-ebook/dp/B018RSC3Z6/ref=sr_1_4?dchild=1&keywords=catastrophizing+and+anxiety&qid=1588099534&sr=8-4
Catastrophizing is an illogical belief a lot of us have in trusting that something is far shoddier than it really is.
Catastrophizing usually can take place in two different kinds of methods.
One is creating a catastrophe out of a present state, and the other one is imagining making a catastrophe out of an upcoming state.
Type 1
The first of these is making a catastrophe out of a condition.
For example, if you are a shop assistant and haven’t made a sale for a moment, you may have faith that you are a complete and utter failure and you will drop your profession.
In reality, it may only be a momentary condition, and there are things that you can do to change this condition.
Alternative instance is trusting that if you make one small error at your job, you may get fired.
This sort of catastrophizing takes a present condition and gives it a truly adverse spin.
Type 2
The second kind of catastrophizing is somewhat related to the first, but it is more cerebral and more upcoming oriented.
This kind of catastrophizing happens when we look to the future and forestall all the things that are going to go wrong. We then make a reality around those opinions.
For the reasons that we trust something will go incorrect, we make it go wrong.
Falling prey to catastrophizing is like striking out in attention before you even get to the plate.
Both of these kinds of catastrophizing restrict your chances in life, effort, relations and more.
It can distress our whole viewpoint in life, and makes a self-fulfilling prediction of failure, dissatisfaction, and underachievement.
Both types may lead you to self-pity, to an irrational, negative belief about the situation, and to a sensation of impossibility about your future forecasts.
Additionally, both of these kinds of catastrophizing will describe either the company or non-appearance of other opportunities, and probably paralyse you from going additional with hard work in the direction of your goal line in life.
Causes of Catastrophizing
It’s unclear what exactly causes catastrophizing. It could be a coping method learned from family or other significant people in a person’s life.
It could be a consequence of something learned, or could be connected to brain chemistry.
Research Trusted Source connecting people who catastrophize and who also have long-lasting pain suggest they may have changes in the hypothalamus and pituitary responses, as well as augmented action in the parts of the brain that register emotions allied with pain.
People who have other circumstances such as unhappiness and anxiety, and people who are often exhausted may also be more likely to catastrophize.
While there are numerous possible reasons and donors to catastrophizing, most fall into one of various groups. These are given as follow:
Uncertainty
Uncertainty or being unclear can open an individual up to catastrophic thinking.
An example would be receiving a text message from a contact or partner that recites, “We have to talk.”
This vague note could be something optimistic or undesirable, but a person cannot know which of these it is with just the evidence they have.
So, they may start to visualise the very foulest news.
Value
Relationships and circumstances that a person grips in high value can result in a propensity to catastrophize.
When something is chiefly important to a person, the concept of loss or trouble can be harder to deal with.
An example would be smearing for a job that an individual wants.
They may start to envision the great dissatisfaction, nervousness, and unhappiness they will be involved in if they do not get the job before the group has even made any choices.
Fear
Fear, particularly illogical fear, plays a big share in catastrophizing.
If a person is frightened of going to the doctor, they could twitch to think about all the bad things a surgeon could tell them, even if they are just going for a check-up.
An individual may also practise catastrophizing connected to a medical disorder or past event in their life.
How Does Catastrophizing Affect You?
Regardless of whether you do it deliberately or not, continually catastrophizing can affect you in two different ways: genuinely and emotionally.
Emotional Effects
In his book Feeling Good, Dr. David Burns portrays catastrophizing as another name for the amplification segment of “Amplification and Minimization,” which positions at number six on his rundown of normal cognitive contortions.
Cognitive contortions are examples of erroneous and negative thinking that stay at the core of temperament issues, for example, tension and sadness.
The thought, created by analyst Aaron Beck and clarified by Burns, is that steady negative thinking prompts consistent negative feelings.
This is the place the side effects of melancholy and tension begin to kick in.
As an individual from a family that exposed them to cognitive mutilation, disastrous thinking looks somewhat like reality, and can really affect the cataclysmic mastermind’s life.
At the point when you catastrophize, your brain takes a little issue and incorporates it with a debacle of immeasurable scope.
That sort of continued thinking is staggeringly poisonous to your emotional atmosphere.
William Ralph Inge is credited with saying, “Stress is intrigue paid on inconvenience before it comes due.”
At the end of the day, investing all your energy stressing and envisioning fiascoes that may never happen denies you of the delight of the current second and acquires with enthusiasm from your future.
Physical Effects
Catastrophizing is such incredible power, that it can impact an individual’s physical wellbeing.
Pain catastrophizing is a genuine wonder that numerous people suffer consistently.
This idea design is intense to such an extent that it prompted the advancement of the catastrophizing pain scale, which basically gauges and inspects the job of catastrophizing in how individuals experience pain.
Steps to manage catastrophic thinking
Cerebral health specialists frequently use methods called cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) to support an individual’s talking about their catastrophic thinking.
These methods need the person to be conscious that they are feeling catastrophic thinking, to know their schedules, and to make an effort to stop and identify where their illogical thinking is coming from.
Following are the instructions to achieve this, which include memorising and making use of the following methods.
These can be supported to manage the conditions.
1. Admitting that unfriendly things occur
Life is filled with trials as well as good and evil days.
Just because one day is not good does not show that all days will be bad.
2. Identifying when opinions are irrational
Catastrophizing frequently follows a separate pattern. A person will start with a belief, such as “I am sad nowadays.”
They will then enlarge on the thought with fear and nervousness, such as, the pain is only going to become inferior.
When a person acquires these opinions, they are healthier prepared to grip them.
3. Saying “stop!”
To stop the boring, catastrophic opinions, an individual may have to say out brash or in their head break.
These arguments can retain the stream of opinions from on-going and support a person to change the sequence of their thinking.
4. Discerning about another consequence
Instead of discerning about an undesirable outcome, consider a positive one or even a less-unfriendly choice.
5. Offering positive confirmations
When it comes to a catastrophic thought, a creature has to trust in themselves and that they can overcome their propensity to fear the foulest.
They may wish to repeat an optimistic assertion to themselves on a daily basis.
6. Excellent self-care
Catastrophic opinions are more likely to take over when an individual is weary and stressed.
Receiving enough rest and appealing in stress-relieving methods, such as exercise, consideration, and journaling, can all support an individual sense better.
Difference between catastrophizing and anxiety
The primary distinction between anxiety and catastrophizing is that anxiety will play a helpful role in every person’s life.
As an example, anxiety is often a positive feeling, because sometimes it will ease someone to take care of themselves.
However, catastrophizing doesn’t typically have any edges.
Having these ruinous thoughts will fill a person’s mind with unnecessary emotions that take time and thought faraway from the truth of a scenario.
Whereas each anxiety and catastrophizing are often harmful, anxiety is helpful in some circumstances.
Treatment
Most people experience worry and worry for a while.
However, if someone perpetually fears the worst or hears from their friends and family that they’re thinking during this means, they’ll have to be compelled to address their ruinous thinking.
For example, if someone experiences this kind of distress due to some underlying medical condition, like depression, a doctor might inflict medicine medications to assist.
Following are the treatments methods:
Choosing Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRI’s)
Fluoxetine (Prozac) and paroxetine (Paxil). These drugs upsurge the quantity of the neurotransmitter serotonin in the human mind.
They are frequently the first-line for dealing for people with unhappiness but may also be prearranged for a variability of nervousness complaints.
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
Duloxetine (Cymbalta) and venlafaxine (Effexor).
These medicines rise the quantity of serotonin as well as norepinephrine in the human brain.
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA’s)
These medications are called amitriptyline and nortriptyline (Pamelor).
Clinicians do not propose TCA’s very frequently nowadays because of their unwanted side effects.
Atypical antidepressants
These medicines do not fit into a specific group concerning how they work. Instances comprise bupropion (Wellbutrin, Aplenzin) and trazodone.
Treatment With the Help of Therapy
Since catastrophizing is carefully related with mental illnesses, it’s no astonishment that therapy can efficiently treat catastrophizing.
Cognitive-behavioural treatment, or CBT, is one of the most shared forms of talk therapy.
A 2017 study Trusted Source found that CBT was real at addressing catastrophizing in fibromyalgia patients, and that it aided them better achieve their pain.
CBT tries to address your rational and behavioural patterns.
In the case of catastrophizing, your psychoanalyst might help you know irrational thoughts and swap them with rational ones.
For example, you might be used to thinking, “I handed this statement in late. I’m a total disappointment, and I’m going to lose my job. I’ll be financially destitute.”
Through CBT, you will know that this is an illogical thought.
From time to time, a doctor may originally recommend one type of medication that may not be real in plummeting both unhappiness and catastrophizing.
In this case, the doctor may suggest other medicines also.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Frequently Asked Questions
Is catastrophizing a mental illness?
No, catastrophizing is not a mental illness on its own.
However, catastrophizing is a symptom of many different mental illnesses, such as anxiety, depression, and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD).
How do I stop myself from catastrophizing?
Take control of your situation.
Understand that what you are feeling is temporary, and is not based on facts, but is instead your mind playing tricks on you.
It may also be helpful to think about what you might tell your best friend; if they were freaking out about something, what would you say to them to help them feel better?
Then, apply that same thing you would do or say to a best friend to yourself.
Resources
- https://psychcentral.com/lib/what-is-catastrophizing/
- https://www.psychologytoday.com/us/basics/catastrophizing
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320844
Interested in why people catastrophize? Here are some links to novels about this topic on Amazon:
- https://www.amazon.com/Dont-Feed-Monkey-Mind-Anxiety/dp/B072HTXPY7/ref=sr_1_1?dchild=1&keywords=catastrophizing+and+anxiety&qid=1588099506&sr=8-1
- https://www.amazon.com/Worry-Trick-Brain-Tricks-Expecting/dp/B01HDXCV12/ref=sr_1_2?dchild=1&keywords=catastrophizing+and+anxiety&qid=1588099518&sr=8-2
- https://www.amazon.com/Generalized-Anxiety-Disorder-Workbook-Comprehensive-ebook/dp/B018RSC3Z6/ref=sr_1_4?dchild=1&keywords=catastrophizing+and+anxiety&qid=1588099534&sr=8-4