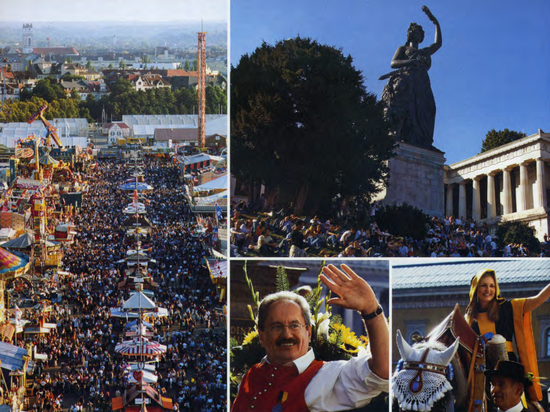
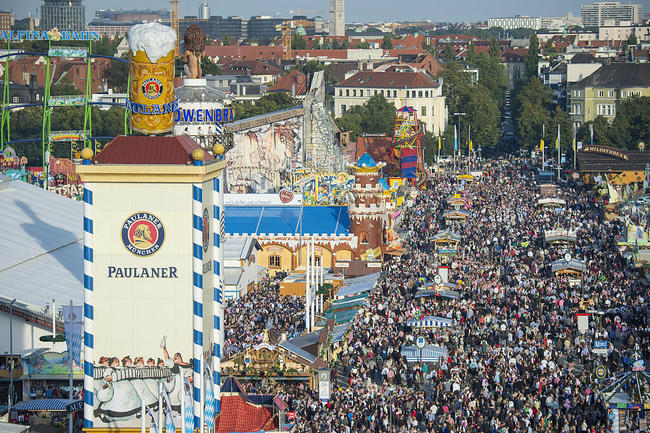
Вряд ли существует пивной фестиваль, более известный, чем мюнхенский Октоберфест, который ежегодно собирает гигантское количество любителей хмельного напитка. На 16 дней город превращается в одну огромную пивную. На улицах, площадях и аллеях, в парках, бройхаузах и кнайпах гости Октоберфеста выпивают миллионы литровых кружек пива, съедают сотни зажаренных на вертеле быков, тысячи свиней и кур, не считая легендарных баварских сосисок. Сердцем же фестиваля является Луг Терезы, где круглые сутки в 14 павильонах происходит настоящее пивное веселье.
В 2019 году Октоберфест официально начнется 21 сентября в 10.45 утра по местному времени. В преддверии главного пивного праздника мира мы расскажем об его истории, правилах, кухне, традициях и, конечно же, о легендарном пиве фестиваля.
История Октоберфеста
Традиция празднования Октоберфеста насчитывает уже более 200 лет
Название фестиваля переводится с немецкого как «праздник октября». Сами же мюнхенцы называют его Wiesn – от немецкого «луг», «лужайка». Историки пивоварения считают, что своими корнями Октоберфест уходит в традиционный крестьянский праздник сбора урожая и завершения работ на полях.
Официально же началом традиции фестиваля принято считать торжества, которые проводились в течение 6 дней октября 1810 года в связи с бракосочетанием кронпринца Людвига (будущего короля Людвига I) и принцессы Терезии Саксонской-Хильдбургхаузен (именно в ее честь и назван Луг Терезы). Отец невесты, король Максимилиан I Иосиф решил отметить свадьбу пышными народными гуляниями и конными скачками на лугу перед городскими воротами, которые длились 6 дней. По разным источникам первым днем торжества стало 12 или 17 октября.
Праздник настолько понравился местным жителям, что год спустя его решили повторить. В течение 9 лет торжества проводились в частном порядке – исключением стал 1813 год, когда праздник отменили из-за вступления Баварии в Наполеоновские войны. В 1819 году фестивалем стал управлять мюнхенский городской совет. Тогда же градоначальники решили сделать Октоберфест регулярным.
В 1850 году на лугу Терезы патриотично настроенные граждане воздвигли 19-метровую бронзовую статую красавицы Баварии, которая стала неофициальным символом фестиваля. Внутри статуи была построена лестница из 125 ступеней, по которым можно было подняться на смотровую площадку.
За свою историю традиция Октоберфеста прерывалась лишь из-за тяжких бедствий. Например, в 1854 и 1873 годах торжества отменяли из-за эпидемии холеры. В 1866 мюнхенцы остались без праздника из-за Прусско-австрийской, а в 1870 – из-за Франко-прусской войны.
В 1872 году городской совет принял решение перенести на последние дни сентября – в это время в Мюнхене еще стоят теплые дни. В 1904 перенос Октоберфеста закрепился окончательно, однако его последнее воскресенье должно было обязательно выпасть на октябрьский день – эта традиция действует и поныне.
В 1881 году на фестивале появилась первая кухня – была открыта жарильня кур. Первые знаменитые на весь мир литровые кружки «массы» ввели в 1892 году. Примерно в это же время на Октоберфесте участники торжества начали ставить пивные палатки. Сначала в них устраивали аттракционы, однако позднее все развлечения сделали уличными, оставив в палатках лишь столы и скамейки, а также площадки для гостей и музыкантов. В 1901 году на празднике построили настоящую бедуинскую деревню с жителями, что стало тогда настоящей сенсацией.
Интересный факт! В 1886 году на Октоберфесте зажглись первые лампочки. За электрификацию отвечал отец Альберта Эйнштейна. По некоторым данным, будущий гениальный физик-теоретик помогал вкручивать лампочки в шатре Шоттенхаммель.
На столетие Октоберфеста в 1910 году гости праздника выпили 1,2 млн литров пива. 3 года спустя был поставлен непреодолимый до сих пор рекорд – на фестивале поставили палатку Bräurosl на 12 000 мест (для сравнения, крупнейшая палатка наших дней –Hofbräu-Festhalle – рассчитана на 10 000 гостей).
С 1914 по 1918 год из-за Первой мировой войны в традиции Октоберфеста вновь наступила пауза. В 1923 и 1924 годах фестиваль вновь не проводился. На этот раз – из-за колоссальной инфляции в Германии. Некоторые изменения на праздники произошли в 30-х годах, когда к власти пришли национал-социалисты. В частности, были запрещены выставки-кунсткамеры, а баварские бело-голубые флаги сменились на нацистские со свастикой. При этом возобновились скачки, которые к тому времени проводились все реже.
Октоберфест не проводился лишь в годы войн и эпидемий
Самый большой перерыв в истории Октоберфеста произошел с 1939 по 1945 год. С 1946 по 1948 год руководство фестиваля запретило «октоберфестовское пиво» – разливали лишь слабоалкогольное с крепостью менее 2 %.
В 1950 году появилась еще одна традиция, которую ввел тогдашний обер-бургомистр Мюнхена Томас Виммер – праздник пива начинался после 12 пушечных выстрелов и откупоривания первой бочки. Кстати, герр Виммер забил пивной кран лишь с 19 ударов – до сих пор этот результат считается худшим. А рекорд в 2006 году поставил градоначальник Кристиан Уде, который открыл бочку с одного удара.
С 1960 года на Октоберфест начали стекаться иностранные туристы.
В 1980 году произошла главная трагедия фестиваля. Вечером 26 сентября праворадикальный экстремист Гундольф Келлер взорвал у входа в туалет самодельную бомбу. В результате теракта погиб сам подрывник, а вместе с ним – 13 гостей Октоберфеста. Ранения получили более 200 человек. Многие были уверены, что традиция фестиваля прервется навсегда, однако уже на следующий год Октоберфест вновь созвал гостей в свои шатры.
Не отменился фестиваль и после террористических актов 11 сентября 2001 года. Тем не менее, в память о жертвах атак на башни-близнецы организаторы отказались от традиции откупоривания первой бочки и шествия хозяев пивных палаток. Кроме того, были усилены меры безопасности: на Лугу Терезы установили камеры видеонаблюдения, а гостей охраняли около 400 полицейских.
Регламент фестиваля
Процессия, которая начинает Октоберфест, собирает несколько тысяч человек
Октоберфест начинается утром в третью субботу сентября с костюмированного шествия фермеров и пивоваров. Считается, что эта традиция восходит к 1887 году, когда Ханс Штайрер, фермер одного из крупнейших мюнхенских хозяйств, вывел работников своей фермы с груженными пивом телегами под духовой оркестр. В своем нынешнем виде шествие появилось в 1935 году, когда в нем впервые приняли участие местные пивоварни.
Шествие возглавляет символ Мюнхена – молодой монах Münchner Kindl, роль которого играет женщина в желто-черном монашеском одеянии с колокольчиком в руках. В процессии, которая выдвигается из Старого города и растягивается на несколько километров, участвуют кареты обер-бургомистра, главы Баварии и членов городского совета, горожане в национальных одеждах, повозки пивоварен и музыканты – всего более 8 000 человек и около 40 экипажей.
Участники шествия прибывают в основном из Баварии, Австрии, Швейцарии, северной Италии. Однако в последние годы среди участников процессии можно заметить и гостей из Восточной и Северной Европы. Организует шествие, готовит повозки и национальные костюмы баварская ассоциация по сохранению местных традиций Festring Munich.
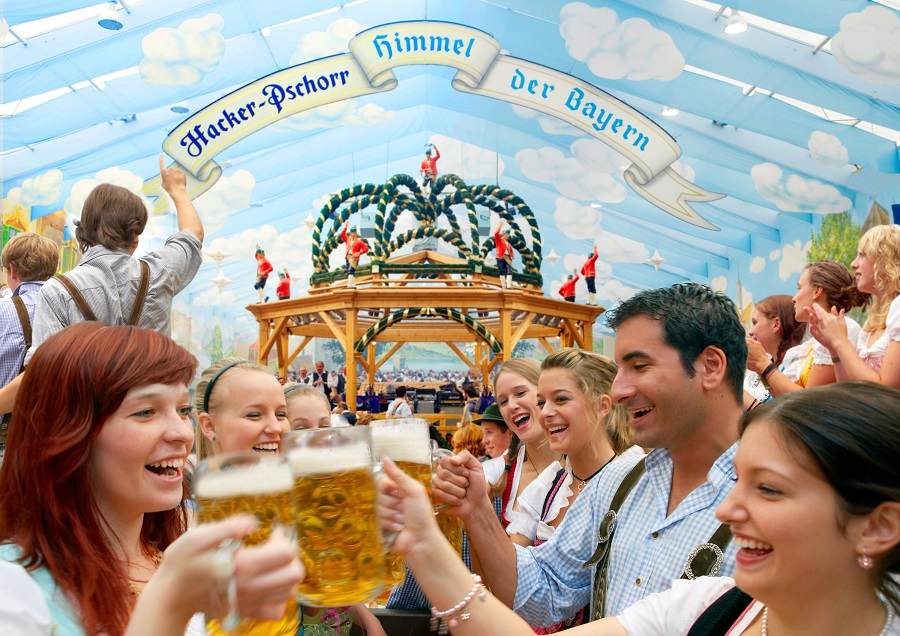
В полдень на Лугу Терезы в павильоне Шоттенхамель-Фестхалле глава Мюнхена забивает пивной кран с возгласом «O`zapft is!» – «Кран забит!». После этого первые кружки пива подают градоначальникам, а далее свежее фестивальное пиво разливают всем желающим. Попутно с этим жители Мюнхена и гости фестиваля кружатся в танцах под национальную баварскую музыку.
Кстати, ищите немецкое пиво у нас в каталоге!
Какие пивоварни обычно принимают участие
Гостям праздника 6 пивоварен готовят специальное фестивальное пиво
Обычай Октоберфеста велит, чтобы гостям праздника подавали пиво только из мюнхенских пивоварен. При этом напиток должен быть сварен в строгом соответствии с мюнхенским законом о чистоте пива 1487 года и немецким законом о чистоте пива 1516 года (вода, солод, хмель, дрожжи, никаких добавок). На площади в 30 га организаторы выставляют 14 или 15 палаток, спонсорами которых являются 6 главных пивоварен Баварии:
- Augustiner;
- Hacker-Pschorr;
- Hofbräu;
- Löwenbräu;
- Paulaner;
- Spaten.
Augustiner
Монахи Августинского ордена основали старейшую и действующую по сей день пивоварню в 1328 году. В 1817 году производство переехало на улицу Нойхаузер, где сегодня о нем напоминает один из самых популярных в городе ресторанов Augustiner.
В конце XIX века штаб-квартира и пивоваренные заводы были перенесены на Ландсбергерштрассе, где пивоварение продолжается и сегодня. Augustiner – единственная пивоварня на Октоберфесте, которая наливает пиво из традиционных 200-литровых деревянных бочек, тогда как остальные используют современные металлические емкости.
На фестивале пиво Augustiner подают в палатках Augustiner Festzelt, Fischer Vroni и Festzelt Tradition.
Hacker-Pschorr
Данная пивоварня впервые упоминается в источниках 1417 года. В те времена она находилась на улице Зендлингерштрассе, где сейчас располагается ресторан Altes Hackerhaus. В XVIII веке пивоварня под руководством Йозефа Пшорра и Марии Терезии Хакер стала крупнейшей в Мюнхене.
Почти полтора столетия хмельной напиток производился на отдельных пивоварнях, которыми руководили потомки двух фамилий. Только с 1972 года Hacker-Pschorr вновь стал единым брендом. Сегодня пивоварня находится в том же помещении, что и Paulaner. На фестивале самый легкий 5,8%-ный напиток пивоварни можно попробовать в палатках Hacker Festzelt, Pschorr Festzelt Bräurosl и Herzkasperl-Festzelt.
Hofbräu
Пивоварня Hofbräuhaus была основана в Мюнхене в 1589 году при Вильгельме V как герцогский пивоваренный завод. С 1939 года компания является государственным предприятием. Первоначально производство находилось в самом центре города, но в XIX веке из-за нехватки места пивоварня переехала на пару кварталов подальше и разместилась на Иннервейнерштрассе. Сейчас здесь находится одна из главных туристических достопримечательностей Мюнхена – пивной ресторан Hofbräukeller с роскошным пивным садом.
Пиво Hofbräu – самое крепкое 6,3%-ное пиво на фестивале. Найти его можно в палатках Hofbräuzelt и Oide Wiesn.
Löwenbräu
Первое упоминание о пивоварне относится к 1746 году. В XIX веке семья Брау превратила Löwenbräu в одну из крупнейших пивоварен Мюнхена. Производство находится на улице Нимфенбургерштрассе, где также располагается фирменный ресторан Löwenbräukeller. Кстати, пивоварня проводит и свои небольшие фестивали вроде Starkbierfest или Night of Tracht.
Попробовать напиток пивоварни можно в павильоне Löwenbräu-Festzelt, Schützen-Festzelt и Haxnbraterei.
Paulaner
Самая молодая мюнхенская пивоварня, которая была основана в 1634 году монахами ордена Пауланер. Особенностью монастырского пива было то, что подавалось оно публично только по праздникам. В остальное время пили его исключительно в монастыре. Сейчас мюнхенская пивоварня находится в районе Лангвид на северо-западе города. На Октоберфесте пиво Paulaner подают в шатрах Paulaner, Kuffler Weinzelt, Heinz и Hühnerbraterei.
Spaten
Пивоварня основана в 1397 году и до XIX века располагалась на поле Нойхаузер Гассе. С той поры и по сей день мюнхенский завод Spaten работает на Марсштрассе. Именно эта пивоварня выпускает главный бестселлер Баварии – мюнхенский светлый лагер (hell).
Пиво Spaten можно приобрести на Октоберфесте в палатках Schottenhamel-Zelt, Spatenbier, Ochsenbraterei, Glöckle Wirt, Goldenen Hahn, Kalbsbraterei и Wirtshaus.
Это интересно! Для Октоберфеста варят специальное выдержанное светлое пиво Oktoberfestbier с ярко выраженным солодовым вкусом. Содержание алкоголя в нем колеблется от 5,8 до 6,3 %. В другое время года такой хмельной напиток называют мартовским или венским пивом. В среднем оборот пива в одной палатке за 16 дней достигает более 3 млн евро.
Кухня на фестивале
На Октоберфесте невозможно остаться голодным
Помимо пива, гости Октоберфеста могут попробовать молодые баварские вина, настойки, морсы и компоты, а также разнообразные коктейли. Из еды «королем закусок» считаются жареные свиные ножки «швайнехаксе» с кислой капустой. Кроме того, на празднике кормят жареными свиными ребрышками «риппхен», кровяной или ливерной колбасой, белыми мюнхенскими сосисками, запеченной рыбой, жареными быками и жареными курочками. Из более легких блюд подают салаты из картофеля и капусты. А любители выпечки точно оценят огромные кренделя «брецны».
Традиции, обряды и другие интересные факты об Октоберфесте
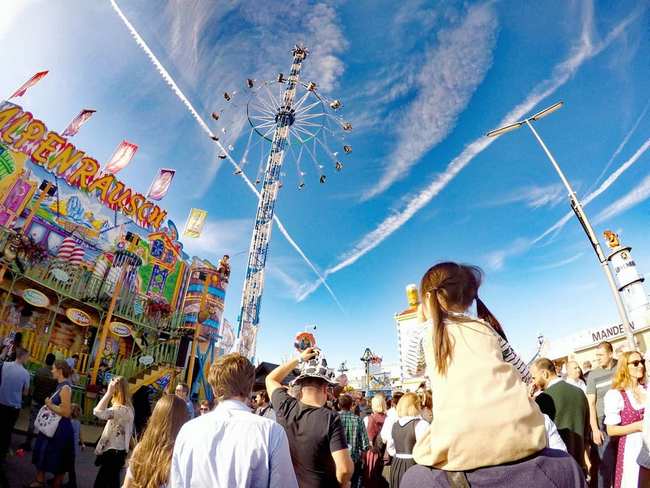
Октоберфест – это гигантская развлекательная зона с аттракционами на любой вкус
Одной из самых интересных традиций фестиваля являются правила завязывания и размещения узла на дирндле – национальном женском костюме. Например, узел справа от фартука показывает, что носительница дирндля замужем, помолвлена или влюблена. Для мужчин – это знак того, что с девушкой на фестивале вряд ли получится удачно пофлиртовать. И наоборот, узел слева носят барышни, готовые к знакам внимания.
Узел посредине фартука спереди покажет, что девушка еще никогда не была в отношениях либо скрывает свой статус. Узел сзади носят на Октоберфесте дети, официантки и вдовы.
Разгоряченные гости фестиваля нередко устраивают своеобразные азартные игры. Например, популярным развлечением считается пробежка голышом от одной палатки до другой. Кстати, баварское телевидение, которое ведет прямые репортажи с фестиваля, особенно любит фиксировать именно такие пикантные моменты.
Вообще, на Октоберфесте нет недостатка в способах времяпрепровождения. Для гостей организаторы праздника готовят десятки аттракционов – от небольших классических каруселей до гигантских американских горок. Самыми популярными развлечениями считаются:
- Olympia Looping – американские горки длиной более 1 250 метров и высотой 38,5 метра, которые за час могут принять до 3 000 человек. Вагончики на горках способны разогнаться до 100 км/ч.
- Колесо обозрения – впервые появилось на Октоберфесте в 1880 году. Сейчас его высота составляет 50 метров и весит 540 тонн. В хорошую погоду с верхней точки можно даже увидеть Альпы.
- Alpina Bahn – американские горки с длиной трассы 910 метров и максимальной скоростью 79,6 км/ч. Являются самым большим в мире передвижным аттракционом без элементов переворота вниз головой.
- Power Tower II – высочайшая в мире передвижная башня со свободным падением (66 метров на скорости более 79 км/ч).
- Блошиный цирк – действует на фестивале более 50 лет.
Октоберфест в цифрах:
- Ежегодно около 6 миллионов посетителей выпивают около 6 миллионов литров пива и съедают 500 000 жареных кур.
- Фестиваль обслуживают 12 000 человек.
- Оборот Октоберфеста составляет около 600 миллионов евро.
- Литр пива на празднике стоит около 8,30 евро.
- Каждый год гости Октоберфеста воруют около 200 000 пивных кружек.
- По правилам фестиваля громкость музыки в палатках до 6 часов вечера не превышает 85 Дб.
- Праздник пива снабжают электроэнергией 18 трансформаторов, для которых прокладывается 43 км кабеля.
- За 16 дней территория Октоберфеста потребляет около 3 млн киловатт-часов, что составляет примерно 13 % ежедневного потребления электроэнергии Мюнхеном.
- Для снабжения палаток газом прокладывается 4 км труб.
За здоровьем гостей праздника следят сотрудники баварского Красного Креста. За медицинской помощью можно обратиться в сервисный центр или два вспомогательных пункта. Для изрядно перебравших любителей пива предусмотрено отдельное помещение на 15–20 коек. Всего на Октоберфесте работают около 100 санитаров-волонтеров и 10 профессиональных врачей.
За безопасность на фестивале отвечают около 300 полицейских, которым иногда помогают коллеги из Южного Тироля. Кроме того, на территории Октоберфеста размещается не менее 15 видеокамер.
По вторникам до 6 часов вечера на празднике проводятся Семейные дни. В это время в палатках и на аттракционах делают скидки для семейных гостей. Детей в шатры допускают только до 8 вечера. После этого на территории фестиваля дети от 6 до 16 лет могут находиться только в сопровождении взрослых. С детскими колясками можно проехать по территории до 6 вечера, после чего проход с ними запрещен.
Курить на Октоберфесте можно только в специально отведенных местах.
Как добраться до фестиваля:
Проще всего – общественным транспортом, например, на метро до станции Theresienwiese по линиям U3, U4, U5 и U6. От главного вокзала до Луга Терезы можно за 12 минут дойти пешком или доехать на электричке до станции Hackerbrücke и оттуда 10 минут пройтись неспешным шагом.
This article is about the original festival in Munich. For Oktoberfest celebrations around the world, see Oktoberfest celebrations.
| Oktoberfest | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Observed by | Munich, Bavaria, Germany |
| Type | National |
| Celebrations | Parades, food, music, drinking |
| 2022 date | 17 September |
| Frequency | Annual |
| Related to | Oktoberfest celebrations |
The Oktoberfest (German pronunciation: [ɔkˈtoːbɐˌfɛst]; Bavarian: Wiesn, Oktobafest) is the world’s largest Volksfest, featuring a beer festival and a travelling carnival. It is held annually in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. It is a 16- to 18-day folk festival running from mid- or late-September to around the first Sunday in October, with more than six million international and national visitors attending the event. Locally, it is called d’Wiesn, after the colloquial name for the fairgrounds, Theresienwiese. The Oktoberfest is an important part of Bavarian culture, having been held since the year 1810. Other cities across the world also hold Oktoberfest celebrations that are modeled after the original Munich event.
During the event, large quantities of Oktoberfest Beer are consumed. For example, during the 16-day festival in 2014, 7.7 million litres (2,000,000 US gal) were served,[1] making it the year where the most beer was consumed at the Oktoberfest.[2] Visitors also enjoy numerous attractions, such as amusement rides, sidestalls, and games. There is also a wide variety of traditional foods available.
The Munich Oktoberfest originally took place in the 16-day period leading up to the first Sunday in October. In 1994, this longstanding schedule was modified in response to German reunification. As a result, if the first Sunday in October falls on the 1st or the 2nd, then the festival would run until 3 October (German Unity Day). Thus, the festival now runs for 17 days when the first Sunday is 2 October and 18 days when it is 1 October. In 2010, the festival lasted until the first Monday in October (4 October), to mark the event’s bicentennial.
History[edit]
Horse race at the Oktoberfest in Munich, 1823
Portrait of a girl wearing a Dirndl dress
Kronprinz Ludwig (1786–1868), later King Ludwig I (reign: 1825–1848), married Princess Therese of Saxe-Hildburghausen on 12 October 1810. The citizens of Munich were invited to attend the festivities held on the fields in front of the city gates to celebrate the royal event. The fields were named Theresienwiese («Theresa’s Meadow») in honour of the Crown Princess, and have kept that name ever since, although the locals have abbreviated the name simply to Wiesn.[3] Horse races, in the tradition of the 15th-century Scharlachrennen (Scarlet Race at Karlstor), were held on 18 October to honor the newlyweds. It is widely believed that Andreas Michael Dall’Armi, a major in the National Guard, proposed the idea. However, the origins of the horse races, and Oktoberfest itself, may have stemmed from proposals offered by Franz Baumgartner, a coachman and sergeant in the National Guard. The precise origins of the festival and horse races remain a matter of controversy. However, the decision to repeat the horse races, spectacle, and celebrations in 1811 launched what is now the annual Oktoberfest tradition.
The fairground, once outside the city, was chosen due to its natural suitability, which it still holds today. The Sendlinger Hill (today Theresienhohe) was used as a grandstand for 40,000 race spectators. The festival grounds remained undeveloped, except for the king’s tent. The tastings of «Traiteurs» and other wine and beer took place above the visitors in the stands on the hill. Before the race started, a performance was held in homage of the bridegroom and of the royal family in the form of a train of 16 pairs of children dressed in Wittelsbach costumes, and costumes from the nine Bavarian townships and other regions. This was followed by the punishing race with 30 horses on a 3,400 metres (11,200 ft) long racetrack, and concluded with the singing of a student choir. The first horse to cross the finish line belonged to Franz Baumgartner (one of the purported festival initiators). Horse racing champion and Minister of State Maximilian von Montgelas presented Baumgartner with his gold medal.[4]
Transformation into a public festival[edit]
19th century[edit]
In 1811, a show was added to promote Bavarian agriculture. In 1813, the festival was canceled due to the involvement of Bavaria in the Napoleonic Wars, after which the Oktoberfest grew from year to year. The horse races were accompanied by tree climbing, bowling alleys, and swings and other attractions. In 1818, carnival booths appeared; the main prizes awarded were of silver, porcelain, and jewelry. The city fathers assumed responsibility for festival management in 1819, and it was decided that Oktoberfest become an annual event. In 1832, the date was moved some weeks later, as a Greek delegation came. It inspired them for the Zappas Olympics which became in 1896 the modern Olympic Games.[citation needed] Later,[when?] the Oktoberfest was lengthened and the date pushed forward because days are longer and warmer at the end of September. The horse race continued until 1960, and the agricultural show still exists today and is held every four years in the southern part of the festival grounds.
To honour the marriage of Prince Ludwig and Therese of Saxe-Hildburghausen, a parade took place for the first time in 1810. Since 1850, the parade has become an annual event and an important component of the Oktoberfest. Eight thousand people—mostly from Bavaria—and dressed in traditional costumes walk from Maximilian Street through the centre of Munich to the Oktoberfest grounds. The march is led by the Münchner Kindl.
Since 1850, the statue of Bavaria has watched over the Oktoberfest. This worldly Bavarian patron was first sketched by Leo von Klenze in a classic style and Ludwig Michael Schwanthaler romanticised and Germanised the draft.[citation needed] The statue was constructed by Johann Baptist Stiglmaier and Ferdinand von Miller.
In 1853, the Bavarian Ruhmeshalle was completed. In 1854, the festival was cancelled after 3,000 residents of Munich including the queen consort died during a cholera epidemic. There was no Oktoberfest in 1866 because Bavaria was involved in the Austro-Prussian War. In 1870, the Franco-Prussian War again forced the cancellation of the festival. In 1873, the festival was cancelled due to yet another cholera epidemic. In 1880, electric light illuminated more than 400 booths and tents. In 1881, booths selling Bratwurst opened and the first beer was served in glass mugs in 1892.
At the end of the 19th century, a re-organization took place. Until then, there were games of skittles, large dance floors, and trees for climbing in the beer booths. Organizers wanted more room for guests and musicians which resulted in the booths becoming beer halls which are still used today.
In 1887, the parade of the Oktoberfest staff and breweries took place for the first time. This event showcases the splendidly decorated horse teams of the breweries and the bands that play in the festival tents. This event always takes place on the first Saturday of the Oktoberfest and serves as the official prelude to the Oktoberfest celebration.
20th century[edit]
At the 100th anniversary of Oktoberfest in 1910, an estimated 120,000 litres of beer were consumed. Three years later, the Bräurosl was founded, which at that time was the largest pavilion to have ever been built, accommodating approximately 12,000 people.[5]
Due to World War I, Oktoberfest was temporarily suspended from 1914 to 1918. The two years after the war, in 1919 and 1920, Oktoberfest was replaced by the so-called kleineres Herbstfest (which can be translated as «smaller autumn celebration»), and in 1923 and 1924 the Oktoberfest was cancelled due to hyperinflation.[5]
During National Socialism, Oktoberfest was used as part of Nazi propaganda.[6] In 1933, Jews were forbidden to work on the Wiesn.[citation needed] Two years later, Oktoberfest’s 125th anniversary was celebrated with all the frills. The main event was a big parade.
The slogan proud city—cheerful country was meant to show the alleged overcoming of differences between social classes, and can be seen as an example of the regime’s consolidation of power. In 1938, after Hitler had annexed Austria and won the Sudetenland via the Munich Agreement, Oktoberfest was renamed to Großdeutsches Volksfest (Greater German folk festival), and as a showing of strength, the Nazi regime transported people from Sudetenland to the Wiesn by the score.[7]
During World War II, from 1939 to 1945, no Oktoberfest was celebrated. Following the war, from 1946 to 1948, Munich celebrated only the «Autumn Fest». The sale of proper Oktoberfest beer—2% stronger in gravity than normal beer—was not permitted; guests could only drink normal beer.
Since its foundation, there have been 26 years in which it was declined.[8]
Since 1950, the festival has always been opened with the same traditional procedure: At noon, a 12-gun salute is followed by the tapping of the first keg of Oktoberfest beer by the Mayor of Munich with the proclamation «O’zapft is!» («It’s tapped!» in the Austro-Bavarian dialect). The Mayor then gives the first litre of beer to the Minister-President of the State of Bavaria. The first mayor to tap a keg was Thomas Wimmer.
Gamsbärte at the entry of the Oktoberfest restaurateurs, 2008
Before the festival officially starts, parades are held with the traditional marksmen’s clubs, beer-tent waitresses, and landlords participating. There are two different parades which both end at the Theresienwiese. They start around 9:45 a.m. to 10.50 am.[9]
During Oktoberfest, some locals wear Bavarian hats (Tirolerhüte), which contain a tuft of chamois hair (Gamsbart). Historically, in Bavaria chamois hair was highly valued and prized. The more tufts of chamois hair on one’s hat, the wealthier one was considered to be. Due to modern technology, this tradition has declined with the appearance of chamois hair imitations on the market.[citation needed]
For medical treatment of visitors, the Bavarian branch of the German Red Cross operates an aid facility and provides emergency medical care on the festival grounds, staffed with around 100 volunteer medics and doctors per day.[10]
They serve together with special detachments of Munich police, the fire department and other municipal authorities in the service centre at the Behördenhof (authorities’ court), a large building specially built for the Oktoberfest at the east side of the Theresienwiese, just behind the tents. There is also a station for lost and found children, a lost property office, a security point for women and other public services.[11]
Since the 1970s, local German gay organizations have organized «Gay Days» at Oktoberfest, which since the 21st century always begin in the Bräurosl tent on the first Sunday.[12]
1980 bombing[edit]
A pipe bomb was set off in a dustbin near the toilets at the main entrance on 26 September 1980 at 22:19. The bomb consisted of an empty fire extinguisher filled with 1.39 kilograms of TNT and mortar shells. Thirteen people were killed and over 225 were injured, 68 seriously. The case is still under criminal investigation by the State Police on behalf of the National Prosecutor General as of 2022 which had been stalled for several decades in between.[13]
This is the second-deadliest terrorist attack in the history of Germany after the Munich massacre.
Federal and state law enforcement authorities initiated numerous official inquiries, concluding that a right-wing extremist, Gundolf Köhler, from Donaueschingen, a social outcast who was killed in the explosion, was the sole perpetrator. However, both this account and the number of perpetrators are strongly disputed by various groups.[14]
Oktoberfest today[edit]
Music entertainment at the Oktoberfest, 2015
To keep the Oktoberfest, and especially the beer tents, amicable for the elderly and families, the concept of the «quiet Oktoberfest» was developed in 2005. Until 6:00 pm, the orchestras in the tents only play brass music, for example traditional folk music. Only after that may Schlager pop or electric music be played, which had led to excessively raucous behaviour in earlier years.[15] The music played in the afternoon is limited to 85 decibels. With these rules, the organisers of the Oktoberfest were able to curb[dubious – discuss] the tumultuous party mentality and preserve the traditional beer-tent atmosphere.
In 2005 Germany’s last travelling enterprise amusement ride, the Mondlift, returned to the Oktoberfest.[16]
Starting in 2008, a new Bavarian law was passed to ban smoking in all enclosed spaces open to the public.[17] Because of problems enforcing the anti-smoking law in the big tents, an exception was granted to the Oktoberfest in 2008, although the sale of tobacco was not allowed. After heavy losses in the 2008 local elections, with the smoking ban being a big issue in political debates, the state’s ruling party implemented general exemptions to beer tents and small pubs.
The change in regulations was aimed in particular to benefit the large tents of the Oktoberfest:[18] smoking in the tents is still legal, but the tents usually have non-smoking areas.[19] The sale of tobacco in the tents is now legal, but is widely boycotted by mutual agreement. However, in early 2010, a referendum held in Bavaria as a result of a popular initiative re-instituted the original, strict, smoking ban of 2008; thus, no beer will be sold to people caught smoking in the tents.[20]
The blanket smoking ban did not take effect until 2011,[17] but all tents instituted the smoking ban in 2010 to do a «dry run» to identify any unforeseeable issues.[21]
Celebrating 200 years of Oktoberfest in 2010
The year 2010 marked the Oktoberfest Bicentennial.[22] For the anniversary, a horse race in historical costumes was held on opening day. A so-called historische Wiesn (historical Oktoberfest) took place,[22] starting one day earlier than usual on the southern part of the festival grounds. A specially brewed beer (solely available at the tents of the historical Oktoberfest), horse races, and a museum tent gave visitors an impression of how the event felt two centuries ago.[22]
In 2013, 6.4 million people visited Oktoberfest, and visitors were served 6.7 million litres of beer.[23]
On 21 April 2020, Bavarian Minister-President Markus Söder and the mayor of Munich, Dieter Reiter, announced the official cancellation of the 2020 Oktoberfest due to the ongoing coronavirus pandemic.[24][25] On 3 May 2021, Minister-President Söder and Mayor Reiter announced that the Oktoberfest hiatus will be extended, deferring the next one to 2022. Söder noted the unfeasibility of social distancing in the festival’s beer tents, adding, «Imagine there was a new wave and it then became a super-spreader event. The brand would be damaged forever and we don’t want that.»[26]
Oide Wiesn[edit]
On the occasion of the 200th anniversary in 2010 a so-called Historisches Oktoberfest (Historical Oktoberfest) was designed on the site of the Central Agricultural Festival at the south end of the Theresienwiese. It opened one day before the official Oktoberfest with the traditional keg tapping by the Lord Mayor.[22] Due to the popularity of the Oide Wiesn, it was established as a permanent feature from 2011.[27]
Main entrance to the Historical Oktoberfest
The comprehensive five acres of fenced grounds presented historic rides, beer tents and other historical attractions such as a Steckerlfisch grilling, a chain swing and a cotton candy stand. Included in the price of admission, an animal tent and the racecourse could be visited next to the museum.
The animal tent included, among other things, a petting zoo, and was managed by the Hellabrunn Zoo and the Bavarian Farmers Association. The Munich Stadtmuseum took over the design of the museum tent. The Oktoberfest anniversary was accompanied by an artistic and cultural program, in which for example the Biermösl Blosn (local entertainers) performed.
The bands performing in the relatively small Herzkasperl Festzelt—offering 850 seats—had to do without electrical amplification.[28]
The fest-tent name derives from a famous stage character of the actor Jörg Hube, who died in 2009.[29]
The six main Munich breweries Augustiner, Hacker-Pschorr, Hofbräu, Löwenbräu, Paulaner and Spaten presented a special exclusively brewed dark beer, which was made after a historic recipe from the early 19th century.
Folk dancers performing at the Historisches Oktoberfest
The beer mugs in the beer tents did not have the company logo of the breweries, but rather the inscription «Munich beer». Unlike the usual Oktoberfest, the Historic Wiesn closed at 8 pm. Instead of the 300,000 guests estimated by the city council, well over half a million visitors came. The festival site had to be temporarily closed several times due to overcrowding.
According to the Munich City Council Decision on 16 October 2012, the entry fee for the Historical Oktoberfest, now called Oide Wiesn (Bavarian for «old fairground»), in 2013 was to be three euros again. For the first time a re-entry was possible with the tickets. The historic rides in 2013 required a 1 Euro fee.
Other changes made at that Munich City Council meeting were that the musicians’ tent increased the number of indoor seats from 1000 to 1,500. Outside tent seating increased from 800 to 1,000. They also supported the Showman Foundation with a contribution of €200,000, so it could run a museum tent, a velodrome, as well as a children’s program.[30] Also in 2013, the total festival area was enlarged and attractive entrances were added.
Lastly, according to a City Council decision, there will be an Oide Wiesn again in 2015 before the Central Agricultural Exhibition claims the location again on the Theresienwiese in 2016.[needs update]
Rosa Wiesn[edit]
The Rosa Wiesn, also known as Gay Oktoberfest, refers to a number of annual LGBT events which take place throughout the Oktoberfest period in Munich. The main feature event is in the Bräurosl (Hacker-Pschorr) tent on the first Sunday and is sometimes called ‘Gay Sunday’. Other events take place throughout the weeks of the festival with some requiring a pre-booking. These include meet and greets, Lion’s night (Löwennacht), brunches and cultural programmes.[31][32][33]
The tradition of Rosa Wiesn traces its origins to the 1970s when friends of the Munich Lion’s Club, MLC (Münchner Löwen Club), a leather and fetish society, first booked the balcony at the Bräurosl festival tent and were mistaken to have been a football club. However, the group was welcomed by the owners and waiters who enjoyed having them, and so the meet-up became an annual event. Rosa Wiesn is now one of the major events in the LGBT calendar in Germany with Gay Sunday alone attracting over 8,000 LGBT festival-goers. It is now the second-biggest LGBT event to take place after Christopher Street Day.[34][35]
Highlights[edit]
Entry of the restaurateurs and breweries[edit]
The Hacker-Pschorr Brewery horse team
The story of the entry of the Oktoberfest restaurateurs and breweries for the opening of the Oktoberfest began in 1887, when the then manager, Hans Steyrer, first marched from his meadow to the Tegernseer Landstraße with his staff, a brass band and a load of beer to the Theresienwiese.[citation needed]
In its current form, the parade has taken place since 1935, where all the breweries first took part. Since then, the parade is led by the Münchner Kindl, followed by the incumbent mayor of Munich in the Schottenhammel family carriage since 1950. This is followed by the decorated horse carriages and floats of the breweries and the carriages of the other restaurateurs and showmen. The music bands from the beer tents accompany the parade.[36]
Beer barrel tapping[edit]
After the parade of the restaurateurs on carriages from downtown to the festival grounds, at exactly 12:00 clock the lord mayor opens the first beer barrel in the Schottenhammel tent. With the initial pass and the Bavarian exclamation, «O’zapft is!» (es ist angezapft—It has been tapped!) the Oktoberfest is declared opened.
Twelve gunshots are then fired on the stairway of Ruhmeshalle. This is the signal for the other restaurateurs to start with the serving of beer.[37] Traditionally, the Bavarian Minister-President is served the first litre of beer. Then in the other tents, the first barrels are tapped and beer is served to the visitors.
Every year, visitors eagerly await to see how many strokes the mayor needs to use before the first beer flows. Bets are even made. The best performance is still two strokes (Christian Ude, 2005, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012 and 2013; Dieter Reiter, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019),[38] and there was also 19 strokes required (Thomas Wimmer, 1950).
Costume and riflemen parade[edit]
In honor of the silver wedding anniversary of King Ludwig I of Bavaria and Princess Therese, a traditional costume parade took place in 1835 for the first time. In 1895, the Bavarian novelist Maximilian Schmidt organized another parade with 1,400 participants in 150 traditional costume groups.[39] Another parade was organized for the 100th anniversary celebrations in 1910 by Julius and Moritz Wallach, promoters of the Dirndl and Lederhosen as fashion.[40][41]
Participants in the 2013 costume and riflemen parade
From 1950 to 2019 and resuming in 2022, this parade is organized annually and has become one of the highlights of the Oktoberfest and one of the world’s largest parades of its kind. On the first festival Sunday, 8000 participants march in the parade in their historic festival costumes from the Maximilianeum on a seven kilometer stretch to the festival grounds.
This parade is also led by the Münchner Kindl; followed by notables of the city council and the city administration and the state of Bavaria, usually the minister-president and his wife, traditional costume and rifle clubs, musical bands, marching bands, flag-wavers and about 40 carriages with decorated horses and carts. The clubs and groups come mostly out of Bavaria, but also from other German states, Austria, Switzerland, Northern Italy and other European countries. The entry of the Wiesnwirte (innkeepers) and the traditional costume and marksmen procession is organized by the Festring München.[42]
Beers[edit]
A waitress with Hacker-Pschorr, one of the traditional beers allowed to be served at Oktoberfest. She wears a Dirndl, a traditional women’s dress of Bavaria.
Only beer conforming to the Reinheitsgebot, and brewed within the city limits of Munich, can be served at the Munich Oktoberfest.[citation needed]
Beers meeting these criteria are designated Oktoberfest Beer[43][44] although the name ‘Oktoberfest beer’ also denotes two distinct beer styles: a traditional Märzen lager and a paler Festbier that is now more commonly served at Oktoberfest itself.[45][46]
The breweries that can produce Oktoberfest beer under the aforementioned criteria are:[47]
- Augustiner-Bräu
- Hacker-Pschorr-Bräu
- Löwenbräu
- Paulaner
- Spatenbräu
- Staatliches Hofbräu-München
Oktoberfest Beer is a registered trademark by the Club of Munich Brewers, which consists of the above six breweries.[43]
Facts and data[edit]
Size[edit]
The Oktoberfest is known as the largest Volksfest (folk festival) in the world.[48]
In 1999 there were six and a half million visitors[49] to the 42-hectare Theresienwiese. 72% of visitors are from Bavaria.[50] 15% of visitors come from foreign countries including surrounding EU countries and other non-European countries such as the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and East Asia.[51]
Besides the Oktoberfest, there are other public festivals that take place at the same location. In April and May the Munich Frühlingsfest (spring festival) is held and the Tollwood Festival is held in December with 650,000 visitors.
After the Oktoberfest the next largest public fairs in Germany are: the Cannstatter Volksfest in Stuttgart with about 4.5 million visitors each year; the Cranger Kirmes in Herne (Wanne-Eickel) (the largest fair in North Rhine-Westphalia) with 4.4 million visitors; the Rheinkirmes in Düsseldorf (called the largest fair on the Rhine); and the Freimarkt in Bremen (the biggest fair in northern Germany) with over 4 million visitors per year each. Also noteworthy is the Schützenfest Hannover, the world’s largest marksmen’s fun fair in Hannover with over 1 million visitors per year, and the Kiel Week, the world’s biggest sailing event and Volksfest in Kiel, with about 3 million visitors.
Dates[edit]
Since 1994, the Oktoberfest runs for 16 days with the last day being the first Sunday in October. However, if day 16 falls before 3 October (German Unity Day), then the festival will continue until the 3rd. (see table below)
| Year | Dates | Special Features |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 16 Sep – 3 Oct | 18 days, with ZLF* |
| 2001 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | |
| 2002 | 21 Sep – 6 Oct | |
| 2003 | 20 Sep – 5 Oct | |
| 2004 | 18 Sep – 3 Oct | with ZLF* |
| 2005 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
| 2006 | 16 Sep – 3 Oct | 18 days |
| 2007 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | |
| 2008 | 20 Sep – 5 Oct | 175th Oktoberfest (with ZLF*) |
| 2009 | 19 Sep – 4 Oct | |
| 2010 | 18 Sep – 4 Oct | 200th Anniversary (with ZLF*) |
| 2011 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
| 2012 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | with ZLF* |
| 2013 | 21 Sep – 6 Oct | |
| 2014 | 20 Sep – 5 Oct | |
| 2015 | 19 Sep – 4 Oct | |
| 2016 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
| 2017 | 16 Sep – 3 Oct | 18 days |
| 2018 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | |
| 2019 | 21 Sep – 6 Oct | |
| 2020 | 19 Sep – 4 Oct | Cancelled, due to the COVID-19 pandemic |
| 2021 | 18 Sep – 3 Oct | |
| 2022 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
* Bayerisches Zentral-Landwirtschaftsfest (Bavarian Central Agriculture Fair)
Security at the Oktoberfest[edit]
Police video surveillance
Technical accidents have rarely occurred throughout Oktoberfest history. The rides are extensively tested in advance, and the examination is performed by the cableways and temporary structures department of today’s TÜV SÜD.
On 30 September 1996, there was a collision on the Euro Star roller coaster, which injured 30, and was caused by a worn safety brake that went unnoticed during inspection. The Munich prosecutor tried to accuse the engineer, from TÜV Munich, of negligent injury, but the proceedings did not come to a conclusion.[52]
To reduce the number of thefts, fights, and sexual assault cases during Oktoberfest, protection measures for visitors have been improved in recent years. For example, in 2003 the campaign Sichere Wiesn für Mädchen und Frauen (Safe Oktoberfest for Girls and Women) was launched.
In 2004, a new service center was placed in the authorities court, in which the police, the Munich Fire Department, medical services, and a department of district administration is located. During the Oktoberfest, a police station specifically for the festival is installed, and can be reached with the emergency number 5003220.
Due to the numerous Italian visitors to the Oktoberfest, since 2005 officers from Bolzano, Italy have also been present. For decades, the Bavarian Red Cross has been responsible for medical service at the Oktoberfest.
Additional medical services are located in the Fischer Vroni tent (Aicher Ambulance), and the Munich U-Bahn has commissioned additional backups in the rapid transit station Theresienwiese provided by the Johanniter-Unfall-Hilfe. In the authorities court, an ambulance and miniature hospital, complete with operating theater, are readily available. During the Oktoberfest, additional emergency vehicles are on the alert at the control centers, and extra staff is on hand in case they are needed.
In 2010, as a public safety measure, a dog and animal ban was put into place. 2012 brought the banning of glass bottles after the increase in the number of injuries and cuts.
The safety concepts of the event have been modified and adapted continuously over the past decades:
- After the bombing in 1980, the main entrance of the Oktoberfest was redesigned in 1981.
- In 2001, a few weeks after 9-11 attacks, security checkpoints were added at the main entrance.
- In 2008, the Theresienwiese was closed off to the public during the construction of the Oktoberfest.
- In 2009, road blocks were raised, and access controls during the festival, due to the perceived threat of attacks by Islamists, were increased.
- 2010 brought the implementation of advances to the security plan, including three lockdown rings around the Theresienwiese as well as access control and flight bans over the festival grounds.[53]
- In addition, 52 two-metre (6 ft 7 in) high concrete bollards were placed in the access roads and pedestrian entrances to prevent vehicle-ramming attacks.
- In 2011, the security measures were once again increased, this time with 170 partially retractable bollards also designed to prevent forcible access to the festival grounds with a vehicle.[54]
- The Bavariaring is closed off to allow security forces adequate space to react. Police can quickly divert the crowds if needed through radio communication, as well as closing down train stations.[55]
- Following the 2016 Munich shooting, a retractable security fence was added. Previously, 350 metres (1,150 ft) of the Oktoberfest were still unfenced.
- Up to 450 security guards will stand at the 13 official entrances and check all incoming guests. Also, backpacks and bags with a volume of more than 3 litres (0.66 imp gal; 0.79 US gal) are no longer allowed on the festival grounds.
- In addition, the front exit of the subway station Theresienwiese has been closed off.[56]
Energy supply[edit]
Oktoberfest 2003 seen at night from the Ferris wheel
The Oktoberfest is powered via 43 kilometers of cable and 18 partially underground transformer stations. The Oktoberfest’s power consumption totals approximately 2.7 million kilowatt hours, not including assembly and dismantling of the attractions.[citation needed]
To supply the tents with natural gas, a four-kilometer long network of gas lines was built. The gas consumption amounts to 180,000 cubic meters for the kitchens of various catering establishments, and 20,000 cubic meters to heat the beer gardens. Most festival tents and rides use green electricity from Stadtwerke München (Munich City Utilities) to reduce pollution.
Because even a short power outage could lead to panic, all power supplies have redundancy and are fed separately. Even the lights of the individual marquees are supplied from two different substations. Despite all the precautions, on 25 September 2007, several hours of power failure occurred after a cable channel had been flooded due to heavy rains. Since the power outage occurred in the morning, there were service shortages in the catering areas, but no panic resulted.[57]
To ensure sufficient capacity of cellular networks, each year several mobile masts are set up in the lawn areas surrounding the festival.
Transportation[edit]
The Münchner Verkehrsgesellschaft (Munich Transport Company) reports transporting almost four million visitors, to and from, the festival grounds each Oktoberfest. Especially at night, the U- and S-Bahn trains are full. The underground station, Theresienwiese, has trains arriving at rush hour in three-minute intervals. The station occasionally needs to be closed due to overcrowding after the closure of the beer tents. To ensure smooth operation and safety of passengers, the Münchner Verkehrsgesellschaft and the Deutsche Bahn have increased their security personnel. People are also encouraged to use the nearby stations Goetheplatz, Schwanthalerhöhe and Hackerbrücke (the latter of the S-Bahn) or walk the short distance from the main railway station on foot.
There are significant negative effects pertaining to traffic. Since numerous festival goers make their way home by car despite having consumed alcohol, the Bavarian State Police carries out large-scale DUI controls. The city ring roads and highways around Munich are periodically blocked to allow only one lane of through traffic, which leads to massive traffic congestion.
Especially during the middle weekend of the festival, many Italians arrive with caravans (this weekend is therefore referred to by the residents of Munich as «the Italians’ weekend»).[58]
In response, the government imposes camping bans in many parts of the city. At the same time, special parking outside the city is established, which can be reached by public transportation. Large parking areas are available, for example, close to the Allianz Arena. Nevertheless, the parking situation around the festival grounds is critical. As a consequence, the effort for controls and towing services is substantial.
2010, in coordination with the new security concept, taxi stands were relocated. They are now found outside of the security ring further away from the fairground.
Trash and toilets[edit]
For safety reasons (bombing 1980), there are no trash bins in public areas.[59]
In 2004, the queues outside the toilets became so long that the police had to regulate access. To keep traffic moving through the toilets, men headed for the toilets were directed first to the urinals (giant enclosed grates) if they only needed to urinate. Consequently, the number of toilets was increased by 20% in 2005. Approximately 1,800 toilets and urinals are available today.[citation needed]
Many guests visit the quiet stalls to use their mobile phones. For this reason, there were plans in 2005 to install a Faraday cage around the toilets or to use Mobile phone jammers to prevent telephoning with those devices. Jamming devices are, however, illegal in Germany, and Faraday cages made of copper would have been too expensive, so these ambitious plans were dropped, and signs were placed instead, warning toilet users not to use cellular phones in the stalls.[citation needed] More recently, amplifying live music in the toilets has led to them no longer representing a quiet retreat for telephoning.
Tents[edit]
There are currently fourteen large tents and twenty small tents at the Oktoberfest. The tents are wooden[60] non-permanent structures which are constructed for and only used during the festival. The beer (or wine) served in each is in the accompanying table.[61]
Large tents[edit]
| Name | Brewery | Seating | |
|---|---|---|---|
| inside | outside | ||
| Large tents | |||
| Marstall | Spaten-Franziskaner-Bräu | 3,200 | 1,000 |
| Armbrustschützenzelt | Paulaner | 5,839 | 1,600 |
| Hofbräu-Festzelt | Hofbräu München | 6,896 | 3,622 |
| Hacker-Festzelt | Hacker-Pschorr | 6,900 | 2,400 |
| Schottenhamel | Spaten-Franziskaner-Bräu | 6,000 | 4,000 |
| Winzerer Fähndl | Paulaner | 8,450 | 2,450 |
| Schützen-Festhalle | Löwenbräu | 4,442 | 0 |
| Käfer Wiesn-Schänke | Paulaner | 1,000 | 1,900 |
| Weinzelt | Nymphenburger Sekt | 1,300 | 600 |
| Paulaner Weißbier | |||
| Löwenbräu-Festhalle | Löwenbräu | 5,700 | 2,800 |
| Bräurosl | Hacker-Pschorr | 6,000 | 2,200 |
| Augustiner-Festhalle | Augustiner Bräu | 6,000 | 2,500 |
| Ochsenbraterei | Spaten | 5,900 | 1,500 |
| Fischer-Vroni | Augustiner | 2,695 | 700 |
- Marstall—one of the larger tents, it is the first tent that many visitors see. Traditionally, in the evening, the Oktoberfest band Münchner Zwietracht plays Oktoberfest classics.[62]
- Armbrustschützenzelt—translates as the «Crossbowman’s Tent», a competition that has been a part of the Oktoberfest since 1895.
- Hofbräu-Festzelt—the counterpart to the famous Hofbräuhaus, this tent is especially popular with Americans, Australians and New Zealanders.[citation needed]
- Hacker-Festzelt—one of the largest tents on the Wiesn, they have a rock band that plays during the brass band’s evening break. This tent markets itself as Himmel der Bayern (Heaven of the Bavarians).
- Schottenhamel—reckoned[by whom?] to be the most important tent at the Oktoberfest, mainly because it is located at the beginning. On the first Saturday of the event, no beer is allowed to be served until the Mayor of Munich (currently Dieter Reiter) taps the first keg, at exactly high noon.[63] Only then can the other tents begin to serve beer. The tent is very popular among younger people. A substantial part of the tent is guaranteed to traditional Studentenverbindungen (a particular form of student fraternities) and outfitted with their distinctive colors and coats of arms.
- Winzerer Fähndl—literally translates as «Winzerer’s little flag» and refers to the name of an old crossbowmen’s guild, itself referring to a military unit for the Thirty Years’ War: Fähnlein being a 16th-17th century German word for the equivalent of a company/battalion of approximately 400 mercenary soldiers. Kaspar III. Winzerer was the famous Bavarian captain of such a unit. This tent is noted for its huge tower, with a Maß of Paulaner beer sitting atop it.
- Schützen-Festhalle—this is a mid-sized tent. Situated under the Bavaria statue, the current tent was newly built in 2004.
- Käfer Wiesn-Schänke—the smallest of the large tents at the Oktoberfest, it is frequented by celebrities, and is known for its especially good—and expensive—food. In contrast to the other tents (which must close by 11 pm), it is open until 12:30 am, and it can be very difficult to gain admittance.
- Weinzelt—translates as «wine tent». This tent offers a selection of more than 15 wines, as well as Weißbier.
- Löwenbräu-Festhalle—above the entrance is a 4.50-meter (15 foot)-high lion who occasionally drinks from his beer. This is overshadowed by yet another tower where an even larger drinking lion sits.
- Bräurosl (Hacker-Pschorr)—translates as «brewer’s Rosemary». Named after the daughter of the original brewery owner (Pschorr), this tent has the usual brass band and yodeler. On the first Sunday of the festival, this tent hosts the hugely popular gay and lesbian party, Rosa Wiesn.
- Augustiner-Festhalle—considered by many locals to be the best tent, due to the fact it sells the favourite local brew, Augustiner, from individually-tapped wooden kegs rather than stainless steel vats used by the other tents.
- Ochsenbraterei—true to its name, this tent offers a great variety of roasted ox dishes.
- Fischer-Vroni—translates as «Fisher’s Veronika». Another of the smaller tents. Fisch is the German word for fish and this tent carries a huge selection on its menu. The main dish is Steckerlfisch, which is grilled outside of the tent.
Small tents[edit]
| Name | Brewery | Seating | |
|---|---|---|---|
| inside | outside | ||
| Small tents | |||
| Able’s Kalbs-Kuchl | Spaten | 300 | 0 |
| Ammer Hühner & Entenbraterei | Augustiner | 450 | 450 |
| Bodo’s Cafezelt | Exotic Cocktails | 450 | 0 |
| Café Kaiserschmarrn | Cocktail bar | 400 | 0 |
| Café Mohrenkopf | XXL cocktails | 420 | 0 |
| Feisingers Ka’s und Weinstubn | Wine & Wheat Beer | 92 | 90 |
| Glöckle Wirt | Spaten | 140 | 0 |
| Heimer Hendl- und Entenbratere | Paulaner | 400 | 0 |
| Heinz Wurst- Und Hühnerbraterei | Paulaner | 360 | 0 |
| Hochreiters Haxnbraterei | Löwenbräu | 250 | 0 |
| Münchner Knödelei | Paulaner | 300 | 90 |
| Poschners Hühner- Und Entenbraterei | Hacker-Pschorr | 350 | 0 |
| Schiebl’s Kaffeehaferl | Irish Coffee | 100 | 0 |
| Wiesn Guglhupf Café-Dreh-Bar | Mix Bar | 60 | 0 |
| Wildmoser Hühnerbraterei | Hacker-Pschorr | 320 | 0 |
| Wildstuben | Augustiner | 271 | 0 |
| Wirtshaus im Schichtl | 120 | 0 | |
| Zum Stiftl | Paulaner | 360 | 0 |
| Zur Bratwurst | Augustiner | 160 | 0 |
- Able’s Kalbs-Kuchl—resembling a large Bavarian hut, the «calf kitchen» has a lively party atmosphere.
- Ammer Hühner & Entenbraterei—in 1885, poultry dealer Joseph Ammer was allowed to construct his small booth at the Oktoberfest, creating the world’s first chicken roastery. Duck is offered as well.
- Bodo’s Cafezelt—this tent offers exotic cocktails, Prosecco, champagne, coffee, donuts, ice cream, pastries, and strudel variations of all kinds.
- Café Kaiserschmarrn—created by Rischart, the café holds a daily commemoration of the occasion of the first Oktoberfest—the wedding of Ludwig I and Therese of Saxony.
- Café Mohrenkopf—since 1950 Café Mohrenkopf has been baking cakes and pies fresh daily in the Oktoberfest tent.
- Feisingers Ka’s und Weinstubn—cheese and everything that complements it is the specialty of the house in this tent.
- Glöckle Wirt—decorated with oil paintings, antique instruments and cooking utensils.
- Heimer Hendl- und Entenbraterei—very popular among the locals, Heimer’s is a family-friendly tent.
- Heinz Wurst- Und Hühnerbraterei—since 1906, the Heinz sausage and chicken grill has been a fixture on the Wiesn, specializing in authentic Oktoberfest tradition.
- Hochreiters Haxnbraterei—barbecue experts prepare pork knuckles in the only Haxenbraterei (pork knuckle roaster) at the Oktoberfest.
- Münchner Knödelei—the dumpling is an icon of Bavarian cuisine, and «preserving and spreading the dumpling culture» is the motto of this smaller tent.
- Poschners Hühner- Und Entenbraterei—Poschner’s roasted chicken and duck have been a tradition of the Wiesn for four generations.
- Schiebl’s Kaffeehaferl—with seating for about 100, Schiebl’s coffeehouse tent is a meeting place for the whole family. Haferl is the Bavarian term for a (coffee or tea) mug or pot.
- Wiesn Guglhupf Café-Dreh-Bar—a Guglhupf is a German cake, like an English bundt cake; this slowly moving carousel bar is easy to spot because it’s shaped like one.
- Wildmoser Hühnerbraterei—owned by the Wildmoser family since 1981, this small tent has been adopted and popularized by the Munich locals.
- Wildstuben—the newest tent at Oktoberfest, featuring intricately detailed woodwork and a hunting lodge ambiance.
- Wirtshaus im Schichtl—»The Schichtl is as essential as beer, radish and chicken,» former mayor Christian Ude once wrote: «An Oktoberfest without Schichtl is inconceivable.»
- Zum Stiftl—famous for its traditional duck and roasted chicken dishes, atmosphere, and daily entertainment.
- Zur Bratwurst—debuting in 2007, the Hochreiter family has brought back the former Bratwurstglöckl.
Other information[edit]
Construction of the marquees
- Experienced waiters need an average of only one and a half seconds to fill a Maß.[64]
- Letters which are placed in the Oktoberfest mailboxes receive a special postmark from the post office.[65]
- One attraction, which does not exist at other festivals, is the flea circus. It has been an attraction at the Wiesn since 1948 and a «team» of about 60 fleas provide for the entertainment especially for the children.[66]
- After the attacks on 11 September 2001, in the same year, the traditional beer tapping was omitted, instead there was a contemplative celebration in Schottenhamel tent.[67]
- Since 2009, the Theresienwiese is closed off during the construction and dismantling of the festival. The city of Munich wants to prevent any accident to visitors at the construction site that the city would be accountable for.[68]
- In 2015, the festival officially served 7.3 million litres (62,000 US bbl) of beer; for perspective, that is enough to fill nearly three (2.9) Olympic-size swimming pools.[69]
- One famous song in a beer tent is «Ein Prosit der Gemütlichkeit» which means translated «A toast to cheer and good times». The band leader plays this song several times to invite the guests to toast and drink.[70]
- With the cancellation of the Oktoberfest since 2020 due to the Coronavirus pandemic, this is the first year that the Oktoberfest has not taken place since 1949.
- In 2022, after 2 years, Oktoberfest was held again in Munich, Germany.[71]
In popular culture[edit]
A German historical drama called Oktoberfest: Beer and Blood was released in 2020.[72] Set in 1900, it focuses on the showman brewer Curt Prank as he transforms the festival into a global tourist attraction by replacing the local brewery stands with one large pavilion.[73] Critics have compared the show’s graphic violence and German new wave music soundtrack to Peaky Blinders.[74] A second season was announced by head writer Ronny Schalk in 2021.[75]
Gallery[edit]
-
Oktoberfest rides and roller coasters
-
-
Gingerbread hearts from Oktoberfest
-
«Skater» at night
See also[edit]
- Beer and Oktoberfest Museum
- Schunkeln (sway dance)
References[edit]
- ^ «Oktoberfest Beer Consumption». 19 October 2014.
- ^ «Oktoberfest in Munich: poured amount of beer 2020». Statista. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ^ «Oktoberfestbier». German Beer Institute. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- ^ «Das erste Oktoberfest». wiesnkini.de (in German). Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ^ a b «History of the Oktoberfest». Oktoberfest. 24 June 2013. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Semmens, Kristin (2005). Seeing Hitler’s Germany: Tourism in the Third Reich. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. p. 65. ISBN 978-1-349-51958-3.
- ^ Tobias Lill (25 September 2008). «Wie Hitler das Oktoberfest stahl». wiesnkini.de (in German). Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ^ Julia Meyer. «Das Münchner Oktoberfest» (in German). München-Lese. Retrieved 21 January 2015. Münchner Oktoberfest (21 April 2020). «Oktoberfest 2020 has been cancelled: The Wiesn 2020 cannot take place because of Covid-19». oktoberfest.de. Münchner Oktoberfest. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ «Parade of the landlords». oktoberfestlederhosen.com.
- ^ «Herzlich Willkommen beim Münchner Roten Kreuz». Bayerisches Rotes Kreuz. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Project «Safe Oktoberfest»«. Project «Safe Oktoberfest» • Oktoberfest.de — The Official Website for the Oktoberfest in Munich. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ The Guardian: Kate Connolly, «Gay times at Munich’s Oktoberfest,» September 22, 2011, accessed 27 January 2012.
- ^ «Die Bayerische Polizei — 26. September 1980 — das Oktoberfestattentat».
- ^ Ganser, Daniele. «Nato-Geheimarmeen und ihr Terror» (PDF) (in German). danieleganser.ch.
- ^ «Rules for Oktoberfest jeered». www.houblon.net. Retrieved 20 September 2008.
- ^ «Wiesn-Fahrgeschäfte: Mondlift (Zehle)». www.ganz-muenchen.de. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ a b Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. «Germany marks five years of smoking ban | DW | 31 August 2012». DW.COM. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ «Up in Smoke: Bavarian Politicians Want to Relax Smoking Ban». Spiegel Online International. 6 March 2008. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Smoking at the Oktoberfest». oktoberfest.de. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Oktoberfest 2010 – Raucher sollen kein Bier kriegen». Spiegel Online (in German). 29 July 2010. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Life After the Smoking Ban – Bacteria To Fight Beer Stench at Oktoberfest». Spiegel Online. 9 October 2010. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ a b c d Schulte-Peevers, Andrea. «Oktoberfest turns 200». www.bbc.com. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ «A History». oktoberfestbeerfestivals.com. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ Zeitung, Süddeutsche. «Corona Bayern: Bayern schließt neue Auflagen nicht aus». Süddeutsche.de (in German). Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ Reuters Staff (21 April 2020). «German Oktoberfest cancelled due to coronavirus». Reuters (in French). Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ «Covid: Germany’s Oktoberfest cancelled for the second time». BBC. 3 May 2021. Retrieved 3 May 2021.
- ^ «Das macht die Oide Wiesn so besonders». Das macht die Oide Wiesn so besonders • Oktoberfest.de — The Official Website for the Oktoberfest in Munich. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ^ «Infos zur Oidn Wiesn». Oktoberfest.de (in German). Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «Das Herzkasperl-Festzelt». Oktoberfest.de (in German). Archived from the original on 9 September 2010. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ Silke Lode (16 October 2012). «Oide Wiesn, junge Kultur» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «Rosa Wiesn Termine 2021 — die schwule Seite vom Oktoberfest München | Munich Gay Octoberfest Dates — MLC Oktoberfesttreffen».
- ^ Free, Sara (4 October 2018). «What Is Oktoberfest’s Gay Sunday?». Hop Culture. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ «Oktoberfest meeting – Münchner Löwen Club e.V.»
- ^ Connolly, Kate (22 September 2009). «Gay times at Munich’s Oktoberfest». The Guardian. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ Porter, Erin (17 September 2020). «Everything You Need to Know About Oktoberfest». Tripsavvy. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ «Einzug der Wirte». Wiesnkini.de (in German). Retrieved 12 October 2015.
- ^ Beate Wild, Maria Berr. «Drei Schläge zum Glück» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. Retrieved 12 October 2015.
- ^ News.de-Redaktion. «Oktoberfest 2019 News-Ticker aktuell: Millionen Besucher strömen auf das traditionelle Gelage». News.de. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- ^ Schmidt, Maximilian (1902). Meine Wanderung durch 70 Jahre. Zweiter Teil (in German). Reutlingen: Enßlin & Laiblin. pp. 247–260.
- ^ Monika Ständecke: Dirndl, Truhen, Edelweiss: die Volkskunst der Brüder Wallach. (in German) / Dirndls, Trunks, and Edelweiss. The Folk Art of the Wallach Brothers (in English). Jüdischen Museum, Munich, 2007. ISBN 978-3-9388-3220-2
- ^ Heidi Hagen-Pekdemir (30 September 2015). «Bielefelder machten das Dirndl erst schick». Neue Westfälische (in German). Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ «Geschichte / Über uns» (in German). Festring München e. V. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ a b «Oktoberfest». Spaten. Retrieved 11 December 2013.
- ^ «10 Things you didn’t know about Oktoberfest». Costume Crazy. Retrieved 7 September 2015.
- ^ «Kein Oktoberfest im Jahr 2021».
- ^ «The Real Oktoberfest Beer».
- ^ «It’s all about the beer…». Oktoberfest.de.
- ^ «How to enjoy Oktoberfest like a local». USA Today. 5 September 2007. Archived from the original on 8 October 2009. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- ^ «Realbeer.com: Beer News: Oktoberfest visitors set records». realbeer.com. Archived from the original on 31 December 2018. Retrieved 24 August 2007.
- ^ «Informationen zum Oktoberfest» (in German). muenchen.de.
- ^ «Oktoberfest Economics» (Press release). muenchen.de.
- ^ Daniel Aschoff (15 July 2008). «Der Eurostar ist jetzt ein Russe» (in German). Abendzeitung. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ «Flugverbot über dem Oktoberfest» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 17 May 2010. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ Stefan Dorner (16 March 2010). «170 Poller sollen die Wiesn schützen» (in German). tz München. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ S. Lode, S. Wimmer (14 March 2011). «Es gibt nie eine hundertprozentige Sicherheit» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ S. Menrad, Jasmin (12 September 2016). «Mobiler Rollzaun: Der Wiesn-Käfig steht!» (in German). Abendzeitung. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- ^ «Dauerregen: Umsatz-Killer und Stromausfall» (in German). Augsburger Allgemeine. 26 September 2007. Retrieved 3 July 2015.
- ^ «The Italian Weekend – Oktoberfest, ti amo!». Oktoberfest.de. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- ^ Stern.de, 2022-06-09
- ^ «Oktoberfest construction – Bavaria’s biggest building project». Building Radar. 16 September 2015.
- ^ «Beer Tents». The Oktoberfest Website.
- ^ «The Marstall».
- ^ «Anzapfen, the opening ritual of Oktoberfest» (in German). Wiesnkini. Retrieved 18 January 2014.
- ^ «O’zapft is – Kurioses um das Oktoberfest». Uniturm.de (in German). 17 September 2011. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «Oktoberfest fun facts». State of Bavaria Quebec Office. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «Flohzirkus». Wiesenkini.de (in German). Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ Karin Truscheit (21 September 2013). «Kraft allein reicht nicht». Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «Aufbau des Oktoberfests: Die Theresienwiese wird zur Baustelle». Oktoberfest.de (in German). Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «History of Oktoberfest – How It Began in Munich Germany». Retrieved 3 July 2016.
- ^ «Octoberfest Customs». Retrieved 29 August 2016.
- ^ «Germany’s 200-year-old beer festival returns to its rhythm after 2 years». News Riddle. 27 October 2022.
- ^ Oktoberfest on IMDB
- ^ Inverse
- ^ Oktoberfest tastes like Peaky Blinders with beer
- ^ Oktoberfest Season 2 release
External links[edit]
This audio file was created from a revision of this article dated 26 September 2013, and does not reflect subsequent edits.
- Oktoberfest website (in German)
- Oktoberfest Map
- Oktoberfest Traditions
- Virtual exhibition: Oktoberfest – History, Background, Highlights, in the culture portal bavarikon
Coordinates: 48°7′53″N 11°32′57″E / 48.13139°N 11.54917°E
This article is about the original festival in Munich. For Oktoberfest celebrations around the world, see Oktoberfest celebrations.
| Oktoberfest | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Observed by | Munich, Bavaria, Germany |
| Type | National |
| Celebrations | Parades, food, music, drinking |
| 2022 date | 17 September |
| Frequency | Annual |
| Related to | Oktoberfest celebrations |
The Oktoberfest (German pronunciation: [ɔkˈtoːbɐˌfɛst]; Bavarian: Wiesn, Oktobafest) is the world’s largest Volksfest, featuring a beer festival and a travelling carnival. It is held annually in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. It is a 16- to 18-day folk festival running from mid- or late-September to around the first Sunday in October, with more than six million international and national visitors attending the event. Locally, it is called d’Wiesn, after the colloquial name for the fairgrounds, Theresienwiese. The Oktoberfest is an important part of Bavarian culture, having been held since the year 1810. Other cities across the world also hold Oktoberfest celebrations that are modeled after the original Munich event.
During the event, large quantities of Oktoberfest Beer are consumed. For example, during the 16-day festival in 2014, 7.7 million litres (2,000,000 US gal) were served,[1] making it the year where the most beer was consumed at the Oktoberfest.[2] Visitors also enjoy numerous attractions, such as amusement rides, sidestalls, and games. There is also a wide variety of traditional foods available.
The Munich Oktoberfest originally took place in the 16-day period leading up to the first Sunday in October. In 1994, this longstanding schedule was modified in response to German reunification. As a result, if the first Sunday in October falls on the 1st or the 2nd, then the festival would run until 3 October (German Unity Day). Thus, the festival now runs for 17 days when the first Sunday is 2 October and 18 days when it is 1 October. In 2010, the festival lasted until the first Monday in October (4 October), to mark the event’s bicentennial.
History[edit]
Horse race at the Oktoberfest in Munich, 1823
Portrait of a girl wearing a Dirndl dress
Kronprinz Ludwig (1786–1868), later King Ludwig I (reign: 1825–1848), married Princess Therese of Saxe-Hildburghausen on 12 October 1810. The citizens of Munich were invited to attend the festivities held on the fields in front of the city gates to celebrate the royal event. The fields were named Theresienwiese («Theresa’s Meadow») in honour of the Crown Princess, and have kept that name ever since, although the locals have abbreviated the name simply to Wiesn.[3] Horse races, in the tradition of the 15th-century Scharlachrennen (Scarlet Race at Karlstor), were held on 18 October to honor the newlyweds. It is widely believed that Andreas Michael Dall’Armi, a major in the National Guard, proposed the idea. However, the origins of the horse races, and Oktoberfest itself, may have stemmed from proposals offered by Franz Baumgartner, a coachman and sergeant in the National Guard. The precise origins of the festival and horse races remain a matter of controversy. However, the decision to repeat the horse races, spectacle, and celebrations in 1811 launched what is now the annual Oktoberfest tradition.
The fairground, once outside the city, was chosen due to its natural suitability, which it still holds today. The Sendlinger Hill (today Theresienhohe) was used as a grandstand for 40,000 race spectators. The festival grounds remained undeveloped, except for the king’s tent. The tastings of «Traiteurs» and other wine and beer took place above the visitors in the stands on the hill. Before the race started, a performance was held in homage of the bridegroom and of the royal family in the form of a train of 16 pairs of children dressed in Wittelsbach costumes, and costumes from the nine Bavarian townships and other regions. This was followed by the punishing race with 30 horses on a 3,400 metres (11,200 ft) long racetrack, and concluded with the singing of a student choir. The first horse to cross the finish line belonged to Franz Baumgartner (one of the purported festival initiators). Horse racing champion and Minister of State Maximilian von Montgelas presented Baumgartner with his gold medal.[4]
Transformation into a public festival[edit]
19th century[edit]
In 1811, a show was added to promote Bavarian agriculture. In 1813, the festival was canceled due to the involvement of Bavaria in the Napoleonic Wars, after which the Oktoberfest grew from year to year. The horse races were accompanied by tree climbing, bowling alleys, and swings and other attractions. In 1818, carnival booths appeared; the main prizes awarded were of silver, porcelain, and jewelry. The city fathers assumed responsibility for festival management in 1819, and it was decided that Oktoberfest become an annual event. In 1832, the date was moved some weeks later, as a Greek delegation came. It inspired them for the Zappas Olympics which became in 1896 the modern Olympic Games.[citation needed] Later,[when?] the Oktoberfest was lengthened and the date pushed forward because days are longer and warmer at the end of September. The horse race continued until 1960, and the agricultural show still exists today and is held every four years in the southern part of the festival grounds.
To honour the marriage of Prince Ludwig and Therese of Saxe-Hildburghausen, a parade took place for the first time in 1810. Since 1850, the parade has become an annual event and an important component of the Oktoberfest. Eight thousand people—mostly from Bavaria—and dressed in traditional costumes walk from Maximilian Street through the centre of Munich to the Oktoberfest grounds. The march is led by the Münchner Kindl.
Since 1850, the statue of Bavaria has watched over the Oktoberfest. This worldly Bavarian patron was first sketched by Leo von Klenze in a classic style and Ludwig Michael Schwanthaler romanticised and Germanised the draft.[citation needed] The statue was constructed by Johann Baptist Stiglmaier and Ferdinand von Miller.
In 1853, the Bavarian Ruhmeshalle was completed. In 1854, the festival was cancelled after 3,000 residents of Munich including the queen consort died during a cholera epidemic. There was no Oktoberfest in 1866 because Bavaria was involved in the Austro-Prussian War. In 1870, the Franco-Prussian War again forced the cancellation of the festival. In 1873, the festival was cancelled due to yet another cholera epidemic. In 1880, electric light illuminated more than 400 booths and tents. In 1881, booths selling Bratwurst opened and the first beer was served in glass mugs in 1892.
At the end of the 19th century, a re-organization took place. Until then, there were games of skittles, large dance floors, and trees for climbing in the beer booths. Organizers wanted more room for guests and musicians which resulted in the booths becoming beer halls which are still used today.
In 1887, the parade of the Oktoberfest staff and breweries took place for the first time. This event showcases the splendidly decorated horse teams of the breweries and the bands that play in the festival tents. This event always takes place on the first Saturday of the Oktoberfest and serves as the official prelude to the Oktoberfest celebration.
20th century[edit]
At the 100th anniversary of Oktoberfest in 1910, an estimated 120,000 litres of beer were consumed. Three years later, the Bräurosl was founded, which at that time was the largest pavilion to have ever been built, accommodating approximately 12,000 people.[5]
Due to World War I, Oktoberfest was temporarily suspended from 1914 to 1918. The two years after the war, in 1919 and 1920, Oktoberfest was replaced by the so-called kleineres Herbstfest (which can be translated as «smaller autumn celebration»), and in 1923 and 1924 the Oktoberfest was cancelled due to hyperinflation.[5]
During National Socialism, Oktoberfest was used as part of Nazi propaganda.[6] In 1933, Jews were forbidden to work on the Wiesn.[citation needed] Two years later, Oktoberfest’s 125th anniversary was celebrated with all the frills. The main event was a big parade.
The slogan proud city—cheerful country was meant to show the alleged overcoming of differences between social classes, and can be seen as an example of the regime’s consolidation of power. In 1938, after Hitler had annexed Austria and won the Sudetenland via the Munich Agreement, Oktoberfest was renamed to Großdeutsches Volksfest (Greater German folk festival), and as a showing of strength, the Nazi regime transported people from Sudetenland to the Wiesn by the score.[7]
During World War II, from 1939 to 1945, no Oktoberfest was celebrated. Following the war, from 1946 to 1948, Munich celebrated only the «Autumn Fest». The sale of proper Oktoberfest beer—2% stronger in gravity than normal beer—was not permitted; guests could only drink normal beer.
Since its foundation, there have been 26 years in which it was declined.[8]
Since 1950, the festival has always been opened with the same traditional procedure: At noon, a 12-gun salute is followed by the tapping of the first keg of Oktoberfest beer by the Mayor of Munich with the proclamation «O’zapft is!» («It’s tapped!» in the Austro-Bavarian dialect). The Mayor then gives the first litre of beer to the Minister-President of the State of Bavaria. The first mayor to tap a keg was Thomas Wimmer.
Gamsbärte at the entry of the Oktoberfest restaurateurs, 2008
Before the festival officially starts, parades are held with the traditional marksmen’s clubs, beer-tent waitresses, and landlords participating. There are two different parades which both end at the Theresienwiese. They start around 9:45 a.m. to 10.50 am.[9]
During Oktoberfest, some locals wear Bavarian hats (Tirolerhüte), which contain a tuft of chamois hair (Gamsbart). Historically, in Bavaria chamois hair was highly valued and prized. The more tufts of chamois hair on one’s hat, the wealthier one was considered to be. Due to modern technology, this tradition has declined with the appearance of chamois hair imitations on the market.[citation needed]
For medical treatment of visitors, the Bavarian branch of the German Red Cross operates an aid facility and provides emergency medical care on the festival grounds, staffed with around 100 volunteer medics and doctors per day.[10]
They serve together with special detachments of Munich police, the fire department and other municipal authorities in the service centre at the Behördenhof (authorities’ court), a large building specially built for the Oktoberfest at the east side of the Theresienwiese, just behind the tents. There is also a station for lost and found children, a lost property office, a security point for women and other public services.[11]
Since the 1970s, local German gay organizations have organized «Gay Days» at Oktoberfest, which since the 21st century always begin in the Bräurosl tent on the first Sunday.[12]
1980 bombing[edit]
A pipe bomb was set off in a dustbin near the toilets at the main entrance on 26 September 1980 at 22:19. The bomb consisted of an empty fire extinguisher filled with 1.39 kilograms of TNT and mortar shells. Thirteen people were killed and over 225 were injured, 68 seriously. The case is still under criminal investigation by the State Police on behalf of the National Prosecutor General as of 2022 which had been stalled for several decades in between.[13]
This is the second-deadliest terrorist attack in the history of Germany after the Munich massacre.
Federal and state law enforcement authorities initiated numerous official inquiries, concluding that a right-wing extremist, Gundolf Köhler, from Donaueschingen, a social outcast who was killed in the explosion, was the sole perpetrator. However, both this account and the number of perpetrators are strongly disputed by various groups.[14]
Oktoberfest today[edit]
Music entertainment at the Oktoberfest, 2015
To keep the Oktoberfest, and especially the beer tents, amicable for the elderly and families, the concept of the «quiet Oktoberfest» was developed in 2005. Until 6:00 pm, the orchestras in the tents only play brass music, for example traditional folk music. Only after that may Schlager pop or electric music be played, which had led to excessively raucous behaviour in earlier years.[15] The music played in the afternoon is limited to 85 decibels. With these rules, the organisers of the Oktoberfest were able to curb[dubious – discuss] the tumultuous party mentality and preserve the traditional beer-tent atmosphere.
In 2005 Germany’s last travelling enterprise amusement ride, the Mondlift, returned to the Oktoberfest.[16]
Starting in 2008, a new Bavarian law was passed to ban smoking in all enclosed spaces open to the public.[17] Because of problems enforcing the anti-smoking law in the big tents, an exception was granted to the Oktoberfest in 2008, although the sale of tobacco was not allowed. After heavy losses in the 2008 local elections, with the smoking ban being a big issue in political debates, the state’s ruling party implemented general exemptions to beer tents and small pubs.
The change in regulations was aimed in particular to benefit the large tents of the Oktoberfest:[18] smoking in the tents is still legal, but the tents usually have non-smoking areas.[19] The sale of tobacco in the tents is now legal, but is widely boycotted by mutual agreement. However, in early 2010, a referendum held in Bavaria as a result of a popular initiative re-instituted the original, strict, smoking ban of 2008; thus, no beer will be sold to people caught smoking in the tents.[20]
The blanket smoking ban did not take effect until 2011,[17] but all tents instituted the smoking ban in 2010 to do a «dry run» to identify any unforeseeable issues.[21]
Celebrating 200 years of Oktoberfest in 2010
The year 2010 marked the Oktoberfest Bicentennial.[22] For the anniversary, a horse race in historical costumes was held on opening day. A so-called historische Wiesn (historical Oktoberfest) took place,[22] starting one day earlier than usual on the southern part of the festival grounds. A specially brewed beer (solely available at the tents of the historical Oktoberfest), horse races, and a museum tent gave visitors an impression of how the event felt two centuries ago.[22]
In 2013, 6.4 million people visited Oktoberfest, and visitors were served 6.7 million litres of beer.[23]
On 21 April 2020, Bavarian Minister-President Markus Söder and the mayor of Munich, Dieter Reiter, announced the official cancellation of the 2020 Oktoberfest due to the ongoing coronavirus pandemic.[24][25] On 3 May 2021, Minister-President Söder and Mayor Reiter announced that the Oktoberfest hiatus will be extended, deferring the next one to 2022. Söder noted the unfeasibility of social distancing in the festival’s beer tents, adding, «Imagine there was a new wave and it then became a super-spreader event. The brand would be damaged forever and we don’t want that.»[26]
Oide Wiesn[edit]
On the occasion of the 200th anniversary in 2010 a so-called Historisches Oktoberfest (Historical Oktoberfest) was designed on the site of the Central Agricultural Festival at the south end of the Theresienwiese. It opened one day before the official Oktoberfest with the traditional keg tapping by the Lord Mayor.[22] Due to the popularity of the Oide Wiesn, it was established as a permanent feature from 2011.[27]
Main entrance to the Historical Oktoberfest
The comprehensive five acres of fenced grounds presented historic rides, beer tents and other historical attractions such as a Steckerlfisch grilling, a chain swing and a cotton candy stand. Included in the price of admission, an animal tent and the racecourse could be visited next to the museum.
The animal tent included, among other things, a petting zoo, and was managed by the Hellabrunn Zoo and the Bavarian Farmers Association. The Munich Stadtmuseum took over the design of the museum tent. The Oktoberfest anniversary was accompanied by an artistic and cultural program, in which for example the Biermösl Blosn (local entertainers) performed.
The bands performing in the relatively small Herzkasperl Festzelt—offering 850 seats—had to do without electrical amplification.[28]
The fest-tent name derives from a famous stage character of the actor Jörg Hube, who died in 2009.[29]
The six main Munich breweries Augustiner, Hacker-Pschorr, Hofbräu, Löwenbräu, Paulaner and Spaten presented a special exclusively brewed dark beer, which was made after a historic recipe from the early 19th century.
Folk dancers performing at the Historisches Oktoberfest
The beer mugs in the beer tents did not have the company logo of the breweries, but rather the inscription «Munich beer». Unlike the usual Oktoberfest, the Historic Wiesn closed at 8 pm. Instead of the 300,000 guests estimated by the city council, well over half a million visitors came. The festival site had to be temporarily closed several times due to overcrowding.
According to the Munich City Council Decision on 16 October 2012, the entry fee for the Historical Oktoberfest, now called Oide Wiesn (Bavarian for «old fairground»), in 2013 was to be three euros again. For the first time a re-entry was possible with the tickets. The historic rides in 2013 required a 1 Euro fee.
Other changes made at that Munich City Council meeting were that the musicians’ tent increased the number of indoor seats from 1000 to 1,500. Outside tent seating increased from 800 to 1,000. They also supported the Showman Foundation with a contribution of €200,000, so it could run a museum tent, a velodrome, as well as a children’s program.[30] Also in 2013, the total festival area was enlarged and attractive entrances were added.
Lastly, according to a City Council decision, there will be an Oide Wiesn again in 2015 before the Central Agricultural Exhibition claims the location again on the Theresienwiese in 2016.[needs update]
Rosa Wiesn[edit]
The Rosa Wiesn, also known as Gay Oktoberfest, refers to a number of annual LGBT events which take place throughout the Oktoberfest period in Munich. The main feature event is in the Bräurosl (Hacker-Pschorr) tent on the first Sunday and is sometimes called ‘Gay Sunday’. Other events take place throughout the weeks of the festival with some requiring a pre-booking. These include meet and greets, Lion’s night (Löwennacht), brunches and cultural programmes.[31][32][33]
The tradition of Rosa Wiesn traces its origins to the 1970s when friends of the Munich Lion’s Club, MLC (Münchner Löwen Club), a leather and fetish society, first booked the balcony at the Bräurosl festival tent and were mistaken to have been a football club. However, the group was welcomed by the owners and waiters who enjoyed having them, and so the meet-up became an annual event. Rosa Wiesn is now one of the major events in the LGBT calendar in Germany with Gay Sunday alone attracting over 8,000 LGBT festival-goers. It is now the second-biggest LGBT event to take place after Christopher Street Day.[34][35]
Highlights[edit]
Entry of the restaurateurs and breweries[edit]
The Hacker-Pschorr Brewery horse team
The story of the entry of the Oktoberfest restaurateurs and breweries for the opening of the Oktoberfest began in 1887, when the then manager, Hans Steyrer, first marched from his meadow to the Tegernseer Landstraße with his staff, a brass band and a load of beer to the Theresienwiese.[citation needed]
In its current form, the parade has taken place since 1935, where all the breweries first took part. Since then, the parade is led by the Münchner Kindl, followed by the incumbent mayor of Munich in the Schottenhammel family carriage since 1950. This is followed by the decorated horse carriages and floats of the breweries and the carriages of the other restaurateurs and showmen. The music bands from the beer tents accompany the parade.[36]
Beer barrel tapping[edit]
After the parade of the restaurateurs on carriages from downtown to the festival grounds, at exactly 12:00 clock the lord mayor opens the first beer barrel in the Schottenhammel tent. With the initial pass and the Bavarian exclamation, «O’zapft is!» (es ist angezapft—It has been tapped!) the Oktoberfest is declared opened.
Twelve gunshots are then fired on the stairway of Ruhmeshalle. This is the signal for the other restaurateurs to start with the serving of beer.[37] Traditionally, the Bavarian Minister-President is served the first litre of beer. Then in the other tents, the first barrels are tapped and beer is served to the visitors.
Every year, visitors eagerly await to see how many strokes the mayor needs to use before the first beer flows. Bets are even made. The best performance is still two strokes (Christian Ude, 2005, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012 and 2013; Dieter Reiter, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019),[38] and there was also 19 strokes required (Thomas Wimmer, 1950).
Costume and riflemen parade[edit]
In honor of the silver wedding anniversary of King Ludwig I of Bavaria and Princess Therese, a traditional costume parade took place in 1835 for the first time. In 1895, the Bavarian novelist Maximilian Schmidt organized another parade with 1,400 participants in 150 traditional costume groups.[39] Another parade was organized for the 100th anniversary celebrations in 1910 by Julius and Moritz Wallach, promoters of the Dirndl and Lederhosen as fashion.[40][41]
Participants in the 2013 costume and riflemen parade
From 1950 to 2019 and resuming in 2022, this parade is organized annually and has become one of the highlights of the Oktoberfest and one of the world’s largest parades of its kind. On the first festival Sunday, 8000 participants march in the parade in their historic festival costumes from the Maximilianeum on a seven kilometer stretch to the festival grounds.
This parade is also led by the Münchner Kindl; followed by notables of the city council and the city administration and the state of Bavaria, usually the minister-president and his wife, traditional costume and rifle clubs, musical bands, marching bands, flag-wavers and about 40 carriages with decorated horses and carts. The clubs and groups come mostly out of Bavaria, but also from other German states, Austria, Switzerland, Northern Italy and other European countries. The entry of the Wiesnwirte (innkeepers) and the traditional costume and marksmen procession is organized by the Festring München.[42]
Beers[edit]
A waitress with Hacker-Pschorr, one of the traditional beers allowed to be served at Oktoberfest. She wears a Dirndl, a traditional women’s dress of Bavaria.
Only beer conforming to the Reinheitsgebot, and brewed within the city limits of Munich, can be served at the Munich Oktoberfest.[citation needed]
Beers meeting these criteria are designated Oktoberfest Beer[43][44] although the name ‘Oktoberfest beer’ also denotes two distinct beer styles: a traditional Märzen lager and a paler Festbier that is now more commonly served at Oktoberfest itself.[45][46]
The breweries that can produce Oktoberfest beer under the aforementioned criteria are:[47]
- Augustiner-Bräu
- Hacker-Pschorr-Bräu
- Löwenbräu
- Paulaner
- Spatenbräu
- Staatliches Hofbräu-München
Oktoberfest Beer is a registered trademark by the Club of Munich Brewers, which consists of the above six breweries.[43]
Facts and data[edit]
Size[edit]
The Oktoberfest is known as the largest Volksfest (folk festival) in the world.[48]
In 1999 there were six and a half million visitors[49] to the 42-hectare Theresienwiese. 72% of visitors are from Bavaria.[50] 15% of visitors come from foreign countries including surrounding EU countries and other non-European countries such as the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and East Asia.[51]
Besides the Oktoberfest, there are other public festivals that take place at the same location. In April and May the Munich Frühlingsfest (spring festival) is held and the Tollwood Festival is held in December with 650,000 visitors.
After the Oktoberfest the next largest public fairs in Germany are: the Cannstatter Volksfest in Stuttgart with about 4.5 million visitors each year; the Cranger Kirmes in Herne (Wanne-Eickel) (the largest fair in North Rhine-Westphalia) with 4.4 million visitors; the Rheinkirmes in Düsseldorf (called the largest fair on the Rhine); and the Freimarkt in Bremen (the biggest fair in northern Germany) with over 4 million visitors per year each. Also noteworthy is the Schützenfest Hannover, the world’s largest marksmen’s fun fair in Hannover with over 1 million visitors per year, and the Kiel Week, the world’s biggest sailing event and Volksfest in Kiel, with about 3 million visitors.
Dates[edit]
Since 1994, the Oktoberfest runs for 16 days with the last day being the first Sunday in October. However, if day 16 falls before 3 October (German Unity Day), then the festival will continue until the 3rd. (see table below)
| Year | Dates | Special Features |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 16 Sep – 3 Oct | 18 days, with ZLF* |
| 2001 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | |
| 2002 | 21 Sep – 6 Oct | |
| 2003 | 20 Sep – 5 Oct | |
| 2004 | 18 Sep – 3 Oct | with ZLF* |
| 2005 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
| 2006 | 16 Sep – 3 Oct | 18 days |
| 2007 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | |
| 2008 | 20 Sep – 5 Oct | 175th Oktoberfest (with ZLF*) |
| 2009 | 19 Sep – 4 Oct | |
| 2010 | 18 Sep – 4 Oct | 200th Anniversary (with ZLF*) |
| 2011 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
| 2012 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | with ZLF* |
| 2013 | 21 Sep – 6 Oct | |
| 2014 | 20 Sep – 5 Oct | |
| 2015 | 19 Sep – 4 Oct | |
| 2016 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
| 2017 | 16 Sep – 3 Oct | 18 days |
| 2018 | 22 Sep – 7 Oct | |
| 2019 | 21 Sep – 6 Oct | |
| 2020 | 19 Sep – 4 Oct | Cancelled, due to the COVID-19 pandemic |
| 2021 | 18 Sep – 3 Oct | |
| 2022 | 17 Sep – 3 Oct | 17 days |
* Bayerisches Zentral-Landwirtschaftsfest (Bavarian Central Agriculture Fair)
Security at the Oktoberfest[edit]
Police video surveillance
Technical accidents have rarely occurred throughout Oktoberfest history. The rides are extensively tested in advance, and the examination is performed by the cableways and temporary structures department of today’s TÜV SÜD.
On 30 September 1996, there was a collision on the Euro Star roller coaster, which injured 30, and was caused by a worn safety brake that went unnoticed during inspection. The Munich prosecutor tried to accuse the engineer, from TÜV Munich, of negligent injury, but the proceedings did not come to a conclusion.[52]
To reduce the number of thefts, fights, and sexual assault cases during Oktoberfest, protection measures for visitors have been improved in recent years. For example, in 2003 the campaign Sichere Wiesn für Mädchen und Frauen (Safe Oktoberfest for Girls and Women) was launched.
In 2004, a new service center was placed in the authorities court, in which the police, the Munich Fire Department, medical services, and a department of district administration is located. During the Oktoberfest, a police station specifically for the festival is installed, and can be reached with the emergency number 5003220.
Due to the numerous Italian visitors to the Oktoberfest, since 2005 officers from Bolzano, Italy have also been present. For decades, the Bavarian Red Cross has been responsible for medical service at the Oktoberfest.
Additional medical services are located in the Fischer Vroni tent (Aicher Ambulance), and the Munich U-Bahn has commissioned additional backups in the rapid transit station Theresienwiese provided by the Johanniter-Unfall-Hilfe. In the authorities court, an ambulance and miniature hospital, complete with operating theater, are readily available. During the Oktoberfest, additional emergency vehicles are on the alert at the control centers, and extra staff is on hand in case they are needed.
In 2010, as a public safety measure, a dog and animal ban was put into place. 2012 brought the banning of glass bottles after the increase in the number of injuries and cuts.
The safety concepts of the event have been modified and adapted continuously over the past decades:
- After the bombing in 1980, the main entrance of the Oktoberfest was redesigned in 1981.
- In 2001, a few weeks after 9-11 attacks, security checkpoints were added at the main entrance.
- In 2008, the Theresienwiese was closed off to the public during the construction of the Oktoberfest.
- In 2009, road blocks were raised, and access controls during the festival, due to the perceived threat of attacks by Islamists, were increased.
- 2010 brought the implementation of advances to the security plan, including three lockdown rings around the Theresienwiese as well as access control and flight bans over the festival grounds.[53]
- In addition, 52 two-metre (6 ft 7 in) high concrete bollards were placed in the access roads and pedestrian entrances to prevent vehicle-ramming attacks.
- In 2011, the security measures were once again increased, this time with 170 partially retractable bollards also designed to prevent forcible access to the festival grounds with a vehicle.[54]
- The Bavariaring is closed off to allow security forces adequate space to react. Police can quickly divert the crowds if needed through radio communication, as well as closing down train stations.[55]
- Following the 2016 Munich shooting, a retractable security fence was added. Previously, 350 metres (1,150 ft) of the Oktoberfest were still unfenced.
- Up to 450 security guards will stand at the 13 official entrances and check all incoming guests. Also, backpacks and bags with a volume of more than 3 litres (0.66 imp gal; 0.79 US gal) are no longer allowed on the festival grounds.
- In addition, the front exit of the subway station Theresienwiese has been closed off.[56]
Energy supply[edit]
Oktoberfest 2003 seen at night from the Ferris wheel
The Oktoberfest is powered via 43 kilometers of cable and 18 partially underground transformer stations. The Oktoberfest’s power consumption totals approximately 2.7 million kilowatt hours, not including assembly and dismantling of the attractions.[citation needed]
To supply the tents with natural gas, a four-kilometer long network of gas lines was built. The gas consumption amounts to 180,000 cubic meters for the kitchens of various catering establishments, and 20,000 cubic meters to heat the beer gardens. Most festival tents and rides use green electricity from Stadtwerke München (Munich City Utilities) to reduce pollution.
Because even a short power outage could lead to panic, all power supplies have redundancy and are fed separately. Even the lights of the individual marquees are supplied from two different substations. Despite all the precautions, on 25 September 2007, several hours of power failure occurred after a cable channel had been flooded due to heavy rains. Since the power outage occurred in the morning, there were service shortages in the catering areas, but no panic resulted.[57]
To ensure sufficient capacity of cellular networks, each year several mobile masts are set up in the lawn areas surrounding the festival.
Transportation[edit]
The Münchner Verkehrsgesellschaft (Munich Transport Company) reports transporting almost four million visitors, to and from, the festival grounds each Oktoberfest. Especially at night, the U- and S-Bahn trains are full. The underground station, Theresienwiese, has trains arriving at rush hour in three-minute intervals. The station occasionally needs to be closed due to overcrowding after the closure of the beer tents. To ensure smooth operation and safety of passengers, the Münchner Verkehrsgesellschaft and the Deutsche Bahn have increased their security personnel. People are also encouraged to use the nearby stations Goetheplatz, Schwanthalerhöhe and Hackerbrücke (the latter of the S-Bahn) or walk the short distance from the main railway station on foot.
There are significant negative effects pertaining to traffic. Since numerous festival goers make their way home by car despite having consumed alcohol, the Bavarian State Police carries out large-scale DUI controls. The city ring roads and highways around Munich are periodically blocked to allow only one lane of through traffic, which leads to massive traffic congestion.
Especially during the middle weekend of the festival, many Italians arrive with caravans (this weekend is therefore referred to by the residents of Munich as «the Italians’ weekend»).[58]
In response, the government imposes camping bans in many parts of the city. At the same time, special parking outside the city is established, which can be reached by public transportation. Large parking areas are available, for example, close to the Allianz Arena. Nevertheless, the parking situation around the festival grounds is critical. As a consequence, the effort for controls and towing services is substantial.
2010, in coordination with the new security concept, taxi stands were relocated. They are now found outside of the security ring further away from the fairground.
Trash and toilets[edit]
For safety reasons (bombing 1980), there are no trash bins in public areas.[59]
In 2004, the queues outside the toilets became so long that the police had to regulate access. To keep traffic moving through the toilets, men headed for the toilets were directed first to the urinals (giant enclosed grates) if they only needed to urinate. Consequently, the number of toilets was increased by 20% in 2005. Approximately 1,800 toilets and urinals are available today.[citation needed]
Many guests visit the quiet stalls to use their mobile phones. For this reason, there were plans in 2005 to install a Faraday cage around the toilets or to use Mobile phone jammers to prevent telephoning with those devices. Jamming devices are, however, illegal in Germany, and Faraday cages made of copper would have been too expensive, so these ambitious plans were dropped, and signs were placed instead, warning toilet users not to use cellular phones in the stalls.[citation needed] More recently, amplifying live music in the toilets has led to them no longer representing a quiet retreat for telephoning.
Tents[edit]
There are currently fourteen large tents and twenty small tents at the Oktoberfest. The tents are wooden[60] non-permanent structures which are constructed for and only used during the festival. The beer (or wine) served in each is in the accompanying table.[61]
Large tents[edit]
| Name | Brewery | Seating | |
|---|---|---|---|
| inside | outside | ||
| Large tents | |||
| Marstall | Spaten-Franziskaner-Bräu | 3,200 | 1,000 |
| Armbrustschützenzelt | Paulaner | 5,839 | 1,600 |
| Hofbräu-Festzelt | Hofbräu München | 6,896 | 3,622 |
| Hacker-Festzelt | Hacker-Pschorr | 6,900 | 2,400 |
| Schottenhamel | Spaten-Franziskaner-Bräu | 6,000 | 4,000 |
| Winzerer Fähndl | Paulaner | 8,450 | 2,450 |
| Schützen-Festhalle | Löwenbräu | 4,442 | 0 |
| Käfer Wiesn-Schänke | Paulaner | 1,000 | 1,900 |
| Weinzelt | Nymphenburger Sekt | 1,300 | 600 |
| Paulaner Weißbier | |||
| Löwenbräu-Festhalle | Löwenbräu | 5,700 | 2,800 |
| Bräurosl | Hacker-Pschorr | 6,000 | 2,200 |
| Augustiner-Festhalle | Augustiner Bräu | 6,000 | 2,500 |
| Ochsenbraterei | Spaten | 5,900 | 1,500 |
| Fischer-Vroni | Augustiner | 2,695 | 700 |
- Marstall—one of the larger tents, it is the first tent that many visitors see. Traditionally, in the evening, the Oktoberfest band Münchner Zwietracht plays Oktoberfest classics.[62]
- Armbrustschützenzelt—translates as the «Crossbowman’s Tent», a competition that has been a part of the Oktoberfest since 1895.
- Hofbräu-Festzelt—the counterpart to the famous Hofbräuhaus, this tent is especially popular with Americans, Australians and New Zealanders.[citation needed]
- Hacker-Festzelt—one of the largest tents on the Wiesn, they have a rock band that plays during the brass band’s evening break. This tent markets itself as Himmel der Bayern (Heaven of the Bavarians).
- Schottenhamel—reckoned[by whom?] to be the most important tent at the Oktoberfest, mainly because it is located at the beginning. On the first Saturday of the event, no beer is allowed to be served until the Mayor of Munich (currently Dieter Reiter) taps the first keg, at exactly high noon.[63] Only then can the other tents begin to serve beer. The tent is very popular among younger people. A substantial part of the tent is guaranteed to traditional Studentenverbindungen (a particular form of student fraternities) and outfitted with their distinctive colors and coats of arms.
- Winzerer Fähndl—literally translates as «Winzerer’s little flag» and refers to the name of an old crossbowmen’s guild, itself referring to a military unit for the Thirty Years’ War: Fähnlein being a 16th-17th century German word for the equivalent of a company/battalion of approximately 400 mercenary soldiers. Kaspar III. Winzerer was the famous Bavarian captain of such a unit. This tent is noted for its huge tower, with a Maß of Paulaner beer sitting atop it.
- Schützen-Festhalle—this is a mid-sized tent. Situated under the Bavaria statue, the current tent was newly built in 2004.
- Käfer Wiesn-Schänke—the smallest of the large tents at the Oktoberfest, it is frequented by celebrities, and is known for its especially good—and expensive—food. In contrast to the other tents (which must close by 11 pm), it is open until 12:30 am, and it can be very difficult to gain admittance.
- Weinzelt—translates as «wine tent». This tent offers a selection of more than 15 wines, as well as Weißbier.
- Löwenbräu-Festhalle—above the entrance is a 4.50-meter (15 foot)-high lion who occasionally drinks from his beer. This is overshadowed by yet another tower where an even larger drinking lion sits.
- Bräurosl (Hacker-Pschorr)—translates as «brewer’s Rosemary». Named after the daughter of the original brewery owner (Pschorr), this tent has the usual brass band and yodeler. On the first Sunday of the festival, this tent hosts the hugely popular gay and lesbian party, Rosa Wiesn.
- Augustiner-Festhalle—considered by many locals to be the best tent, due to the fact it sells the favourite local brew, Augustiner, from individually-tapped wooden kegs rather than stainless steel vats used by the other tents.
- Ochsenbraterei—true to its name, this tent offers a great variety of roasted ox dishes.
- Fischer-Vroni—translates as «Fisher’s Veronika». Another of the smaller tents. Fisch is the German word for fish and this tent carries a huge selection on its menu. The main dish is Steckerlfisch, which is grilled outside of the tent.
Small tents[edit]
| Name | Brewery | Seating | |
|---|---|---|---|
| inside | outside | ||
| Small tents | |||
| Able’s Kalbs-Kuchl | Spaten | 300 | 0 |
| Ammer Hühner & Entenbraterei | Augustiner | 450 | 450 |
| Bodo’s Cafezelt | Exotic Cocktails | 450 | 0 |
| Café Kaiserschmarrn | Cocktail bar | 400 | 0 |
| Café Mohrenkopf | XXL cocktails | 420 | 0 |
| Feisingers Ka’s und Weinstubn | Wine & Wheat Beer | 92 | 90 |
| Glöckle Wirt | Spaten | 140 | 0 |
| Heimer Hendl- und Entenbratere | Paulaner | 400 | 0 |
| Heinz Wurst- Und Hühnerbraterei | Paulaner | 360 | 0 |
| Hochreiters Haxnbraterei | Löwenbräu | 250 | 0 |
| Münchner Knödelei | Paulaner | 300 | 90 |
| Poschners Hühner- Und Entenbraterei | Hacker-Pschorr | 350 | 0 |
| Schiebl’s Kaffeehaferl | Irish Coffee | 100 | 0 |
| Wiesn Guglhupf Café-Dreh-Bar | Mix Bar | 60 | 0 |
| Wildmoser Hühnerbraterei | Hacker-Pschorr | 320 | 0 |
| Wildstuben | Augustiner | 271 | 0 |
| Wirtshaus im Schichtl | 120 | 0 | |
| Zum Stiftl | Paulaner | 360 | 0 |
| Zur Bratwurst | Augustiner | 160 | 0 |
- Able’s Kalbs-Kuchl—resembling a large Bavarian hut, the «calf kitchen» has a lively party atmosphere.
- Ammer Hühner & Entenbraterei—in 1885, poultry dealer Joseph Ammer was allowed to construct his small booth at the Oktoberfest, creating the world’s first chicken roastery. Duck is offered as well.
- Bodo’s Cafezelt—this tent offers exotic cocktails, Prosecco, champagne, coffee, donuts, ice cream, pastries, and strudel variations of all kinds.
- Café Kaiserschmarrn—created by Rischart, the café holds a daily commemoration of the occasion of the first Oktoberfest—the wedding of Ludwig I and Therese of Saxony.
- Café Mohrenkopf—since 1950 Café Mohrenkopf has been baking cakes and pies fresh daily in the Oktoberfest tent.
- Feisingers Ka’s und Weinstubn—cheese and everything that complements it is the specialty of the house in this tent.
- Glöckle Wirt—decorated with oil paintings, antique instruments and cooking utensils.
- Heimer Hendl- und Entenbraterei—very popular among the locals, Heimer’s is a family-friendly tent.
- Heinz Wurst- Und Hühnerbraterei—since 1906, the Heinz sausage and chicken grill has been a fixture on the Wiesn, specializing in authentic Oktoberfest tradition.
- Hochreiters Haxnbraterei—barbecue experts prepare pork knuckles in the only Haxenbraterei (pork knuckle roaster) at the Oktoberfest.
- Münchner Knödelei—the dumpling is an icon of Bavarian cuisine, and «preserving and spreading the dumpling culture» is the motto of this smaller tent.
- Poschners Hühner- Und Entenbraterei—Poschner’s roasted chicken and duck have been a tradition of the Wiesn for four generations.
- Schiebl’s Kaffeehaferl—with seating for about 100, Schiebl’s coffeehouse tent is a meeting place for the whole family. Haferl is the Bavarian term for a (coffee or tea) mug or pot.
- Wiesn Guglhupf Café-Dreh-Bar—a Guglhupf is a German cake, like an English bundt cake; this slowly moving carousel bar is easy to spot because it’s shaped like one.
- Wildmoser Hühnerbraterei—owned by the Wildmoser family since 1981, this small tent has been adopted and popularized by the Munich locals.
- Wildstuben—the newest tent at Oktoberfest, featuring intricately detailed woodwork and a hunting lodge ambiance.
- Wirtshaus im Schichtl—»The Schichtl is as essential as beer, radish and chicken,» former mayor Christian Ude once wrote: «An Oktoberfest without Schichtl is inconceivable.»
- Zum Stiftl—famous for its traditional duck and roasted chicken dishes, atmosphere, and daily entertainment.
- Zur Bratwurst—debuting in 2007, the Hochreiter family has brought back the former Bratwurstglöckl.
Other information[edit]
Construction of the marquees
- Experienced waiters need an average of only one and a half seconds to fill a Maß.[64]
- Letters which are placed in the Oktoberfest mailboxes receive a special postmark from the post office.[65]
- One attraction, which does not exist at other festivals, is the flea circus. It has been an attraction at the Wiesn since 1948 and a «team» of about 60 fleas provide for the entertainment especially for the children.[66]
- After the attacks on 11 September 2001, in the same year, the traditional beer tapping was omitted, instead there was a contemplative celebration in Schottenhamel tent.[67]
- Since 2009, the Theresienwiese is closed off during the construction and dismantling of the festival. The city of Munich wants to prevent any accident to visitors at the construction site that the city would be accountable for.[68]
- In 2015, the festival officially served 7.3 million litres (62,000 US bbl) of beer; for perspective, that is enough to fill nearly three (2.9) Olympic-size swimming pools.[69]
- One famous song in a beer tent is «Ein Prosit der Gemütlichkeit» which means translated «A toast to cheer and good times». The band leader plays this song several times to invite the guests to toast and drink.[70]
- With the cancellation of the Oktoberfest since 2020 due to the Coronavirus pandemic, this is the first year that the Oktoberfest has not taken place since 1949.
- In 2022, after 2 years, Oktoberfest was held again in Munich, Germany.[71]
In popular culture[edit]
A German historical drama called Oktoberfest: Beer and Blood was released in 2020.[72] Set in 1900, it focuses on the showman brewer Curt Prank as he transforms the festival into a global tourist attraction by replacing the local brewery stands with one large pavilion.[73] Critics have compared the show’s graphic violence and German new wave music soundtrack to Peaky Blinders.[74] A second season was announced by head writer Ronny Schalk in 2021.[75]
Gallery[edit]
-
Oktoberfest rides and roller coasters
-
-
Gingerbread hearts from Oktoberfest
-
«Skater» at night
See also[edit]
- Beer and Oktoberfest Museum
- Schunkeln (sway dance)
References[edit]
- ^ «Oktoberfest Beer Consumption». 19 October 2014.
- ^ «Oktoberfest in Munich: poured amount of beer 2020». Statista. Retrieved 8 April 2022.
- ^ «Oktoberfestbier». German Beer Institute. Archived from the original on 20 October 2013. Retrieved 16 December 2013.
- ^ «Das erste Oktoberfest». wiesnkini.de (in German). Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ^ a b «History of the Oktoberfest». Oktoberfest. 24 June 2013. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ Semmens, Kristin (2005). Seeing Hitler’s Germany: Tourism in the Third Reich. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. p. 65. ISBN 978-1-349-51958-3.
- ^ Tobias Lill (25 September 2008). «Wie Hitler das Oktoberfest stahl». wiesnkini.de (in German). Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ^ Julia Meyer. «Das Münchner Oktoberfest» (in German). München-Lese. Retrieved 21 January 2015. Münchner Oktoberfest (21 April 2020). «Oktoberfest 2020 has been cancelled: The Wiesn 2020 cannot take place because of Covid-19». oktoberfest.de. Münchner Oktoberfest. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ «Parade of the landlords». oktoberfestlederhosen.com.
- ^ «Herzlich Willkommen beim Münchner Roten Kreuz». Bayerisches Rotes Kreuz. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Project «Safe Oktoberfest»«. Project «Safe Oktoberfest» • Oktoberfest.de — The Official Website for the Oktoberfest in Munich. Retrieved 25 June 2022.
- ^ The Guardian: Kate Connolly, «Gay times at Munich’s Oktoberfest,» September 22, 2011, accessed 27 January 2012.
- ^ «Die Bayerische Polizei — 26. September 1980 — das Oktoberfestattentat».
- ^ Ganser, Daniele. «Nato-Geheimarmeen und ihr Terror» (PDF) (in German). danieleganser.ch.
- ^ «Rules for Oktoberfest jeered». www.houblon.net. Retrieved 20 September 2008.
- ^ «Wiesn-Fahrgeschäfte: Mondlift (Zehle)». www.ganz-muenchen.de. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ a b Welle (www.dw.com), Deutsche. «Germany marks five years of smoking ban | DW | 31 August 2012». DW.COM. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ «Up in Smoke: Bavarian Politicians Want to Relax Smoking Ban». Spiegel Online International. 6 March 2008. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Smoking at the Oktoberfest». oktoberfest.de. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Oktoberfest 2010 – Raucher sollen kein Bier kriegen». Spiegel Online (in German). 29 July 2010. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ «Life After the Smoking Ban – Bacteria To Fight Beer Stench at Oktoberfest». Spiegel Online. 9 October 2010. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ^ a b c d Schulte-Peevers, Andrea. «Oktoberfest turns 200». www.bbc.com. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ «A History». oktoberfestbeerfestivals.com. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ Zeitung, Süddeutsche. «Corona Bayern: Bayern schließt neue Auflagen nicht aus». Süddeutsche.de (in German). Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ Reuters Staff (21 April 2020). «German Oktoberfest cancelled due to coronavirus». Reuters (in French). Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ «Covid: Germany’s Oktoberfest cancelled for the second time». BBC. 3 May 2021. Retrieved 3 May 2021.
- ^ «Das macht die Oide Wiesn so besonders». Das macht die Oide Wiesn so besonders • Oktoberfest.de — The Official Website for the Oktoberfest in Munich. Retrieved 4 November 2022.
- ^ «Infos zur Oidn Wiesn». Oktoberfest.de (in German). Archived from the original on 5 October 2016. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «Das Herzkasperl-Festzelt». Oktoberfest.de (in German). Archived from the original on 9 September 2010. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ Silke Lode (16 October 2012). «Oide Wiesn, junge Kultur» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. Retrieved 21 January 2015.
- ^ «Rosa Wiesn Termine 2021 — die schwule Seite vom Oktoberfest München | Munich Gay Octoberfest Dates — MLC Oktoberfesttreffen».
- ^ Free, Sara (4 October 2018). «What Is Oktoberfest’s Gay Sunday?». Hop Culture. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ «Oktoberfest meeting – Münchner Löwen Club e.V.»
- ^ Connolly, Kate (22 September 2009). «Gay times at Munich’s Oktoberfest». The Guardian. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ Porter, Erin (17 September 2020). «Everything You Need to Know About Oktoberfest». Tripsavvy. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ «Einzug der Wirte». Wiesnkini.de (in German). Retrieved 12 October 2015.
- ^ Beate Wild, Maria Berr. «Drei Schläge zum Glück» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. Retrieved 12 October 2015.
- ^ News.de-Redaktion. «Oktoberfest 2019 News-Ticker aktuell: Millionen Besucher strömen auf das traditionelle Gelage». News.de. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- ^ Schmidt, Maximilian (1902). Meine Wanderung durch 70 Jahre. Zweiter Teil (in German). Reutlingen: Enßlin & Laiblin. pp. 247–260.
- ^ Monika Ständecke: Dirndl, Truhen, Edelweiss: die Volkskunst der Brüder Wallach. (in German) / Dirndls, Trunks, and Edelweiss. The Folk Art of the Wallach Brothers (in English). Jüdischen Museum, Munich, 2007. ISBN 978-3-9388-3220-2
- ^ Heidi Hagen-Pekdemir (30 September 2015). «Bielefelder machten das Dirndl erst schick». Neue Westfälische (in German). Retrieved 18 April 2020.
- ^ «Geschichte / Über uns» (in German). Festring München e. V. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- ^ a b «Oktoberfest». Spaten. Retrieved 11 December 2013.
- ^ «10 Things you didn’t know about Oktoberfest». Costume Crazy. Retrieved 7 September 2015.
- ^ «Kein Oktoberfest im Jahr 2021».
- ^ «The Real Oktoberfest Beer».
- ^ «It’s all about the beer…». Oktoberfest.de.
- ^ «How to enjoy Oktoberfest like a local». USA Today. 5 September 2007. Archived from the original on 8 October 2009. Retrieved 20 May 2010.
- ^ «Realbeer.com: Beer News: Oktoberfest visitors set records». realbeer.com. Archived from the original on 31 December 2018. Retrieved 24 August 2007.
- ^ «Informationen zum Oktoberfest» (in German). muenchen.de.
- ^ «Oktoberfest Economics» (Press release). muenchen.de.
- ^ Daniel Aschoff (15 July 2008). «Der Eurostar ist jetzt ein Russe» (in German). Abendzeitung. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ «Flugverbot über dem Oktoberfest» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. 17 May 2010. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ Stefan Dorner (16 March 2010). «170 Poller sollen die Wiesn schützen» (in German). tz München. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ S. Lode, S. Wimmer (14 March 2011). «Es gibt nie eine hundertprozentige Sicherheit» (in German). Süddeutsche Zeitung. Retrieved 31 January 2015.
- ^ S. Menrad, Jasmin (12 September 2016). «Mobiler Rollzaun: Der Wiesn-Käfig steht!» (in German). Abendzeitung. Retrieved 14 September 2016.
- ^ «Dauerregen: Umsatz-Killer und Stromausfall» (in German). Augsburger Allgemeine. 26 September 2007. Retrieved 3 July 2015.
- ^ «The Italian Weekend – Oktoberfest, ti amo!». Oktoberfest.de. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- ^ Stern.de, 2022-06-09
- ^ «Oktoberfest construction – Bavaria’s biggest building project». Building Radar. 16 September 2015.
- ^ «Beer Tents». The Oktoberfest Website.
- ^ «The Marstall».
- ^ «Anzapfen, the opening ritual of Oktoberfest» (in German). Wiesnkini. Retrieved 18 January 2014.
- ^ «O’zapft is – Kurioses um das Oktoberfest». Uniturm.de (in German). 17 September 2011. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «Oktoberfest fun facts». State of Bavaria Quebec Office. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «Flohzirkus». Wiesenkini.de (in German). Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ Karin Truscheit (21 September 2013). «Kraft allein reicht nicht». Faz.net (in German). Frankfurter Allgemeine. Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «Aufbau des Oktoberfests: Die Theresienwiese wird zur Baustelle». Oktoberfest.de (in German). Retrieved 20 October 2015.
- ^ «History of Oktoberfest – How It Began in Munich Germany». Retrieved 3 July 2016.
- ^ «Octoberfest Customs». Retrieved 29 August 2016.
- ^ «Germany’s 200-year-old beer festival returns to its rhythm after 2 years». News Riddle. 27 October 2022.
- ^ Oktoberfest on IMDB
- ^ Inverse
- ^ Oktoberfest tastes like Peaky Blinders with beer
- ^ Oktoberfest Season 2 release
External links[edit]
This audio file was created from a revision of this article dated 26 September 2013, and does not reflect subsequent edits.
- Oktoberfest website (in German)
- Oktoberfest Map
- Oktoberfest Traditions
- Virtual exhibition: Oktoberfest – History, Background, Highlights, in the culture portal bavarikon
Coordinates: 48°7′53″N 11°32′57″E / 48.13139°N 11.54917°E
Дата события уникальна для каждого года. В 2023 году эта дата — 16 сентября
Октоберфест (Oktoberfest) — крупнейший в мире фестиваль пива. Он проходит в столице Баварии — Мюнхене, начинается во второй половине сентября и продолжается более двух недель.
Все началось с бракосочетания Баварского наследника престола, кронпринца Людвига I и принцессы Терезы Саксонской. 12 октября 1810 года, в день, когда состоялась их свадьба, на праздничные гуляния были приглашены все жители города. Их собрали на большом лугу, в то время находившемся за чертой города. Теперь, в честь принцессы, его называют Луг Терезы (Theresienwiese). Для мюнхенцев в тот день были устроены гуляния с бесплатным пивом и конными скачками.
Все прошло настолько живо и весело, что Людвиг отдал распоряжение праздновать Октоберфест ежегодно. С каждым годом традиции прошлых лет сохранялись, а к ним добавлялись новые. Так, в 1811 году к скачкам добавился праздник фермеров с показом красивейших коней и быков. В 1818 были установлены карусели и качели. Тогда же поставили первые пивные ларьки. В 1881 году открылась первая и крупнейшая в мире жаровня цыплят.
С 1810 года традиция ежегодного проведения фестиваля прерывалась только во время мировых войн. После Второй мировой войны фестиваль пива открылся в 1950 году, по распоряжению тогдашнего мэра Мюнхена Томаса Виммера. С тех пор он проходит ежегодно.
Традиция Октоберфеста — открытие гигантских пивных шатров (Фото: Losevsky Pavel, по лицензии Shutterstock.com)
По традиции, в день открытия, ровно в 12 часов, мэр города откупоривает бочку с пивом. Это символическое действие дает старт «пивному марафону». Затем по центральным улицам города начинает движение праздничная процессия. Во главе ее — «Munchner Kindi» — символ города — молоденькая девушка с большим колокольчиком в руке верхом на разукрашенной лошади. Она одета в монашескую одежду желто-черного цвета.
Рядом с ней движутся кареты мэра Мюнхена и администрации Баварии. За ними следует вереница украшенных карет и телег с пивом из всех районов Германии, прежде всего из Баварии. Кроме них в процессии участвуют колонна стрелков, артисты и исполнители фольклора, духовые оркестры, отряды в исторических униформах, а также представители всех земель Германии. В руках участников процессии — музыкальные инструменты разных районов страны, использующиеся с давних времен и по сей день. На ходу разыгрываются традиционные жанровые сценки, люди несут украшенные ветви и гирлянды.
Эта традиционная костюмированная процессия получила почетное звание самой красивой, исторически важной и лучше всего организованной в мире. Шествие всегда проходит по одному и тому же маршруту, длина которого составляет 6 километров. Он начинается в Siegestor и проходит через великолепные улицы внутреннего города к основному месту празднования — Лугу Терезы.
Хозяева и гости не только пьют пиво, но и музицируют… (Фото: Dennis Cox, по лицензии Shutterstock.com)
Другая традиция Октоберфеста — открытие гигантских пивных шатров, именуемых в народе «палатками». Каждый год их ровно 14 больших и около двух десятков средних и маленьких. Первые такие «палатки» появились в 1896 году. В самой большой из них, принадлежащей мюнхенской пивной «Hofbrauhaus», помещается 11000 человек. Причем речь идет только о сидячих местах: немцы предпочитают пить пиво только сидя. Практически во всех шатрах люди располагаются все вместе, за длинными столами.
У каждого шатра — своя вместимость и своя особенность. Например, в пивоварне августинцев (Augustiner-Festhalle), рассчитанной на 10000 человек, подают пиво из деревянных бочек, сваренное монахами. В Schottenhamel (6000 мест) чаще всего ходят студенты. Рядом со старейшей пивной города — пивной стрелков-арбалетчиков (Armbrustschutzenzelt) — тир с 14 стендами для стрельбы из арбалета. А в Winzerer Fahndl можно прийти и с детьми — там тихо, спокойно, по-семейному.
Пиво можно купить не только в шатрах: во время пивного фестиваля в праздник погружается весь город, открываются многочисленные пивные точки на свежем воздухе — биргартены (пивные сады).
Пиво разносят официантки, одетые в старинные немецкие костюмы. Поражает выносливость этих женщин, без труда поднимающих по 3-4 кружки пива. А ведь пиво на Октоберфесте пьют литровыми кружками, называемыми «масс». Впервые «масс» появилась аж в 1892 году. Интересно, что за время праздника посетители уносят с собой, на память о фестивале, более 70 000 таких кружек!
Несмотря на то, что пиво — напиток сугубо для взрослых, о детях в дни праздника тоже не забывают. Для будущих потенциальных участников фестивалей специально строятся карусели, продается мороженое и прочие сладости. Дети катаются по детской железной дороге, ездят в повозках, запряженных лошадьми, для них устраиваются специальные представления. На каждом углу продают светящиеся рожки, сердечки, шапки с мигающими лампочками.
Однако, покупают их не только дети, но и взрослые. Причем иногда из практических соображений. По мигающим в темноте сердечкам и звездочкам специальная служба опознает тех, кто, слегка перебрав пива, заснул на свежем воздухе. На тележках их отвезут в специальное место, где бедолаги смогут выспаться, и откуда их заберут друзья и родственники.
…и поедают разнообразные деликатесы (Фото: Lilyana Vynogradova, по лицензии Shutterstock.com)
Все фестивальные дни распития пива сопровождаются насыщенной шоу-программой. Костюмированные парады, шествия стрелков, скачки, концерты сменяют друг друга. Близ пивных часто можно увидеть танцоров в традиционных баварских костюмах с кожаными штанами, отбивающих чечетку «шуплаттль» тяжелыми альпийскими ботинками. Также вас ждут со своими экскурсиями пивоварни города и музеи пива.
О размахе праздника лучше всего говорят цифры статистики. За время фестиваля выпивается около 7 миллионов литров пива (с каждым годом этот объем увеличивается), съедается порядка 1,5 миллионов жареных цыплят и сосисок, 84 быка. Пиво, предоставляемое шестью пивоварнями Мюнхена, продается в 650 пивных местах. Дополнительно открывается 363 магазина с сувенирами. Посетителей развлекают 200 аттракционов и концертных площадок.
Во время фестиваля Мюнхен посещают более 7 миллионов туристов со всех континентов земли. Сам праздник освящается в прямом эфире телеканалами различных стран мира. За все это пивной фестиваль «Октоберфест» был занесен в Книгу рекордов Гиннесса как самый большой в мире праздник.
На чтение 13 мин. Просмотров 1.9k. Опубликовано 28.08.2022
Содержание
- Где проходит фестиваль пива Октоберфест
- Даты проведения в 2023 году
- Цена билета
- Цены на пиво и еду
- Режим работы фестиваля Октоберфест
- Шатры и пивные палатки
- Ярмарочные аттракционы
- Oide Wiesn (Старый Октоберфест)
- Программа фестиваля
- Аттракционы
- Шатры и палатки
- Как добраться до «Октоберфеста»
- Правила входа на территорию фестиваля
- Официальный сайт Октоберфеста
- Почему фестиваль называется Октоберфест, если проходит в сентябре
- История фестиваля
Где проходит фестиваль пива Октоберфест
Ежегодный фестиваль пива «Октоберфест» проводится администрацией Мюнхена – главным городом немецкой земли Бавария. Мероприятия праздника проходят в центре города, на Theresienwiese (луг Терезы), почти рядом с главным вокзалом.
На площади 42 гектара размещаются пивные палатки и шатры, магазины сувениров, аттракционы, площадки для выступления артистов и др.
Фото: Marc Müller
Гуляния проходят и во многих других городах Германии и даже в других странах, где много жителей-выходцев с Баварии. Но самые популярные и многолюдные – именно в Мюнхене, ежегодно их посещает более 6 млн. человек.
Даты проведения в 2023 году
В 2023 году пивной фестиваль начнется 16 сентября и продлится до 3 октября.
Два года подряд Октоберфест не проводился в связи с пандемией коронавируса (2020 и 2021 годы), поэтому ожидается большой наплыв туристов как с самой Германии, так и всего мира.
Цена билета
Сам вход на Терезиенвизе бесплатный, нужно заплатить 4 евро только за вход в историческую часть фестиваля «Oide Wiesn». Это закрытая территория, где можно увидеть, каким был фестиваль раньше. Но даже здесь вход после 21.00 свободный. Вход на любой аттракцион стоит 1 евро.
Во все пивные палатки проходят бесплатно, но чтобы гарантированно найти там место, особенно в выходные и по вечерам, лучше заранее подумать о брони. Тем более, что обслуживаются только те, кто сидит за столом.
Бронирование происходит через палатку, столик в которой вы хотите зарезервировать. Обычно цена ваучера складывается из стоимости одного литрового бокала пива и еды к ней, чаще всего половины жареной курицы. Это составит около 25 евро. При оплате заказа данная сумма будет вычтена из чека.
Если же заранее обеспечить себя местом в павильоне не удалось, тоже нет причин для особого беспокойства: в рабочие дни четверть мест остается доступной для свободного посещения. А в выходные дни до 15 часов оставляются свободными половина мест, а после – 35%. Только Käfer Wiesn-Schänke и Kufflers Weinzelt не подчиняются этим ограничениям.
Цены на пиво и еду
Для праздника мюнхенские пивовары готовят особые сорта пива, которые продаются только здесь. У каждого бренда своя марка, а в целом они называются Октоберфестбиер. Крепость октябрьского пива составляет от 5,8 до 6,3%.
Стоимость литровой кружки пива составляет в среднем 13,80 €, что на 15,8% выше, чем в 2019 году.
Цены на фестивале устанавливаются не городом, а самими пивоварами. Но за справедливостью цен администрация смотрит, сравнивая их со стоимостью одного литра пива в крупных ресторанах как Мюнхена, так и городов этой агломерации.
На 2022 год зафиксированы следующие цены*
*(название шатра – цена за литр в евро):
В крупных шатрах
- Armbrustschützen-Festzelt – 13,5
- Augustiner-Festhalle – 12,8
- Bräurosl – 13,4
- Fischer-Vroni – 12,9
- Hacker-Festzelt – 13,4
- Hofbräuhaus-Festzelt – 13,6
- Käfer Wiesn-Schänke – 13,7
- Löwenbräu-Festzelt – 13,6
- Marstall – 13,7
- Ochsenbraterei – 13,5
- Paulaner-Festzelt – 13,5
- Schottenhamel-Festhalle – 13,6
- Schützen-Festzelt – 13,7
- Weinzelt (Weißbier) – 13,6
Oide Wiesn (Старый Октоберфест)
- Festzelt Tradition – 13,2
- Herzkasperl Festzelt – 13,4
- Museumszelt – 12,6
- Volkssängerzelt – 12,9
Средние цены на безалкогольные напитки за литр составляют: 9,67 евро за столовую воду, 10,85 евро за шпеци (немецкий сладкий прохладительный напиток, смесь колы и апельсинового лимонада) и 10,35 евро за лимонад.
В качестве закуски предложат не только традиционные блюда баварской кухни (жареный цыпленок, жаркое из свинины, мясной рулет Leberkäse, колбаса вайсвурст и другие), салаты из капусты, картофеля, фруктовые, квашеную капусту.
Любители сладкого будут рады засахаренным яблокам, сахарной вате, жареному миндалю, имбирным пряникам и т.д. Есть много блюд вегетарианской и веганской кухни, как шпецле с сыром Allgäu, различные макаронные изделия, вареники, клецки… Также предусмотрена еда без глютена и лактозы.
Фото @kalucky1015
Режим работы фестиваля Октоберфест
Шатры и пивные палатки
Работают по графику:
- Понедельник-пятница: с 10:00 до 23:30
- Суббота и воскресенье: с 9:00 до 23:30
Важно! Последнее пиво в больших палатках наливают в 22:30, в маленьких – в 23:00.
Исключения: Käfer Wiesn-Schänke и Kuffler’s Weinzelt (винная палатка) открыты до 1 часа ночи, последний бокал наливают в 00:30.
Ярмарочные аттракционы
- В первый день фестиваля (17 сентября) – с 9:00 до 00:00
- С воскресенья по четверг – с 9:00 до 23:30
- С пятницы по субботу – с 9:00 до 00:00
- 2 октября – с 9:00 до 00:00
Фото @kumamimi55
Oide Wiesn (Старый Октоберфест)
Oide Wiesn имеет собственную зону на юге территории фестиваля и работает по графику (без привязки к дню недели):
- Вход на территорию – с 10:00 до 23:00
- Продажа пива – с 10:00 до 21:30
- Аттракционы – с 10:00 до 22:30
Обратите внимание! В день открытия (17 сентября) подача пива и аттракционы начинаются в 12:00.
Программа фестиваля
Октоберфест начинается с парада пивоваров, которые на празднично украшенных повозках везут бочки с пивом на праздник. Это торжественное шествие осталось с тех пор, когда луг Терезы еще не был частью Мюнхена, и пиво туда доставляли на конных повозках. Представители пивоварен в традиционных костюмах, разукрашенные лошади, огромные бочки октябрьского пива – здесь есть на что посмотреть. Это мероприятие запланировано на 10:45 17 сентября.
В 12.00 состоится открытие праздника. В шатре Schottenhamel действующий бургомистр специальным молотком вставляет кран в бочку с октоберфестбиер, сопровождая свое действие возгласом «O’zapft is!» («Откупорено!»). Это становится сигналом к началу праздника, во всех палатках вскрывают бочки с пивом и начинают разливать.
В воскресенье, 18 сентября, в 10.00 начнется торжественное праздничное шествие в национальных костюмах, в котором ежегодно принимает участие около 8 тысяч человек, в том числе охотничьи клубы, группы в исторических костюмах, оркестры и знаменосцы. Во главе процессии, движущейся от здания парламента земли Бавария к Theresienwiese, находится «дитя Мюнхена» — официальный талисман города, сейчас изображаемый в виде юной девушки. За ним идут представители городской администрации и правительства Баварии, а затем все остальные участники в традиционных одеждах. Вдоль пути шествия стоят трибуны, с которых можно наблюдать за красочным зрелищем.
Кстати, Вы знали, что прийти на фестиваль в национальном костюме может любой желающий! Костюмы продаются в специализированных магазинах!
Четверг, 23 сентября, начнется с церковной службы в фестивальной палатке Marstall. Все присутствующие поминают покойных сотрудников Октоберфеста, а также молятся за мирный фестиваль. Также проводятся обряды крестин, первого причастия, конфирмации детей сотрудников.
Воскресенье, 25 сентября, ознаменуется грандиозным совместным концертом всех оркестров – участников фестиваля.
Последний день Октоберфеста – 3 октября – совпадает с Днем объединения Германии. Спортивный стрелковый клуб Баварии завершит фестиваль салютом из легких мортир рядом со статуей Баварии.
Аттракционы
Октоберфест – это не только пиво. Это народные гуляния с различными развлечениями. Главным аттракционом можно считать колесо обозрения, с которого открывается вид на сам Визн («луг») с его шатрами, лавочками, гуляющими людьми, а с другой стороны – вид на город и его исторический центр.
Любителям пощекотать нервы можно прокатиться на Wellenflug. Эти качели-карусели являются одним из символов фестиваля, на них одновременно кружишься по кругу и совершаешь волнообразные движения, и это на большой высоте.
Веселый аттракцион Teufelsrad (Колесо Дьявола) заключается в попытках удержаться на большом диске, вращающемся все быстрее. Игра осложняется большим тяжелым мячом, который выбивает участников с диска, а комментарии острого на язык ведущего только подогревают интерес к зрелищу.
Разнообразие аттракционов поражает: SkyFall со стремительным падением с высоты 80 м; Olympia Looping – единственные в мире американские горки с пятью полными переворотами , со скоростями до 100 км/ч и перегрузкой в 5,2 g; Кринолин, Хищник, Калипсо, Джуманджи, Башня Жюля Верна… Это далеко не полный перечень развлечений.
Шатры и палатки
Большие палатки:
- Augustiner Festhalle
- Armbrustschützenzelt
- Festzelt Tradition
- Fischer-Vroni
- Hacker-Festzelt
- Herzkasperl-Festzelt
- Hofbräu-Festzelt
- Käfer Wiesn-Schänke
- Kufflers Weinzelt
- Löwenbräu-Festzelt
- Marstall Festzelt
- Ochsenbraterei
- Paulaner Festzelt
- Pschorr-Festzelt Bräurosl
- Schottenhamel-Festhalle
- Schützen-Festzelt
- Volkssängerzelt Schützenlisl
Узнать больше здесь.
Маленькие палатки:
- Ammer Hühner- und Entenbraterei
- Bodo’s Cafézelt
- Café Kaiserschmarrn
- Feisingers Kas- und Weinstubn
- Fisch-Bäda
- Glöckle Wirt
- Goldener Hahn
- Heimer Enten- und Hühnerbraterei
- Heinz Wurst- und Hühnerbraterei
- Hochreiters Haxnbraterei
- Kalbsbraterei
- Münchner Knödelei
- Hühner- und Entenbraterei Poschner
- Schiebl’s Kaffeehaferl
- Vinzenzmurr Metzger Stubn
- Wiesn Guglhupf
- Wildstuben
- Wirtshaus im Schichtl
- Münchner Stubn
- Zur Bratwurst
- Café Theres’
Узнать больше здесь.
Как добраться до «Октоберфеста»
Главный пивной фестиваль Германии проходит буквально в 15 минутах ходьбы от центрального ж/д вокзала города (München Hauptbahnhof). Можно дойти пешком или подъехать 1 остановку на метро до станции «Терезиенвизе» (Theresienwiese).
Метро:
- U4 и U5 – до станций «Theresienwiese» или «Schwanthalerhöhe».
- U3 и U6 – до станций метро «Goetheplatz» и «Poccistraße»
Городские электрички (S-bahn):
- S1-S8 – до станции «Hackerbrücke» и Главного ж/д вокзала Мюнхена (München Hbf);
- S2, S7 и S20 – до станции «Heimeranplatz».
Автобусы:
- 62 – до «Hans-Fischer-Straße», «Poccistraße» и «Herzog-Ernst-Platz»;
- 53 – до «Schwanthalerhöhe»;
- 58 – до «Georg-Hirth-Platz», «Beethovenplatz» и «Goetheplatz»;
- 134 – до «Schwanthalerhöhe» или «Theresienhöhe».
Трамваи:
- 18 и 19 – до «Holzapfelstraße» или «Hermann-Lingg-Straße»;
- 16 и 17 – до «Hackerbrücke»
Правила входа на территорию фестиваля
- Проносить на территорию проведения фестиваля допускается рюкзаки и сумки вместимостью не более 3-х литров, габариты (см): 20х15х10. Все лишнее можно оставить в камерах хранения.
- Запрещено проносить на Октоберфест: аэрозольные баллончики с опасным содержимым, вещества, которые могут вызывать раздражение или окрашивать, а также предметы, которые могут быть использованы в качестве оружия (колющие, режущие или режущие). Стеклянные бутылки также запрещены.
- Запрещен вход с питомцами.
- Курить можно только в специально отведенных местах.
- На территории проведения «Октоберфеста» запрещено ездить на велосипедах и скутерах, кататься на досках и коньках, приводить животных.
- Запрещено приносить с собой в шатры еду и напитки.
- За кражу кружек полагается штраф. Дешевле купить в сувенирной лавке.
Официальный сайт Октоберфеста
www.oktoberfest.de – информация доступна на немецком и английском.
Почему фестиваль называется Октоберфест, если проходит в сентябре
Первоначально праздник проводился в октябре, что и отражено в названии фестиваля. Но в 1872 году приняли решение сдвинуть народные гуляния на середину сентября, чтобы воспользоваться более мягкой и теплой погодой. Поэтому сейчас приняты следующие даты: с первой субботы после 15 сентября и до первого воскресенья октября, длится праздник 16 дней.
История фестиваля
Первый в истории пивной фестиваль Октоберфест прошел 12 октября 1810 года. Мероприятие было приурочено к свадьбе принцессы Терезы Саксонской-Хильдбургхаузской и кронпринца Людвига Баварского.
Как Вы уже наверняка догадались место проведения Октоберфеста (Луг Терезы) получило свое название в честь невесты-принцессы.
До 1819 года фестиваль проводился в частном порядке, а после организация и управление праздником были отданы в руки городского совета Мюнхена. Тогда и порешили, что фестиваль должен проводиться каждый год без исключения.
Хотя исключения, конечно, были. В частности, дважды праздник отменялся из-за эпидемии холеры, дважды из-за гиперифляции в стране, n раз по причине военных действий, а в 2020 и 2021 – из-за пандемии коронавируса.
В 1872 году было принято решение перенести празднование с октября на конец сентября, так как погода в городе в это время мягче и теплее. Такая традиция и сохранилась до наших дней.
Отктоберфест — история праздника, как все начиналось
Перед тем как рассказать про октоберфест 2023 давайте окунёмся в историю этого праздника. История Октоберфеста открылась знаменательным для королевской семьи Баварии событием, которое заключалось в бракосочетании принца Людвига и его невесты принцессы Терезы (коренной саксонки). Празднования предстоящей свадьбы королевских особ было назначено на 12 октября 1810 года. Чтобы отметить такое важное и приятное событие королевская семья пригласила всех жителей Мюнхена, на организованные за чертой города, народные гуляния.
Развлечением этого дня были конные скачки и пиво для любого желающего за счет короля. Луг, на котором проводились массовые гуляния, назвали в честь невесты – Луг Терезы. Прошедший праздник удивил всех участников своей атмосферой и положительными эмоциями.
Поэтому, по приказу короля было назначено ежегодное проведение пира – вот что это такое – фестиваль Октоберфест в Германии. С каждым последующим годом к развлекательным мероприятиям прошлых лет добавлялись новые традиции и инновации. Появлялись:
- показы фермерского скота;
- парки развлечений с качелями для детей и
взрослых; - жаровни для приготовления цыплят, колбас и
сосисок.
С первого дня проведения Мюнхен праздновал праздник каждый год.
Только сильные эпидемии и затяжные войны заставляли жителей этого города
отказаться от своего любимого мероприятия.
Про этот пир знает каждый школьник в Мюнхене — столице Баварии. Это самое большое торжество пива в мире и самый известный немецкий праздник. Длится такое мероприятие две с половиной недели. Привлекает внимание около 7 миллионов людей, приезжающих, весело провести время и попробовать эксклюзивные сорта популярного напитка, специально приготовленные для этого мероприятия.
Изначально он проводился в октябре, но с 1872 года его открытие было перенесено на конец сентября. Такой выбор был сделан в связи с погодными условиями, в Германии – это время бабьего лета, что как раз подходит для развлечений на открытом воздухе.
Октоберфест, дата, когда он проходит обязательно планируется на субботу, поэтому мероприятие, которое длится около 16 дней, не привязано к какому-либо конкретному числу в сентябре. Однако, существует одно условие: окончание должно приходиться на первое воскресенье октября. Если оно попадает на 1 или 2 число этого месяца, то торжество продлевается до Дня Объединения Германии (Стена), которое празднуется 3 октября.
Октоберфест в 2023 пройдет с 16 сентября по 3 октября. Это информация с официального сайта мероприятия.
Октоберфест 2023 — как добраться
Добраться на Луг Терезы собственным транспортом конечно можно, но вот поставить автомобиль на парковку, когда в Германии Октоберфест, получится лишь за несколько кварталов от проводимого мероприятия. Стояночные зоны занимают местные жители, которые лучше знакомы с инфраструктурой и вариантами подъездов к месту проведения фестиваля.
Лучшей альтернативой для комфортного проезда будет использование пригородного поезда или муниципального транспорта:
- метро;
- автобуса;
- трамвая.
Также можно пройти до места проведения фестиваля пешком, для удобства следует заранее скачать карту города и загрузить ее в свой гаджет.
Дешевые авиабилеты в Мюнхен
В какие дни предпочтительнее посещать праздник Октоберфест 2023?
Перед тем, как выбрать, в какой день посетить фестиваль, необходимо определиться в своих предпочтениях. Наибольшее количество гостей собирается в последние три дня недели: пятницу, субботу, воскресенье. Соответственно в это время атмосфера города наполнена шумом и безудержным весельем. Будни намного спокойнее, можно в более короткий срок пробраться через очередь и занять столик в выбранной палатке, либо попасть на аттракцион.
Значительно поможет с выбором дня посещения мероприятия изучение программы гуляний. Для тех, кто хочет посетить фестиваль в семейном кругу, прихватив с собой детей, следует обратить внимание на семейные дни Октоберфеста. В это время цены на семейные развлечения значительно понижены.
Что входит в программу Октоберфеста
Начало пивного праздника Октоберфест в Германии (его первый день) знаменуется шествием хозяев палаток с напитками. Телеги с бочками выстраиваются в очередь и во главе с символом города (молодой девушкой, переодетой в монашку верхом на коне) и мэром направляются к месту проведения празднования.
Далее, ровно в полдень, происходит открытие первой бочки с напитком. Для этого бургомистр собственноручно забивает в нее кран при помощи специального молота. Звучит возглас – «Откупорено». С этого момента разрешается работа всех заведений на лугу Терезы.
Следующий день (это, как правило, воскресенье) знаменуется костюмированным шествием. Такая традиция появилась в 1835 году, когда праздновалась серебряная годовщина свадьбы королевской семьи, основателей фестиваля, Людвига и Терезы. Участники парада (около 8000 человек) одеваются в наряды исторического и национального направления. Используются конные упряжки.
Шествие сопровождают оркестры и отряды стрелков в праздничном обмундировании. Участвовать в параде могут все желающие: жители и гости города. Обязательно шествие возглавляют члены городской администрации Баварии. Длина маршрута церемонии, который соединяет Парламент Мюнхена и место празднования, составляет 7 километров.
Традиционным завершением фестиваля становятся стрелковые
соревнования, проводимые у подножия статуи Терезы.
Октоберфест 2023 — что едят и пьют на немецком празднике
Основным напитком популярного мероприятия однозначно является пиво. Готовится оно по специальному рецепту с применением секретных технологий. Оно доступно к приобретению только во время прохождения фестиваля. Его крепость превышает стандартные показатели светлого вида напитка, составляет 5,8 – 6,3%, при этом вкус солода более насыщенный, чем у других сортов, продаваемых в магазинах города.
Кроме главного напитка, приготовленного специально для праздника, можно приобрести также:
- вина, разных годов производства;
- коктейли;
- алкогольные напитки разной крепости и
производства.
Любителям покушать придется по вкусу огромный выбор закусок,
которые предлагают организаторы празднований. В их число входят:
- знаменитые жареные цыплята;
- белые мюнхенские сосиски;
- кренделя достойного размера;
- салаты из капусты и картофеля;
- рыба, запеченная на палочке;
- говяжий и свиной окорок, жаренный на открытом
огне.
Каждая палатка представляет свой ассортимент различных закусок
не похожий на выбор, представленный конкурентами. Поэтому гостям, желающим
опробовать все существующие предложения, может не хватить сил и времени
отведенного на проведение фестиваля.
Напитки
Специально приготовленных сортов напитка насчитывается 6 видов,
каждый из которых отличается своеобразным вкусом и хмельным действием. Разные
палатки представляют праздничный напиток в большом ассортименте. Не каждый
шатер может похвастаться наличием всех заявленных к продаже сортов.
Угощения
Фестиваль пива Октоберфест предлагает своим гостям огромный
выбор угощений. В качестве популярных закусок предлагаются жареные белые
сосиски с горчицей и бреценом, свиные ножки, приготовленные по праздничному
рецепту. Десерт порадует даже самого привередливого гурмана – ассортимент
баварской выпечки и глазированных фруктов заставляет учащенно биться сердце
самого искушенного сладкоежки.
Самой востребованной немецкой закуской являются два вида
сосисок:
- вареного вида (мюнхенские);
- поджаренные до золотистой корочки колбаски
(нюрнбергские).
В качестве приправы используется сладкая горчица, а вместо хлеба
– соленые кренделя, которые могут компоноваться зеленью, овощами и сыром. Все
эти ингредиенты кладутся сверху разрезанной булки.
Знаменитая курица гриль стала неотъемлемой частью празднования.
При заказе на одну порцию приходится половина зажаренной тушки птицы. Перед
приготовлением курица маринуется с добавлением секретных специй.
Где проводится Октоберфест, всегда предлагается запеченная
свиная рулька, которая в процессе обжаривания поливается соусом из меда и пива.
Такой способ приготовления делает мясо очень нежным и сочным. Также существует
возможность попробовать:
- печеную в пиве свинину со специями;
- обжаренные свиные ребрышки;
- жареную утку;
- стейки из говядины и свинины;
- рыбу в ассортименте, особенно востребованное блюдо – это поджаренная на шпажках речная форель;
- сырные блюда, специально приготовленные, как закуска для хмельных напитков;
- пироги с изюмом в шоколадной глазури.
Интересные факты и рекорды Октоберфеста
Фестиваль является самым большим на планете, соответственно,
этот факт не обошел стороной Книгу Рекордов Гиннесса, в которой имеется
соответствующая запись.
Во время празднования гости выпивают более 7 миллионов литров
главного напитка этого периода – пива.
Также за этот период продается:
- более 500 тысяч куриц-гриль;
- 600 тысяч колбасок;
- около 70 тысяч свиных ножек;
- 90 быков.
Расход ресурсов на проведение мероприятий:
- до 3000 МВТ электрической энергии;
- газа – 200 000 кубических метров;
- более 500 000 тонн мусора.
Многие гости желают забрать в качестве сувенира кружку, в
которой им приносили питье. Такое желание пресекается законом, но, несмотря на
этот факт, в течение праздника уносится до 100 000 литровых емкостей для пива.
Октоберфест 2023 — полезные советы гостям
Чтобы избежать непредвиденных расходов и незапланированных
ситуаций, нужно ознакомиться с ценами и условиями бронирования мест в шатрах.
Правила прохода и поведения также регламентированы. Во время Октоберфеста,
когда начинается мероприятие, следует четко следовать установленным традициям,
чтобы не попасть в черный список.
Сколько стоит вход на Октоберфест 2023?
Для того, чтобы попасть в шатер, не требуется покупать входной билет. При большом количестве посетителей, когда все сидячие места заняты, двери палатки закрываются. В таком случае для входа внутрь потребуется предъявить документ на заранее забронированное кресло. В ваучере указывается определенное время посещения, опоздать можно, но не более чем на 15 минут.
Стоимость резервирования составляет 30 евро, в комплект брони входит 2 литра пива и половина курицы гриль. Бронирование в шатрах разрешается с понедельника по пятницу включительно (для этих целей выделяется 70% сидений в центре), в выходные дни вход в палатки происходит в порядке живой очереди.
Если в больших шатрах все занято, расстраиваться не стоит,
достаточно комфортно можно разместится в палатках меньшего размера или за
столами, которые установлены на улице вокруг больших палаток.
Сколько стоит бокал
пива?
Стоимость литровой кружки составляет 10 евро. Курица гриль
продается за 18 – 20 евро. Цена за 1 литр вина или сока начинается от 6 евро.
Во сколько открываются/закрываются павильоны?
В будние дни павильоны начинают свою работу с 10 утра. В субботу
и воскресенье они открываются на час раньше. Раздачу угощений начинают в момент
открытия дверей и выполнения заказа первыми посетителями.
Обслуживать клиентов заканчивают в 22:30, сам праздник
заканчивает свою работу в 23:00.
Можно ли брать с собой
рюкзаки?
Специально установленными правилами безопасности запрещается
входить на территорию с рюкзаками и большими сумками. Для их хранения
предусмотрены специальные места, которые находятся при входе. Можно проходить с
ручной кладью, с сумкой или пакетом размером 25х15х10 см. Содержимое сумок,
проносимых с собой, обязательно проверяется на наличие запрещенных предметов:
- газовых баллончиков;
- колющих или режущих предметов;
- стеклянные емкости.
Возможно ли вкусно
поесть на Октоберфесте?
Для любителей вкусно покушать под бокал другой пива, хозяева пивного фестиваля Октоберфест предлагают огромный ассортимент мясных блюд, салатов, гарниров, десертов. Цены на съестное меняются в зависимости от времени посещения празднований.
В будничные дни некоторые пункты питания делают скидки на продукты и напитки во время обеденного перекуса, который длится с 10 – 15 часов дня. Наиболее экономным способом утолить голод по своему вкусу является имеющаяся возможность принести любимую еду с собой.
Вход в павильоны
разрешен для всех?
Зайти в павильон может любой человек или компания из нескольких
лиц. Однако, существуют следующие ограничения:
- заказывать пиво можно, только если сидишь за
столом; - когда сидячие места заканчиваются двери шатра
закрываются и войти можно только в порядке живой очереди по мере выхода
посетителей из палатки.
Чтобы занять столик или кресло в приглянувшемся павильоне нужно
приходить к утреннему открытию Октоберфеста. Сколько длится этот промежуток
между многолюдным потоком и свободными столиками удается понять только на
месте. Можно заказать бронь заранее (такая услуга доступна только в будние
дни).
Можно ли курить в
павильонах?
К радости приверженцев здорового образа жизни, закон Германии
запрещает курение на территории общественного питания. Поэтому правила с 2010
года также подтверждают такое решение государства во избежание административных
наказаний. Курить разрешается только в специально отведенных для этогозонах.
В Осtoberfest, когда у посетителей возникает желание нарушить
закон, появляются неприятности:
- минимум — игнорирование в обслуживании;
- выгоняют из павильона на улицу с оформлением
административного взыскания.
Развлечения и
аттракционы
Октоберфест предлагает на выбор огромное количество развлечений., многие из которых следует посещать в трезвом виде, чтобы избежать казусных ситуаций.
Стоимость любого аттракциона начинается с 6 евро за один сеанс.
Провести весело время можно несколькими способами: во многих развлечениях можно принять участие лично, либо посмотреть, как выполняют трюки опытные каскадеры. Большая часть аттракционов насчитывает достаточно длинную историю эксплуатации, являясь классикой предлагаемого отдыха для посетителей.
Участники фестиваля
В настоящее время праздник пива набирает все большую популярность среди жителей Европы, Америки и Азии. Когда проходит Октоберфест в Германии, тысячи иностранных туристов стараются посетить данное мероприятие. Они настолько проникаются духом события, что сливаются с местными жителями в единое целое.
Большую часть посетителей, конечно, составляют коренные жители Мюнхена и Баварии. Для них посетить это великолепное мероприятие стало делом чести, но в тоже самое время, все они рады пропустить несколько литровых кружек праздничного пива под любимую закуску, поэтому каждый год с нетерпением ждут осени.
Гости фестиваля
Как известно, празднование, проводимое в Мюнхене, сопровождается массовым приемом гостей. Однако существуют рамки приличия, которые навсегда могут закрыть двери слишком развязному посетителю. Служба безопасности этого осеннего мероприятия охраняет порядок на территории праздника. Провинившиеся гости заносятся в черный список (он каждый год постоянно растет) и больше не допускаются к празднованию.
Найти туры в Германию на Октоберфест 2023 можно на сайте туристического агентства Travelata по ссылке — Туры в Мюнхен. А если использовать промо-код AF300kudapoedem то можно сэкономить 300р. от стоимости тура (если тур дороже 20 000р.).
Посмотрите куда ещё можно отправить отдыхать осенью. В этой статье мы подробно рассмотрели все варианты осеннего отдыха за границей.
Чтобы забронировать отдельно отель и авиабилеты на Октоберфест 2023 воспользуйтесь соответствующими разделами нашего сайта: авиабилеты, отели.
Раз в год педантичный и спокойный Мюнхен охватывает настоящий кутеж и пьянство, город становится эпицентром мирового веселья. В сентябре в сердце Баварии едут с одной целью — пуститься во все тяжкие, оказаться в самой гуще событий и опустошить свои кошельки. Тонны пива, десятки килограммов колбасок и все, чем может похвастаться гастрономическая сторона Баварии. Кажется, что в сентябре Мюнхен переворачивается с ног на голову, ведь пришло время знаменитого Октоберфеста. Но так ли беззаботен этот фестиваль? Я решила проверить это!
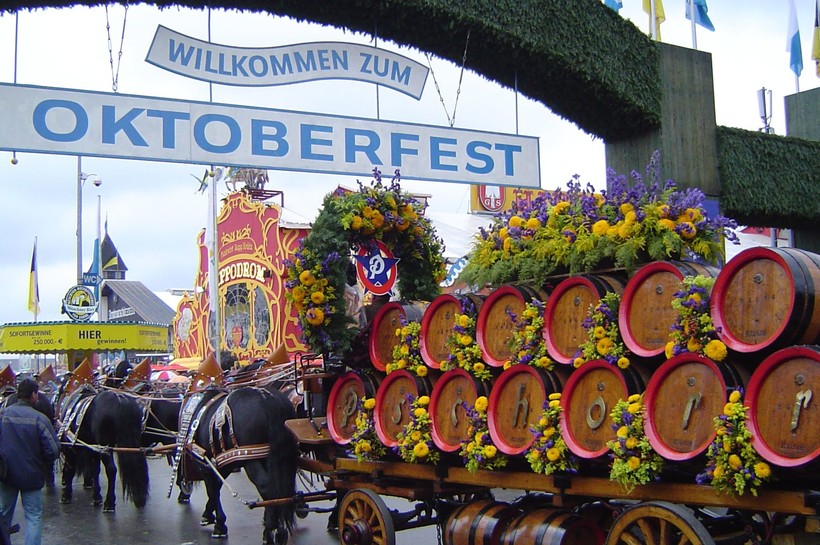

История
История этого фестиваля началась 10 октября 1810 года. Именно в тот день принц Людвик, который был наследником немецкого престола, вступил в брак с принцессой Терезой. Королевский двор решил поделиться этой радостной новостью и отпраздновать бракосочетание со всеми жителями Баварии. Для этого королевские подданные пригласили всех желающих для празднования бракосочетания на просторные поля, что простирались у ворот королевских покоев.
Вскоре эта территория была названа Лугом Терезы, в честь новоиспеченной супруги наследника престола, которая, кстати, на правах жены немецкого принца, потребовала завершить празднование лошадиными скачками.
Это зрелище так понравилось жителям Баварии, что они решили проводить подобные мероприятия раз в год и именно 10 октября. И уже спустя пару десятилетий, это празднование стало собирать не только простых рабочих, но и торговцев, которым было разрешено продавать свой товар на территории Луга Терезы.
Спустя пару лет после этого около палаток стали появляться аттракционы и памятники, в частности, первая Статуя Баварии. Однако, праздник отмечался не всегда, иногда власти города отменяли фестиваль из-за вспышек опасных болезней или из-за военных действий, в которых участвовали немецкие войска. Но как бы то ни было, местные жители продолжали осваивать территории Луга Терезы, строя павильоны и проводя туда все необходимые коммуникации. Первыми и последними хозяевами этих самых крытых площадок стали торговцы пивом, которые, к слову, и стояли у истоков создания этого фестиваля.
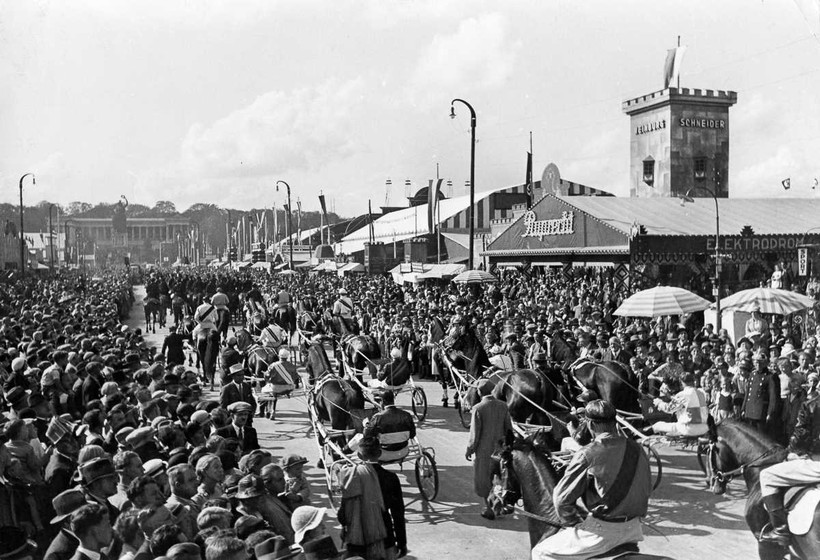

Со временем проведение лошадиных скачек плавно сошло на нет, ведь теперь основное внимание посетителей было приковано не к этим состязаниям, а к пивным павильоном, где каждый год появлялись новые сорта пива, а ассортимент вводил в восторг даже самых искушенных любителей этого хмельного напитка.
Пару десятилетий назад организаторы решили перенести начало празднования на 20-ые числа сентября, такое решение объяснялось погодными условиями, ведь в октябре в Германии становится довольно прохладно. Многие жители Баварии поддержали эту инициативу и так же настояли на сохранении исторического название фестиваля.
На сегодняшний день Октоберфест является настоящим национальным праздником, фестивалем мирового масштаба, на котором побывали практически все знаменитые деятели Германии. Ежегодно Октоберфест принимает порядка шести миллионов людей, которые приезжают из соседних городов и стан, чтобы окунуться в безумное веселье.
Что же еще интересного таят в себе эти две с половиной недели?
Дата проведения
Начинается фестиваль всегда в субботу (но в редких случаях дату могут перенести), именно в первый день жители и гости Мюнхена направляются к воротам Луга Терезы, чтобы занять очередь и оказаться в гуще событий. Длится Октоберфест примерно 17-19 дней, его окончание приходится на первое воскресенье октября. Однако, бывают случаи переноса финала Октоберфеста, все зависит от программы, погодных условий и организаторов.

Как добраться?
Луг Терезы, где и проходит ежегодный фестиваль пива, расположен недалеко от центра города. Однако, до этого места не ездит ни один наземный транспорт. Поэтому самым удобным способом добраться до Луга Терезы от Мариенплатц будет либо пешая прогулка, либо поездка на метро.
По своему опыту могу сказать, что лучше всего добираться пешком, в дни Октоберфеста метро просто загружено, однако, путь до Луга Терезы от главной площади не так уж и прост. Первый раз добираясь до Луга, я пользовалась помощью прохожих, к тому же, можно сразу понять кто из них идет в том же направлении и следовать за ними.
Итак, отправляясь с Мариенплатц, вы должны идти вдоль по улице Зендлингерштрассе (Sendlinger Straße). Это довольно спокойная, чаще всего пешеходная улица, которая усыпана магазинами, в Мюнхене местные жители обозначают ее не иначе, как улица шопоголиков. Дойдя до ее конца, вы уткнетесь в Зоненштрассе (Sonnenstraße), солнечную улицу, которая представляет из себя трассу. Перейдя ее, двигайтесь по Нусбаумштрассе (Nußbaumstraße). Пройдя ее до конца, вы и упретесь в Луг Терезы.
Если вы решили спуститься в подземку, то вам необходимо сесть на станции Мариенплатц и двигаться по U4(бирюзовая ветка) до станции Theresienwiese. Поднявшись наверх вы и окажитесь у входа на праздник.
Чем заняться?
Вообще, организаторы Октоберфеста подходят к празднованию фестиваля довольно серьезно. Они заранее составляют развлекательную программу, которая включает в себя народные немецкие забавы с гастрономическими призами. Но нужно быть готовым к тому, что для того, чтобы посостязаться в каком-то соревновании, вам будет необходимо отстоять часовую очередь.
Например, одно из типичных развлечений — накинуть на вбитый в землю кол круглую чесночную колбаску. Если у вас получилось с первой попытки, то ведущий конкурса подарит вам одну кружку пива. Наверное, не нужно говорить, что сделать это практически невозможно — большое расстояние, толкающаяся толпа и крики стоящих в очереди явно не играют на руку. Однако, и тут находятся счастливчики.
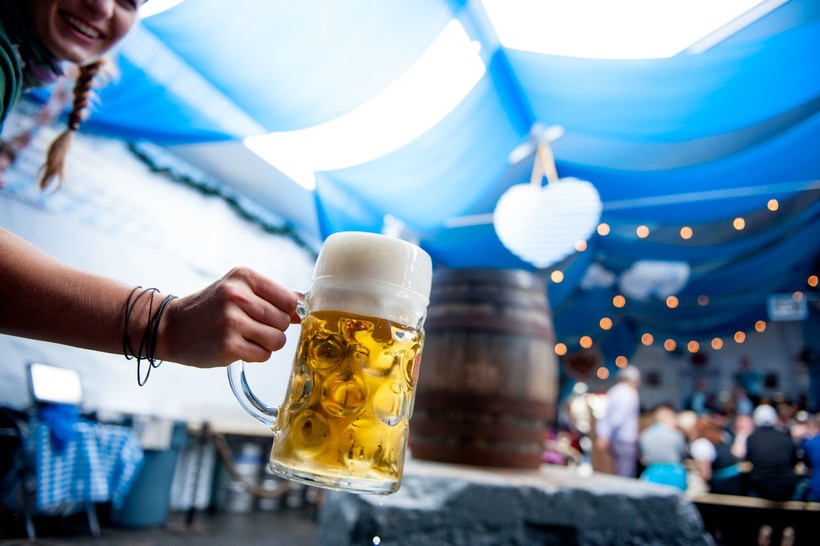


Но, вообще, нужно сказать, что Октоберфест все-таки направлен на распитие пива и поглощение большого количество всевозможных немецких закусок и других гастрономических изысков. Ведь изначальная функция этого современного празднования заключалась в создании площадки для того, чтобы набить свои животы всевозможными кушаньями, выпить несколько кружек пива и, возможно, пуститься в танцы и распевание национального гимна Германии.

И действительно, побывав на этом празднике два раза подряд, я могу сделать главный вывод: Октоберфест сегодня — это место огромной пьянки и безудержного кутежа немецкой молодежи.
Конечно, тут стоит отметить и то, что на территории Луга Терезы есть аттракционы, которые работают круглый год. Однако, во время проведения фестиваля пива многие из них проводят свой «фэйсконтроль». Такие ограничения объясняются техникой безопасности, поскольку прокатиться на колесе обозрения и посмотреть на Мюнхен с высоты птичьего полета можно только трезвому посетителю, которых в период проведения Октоберфеста практически не бывает. Но более безопасные виды развлечения, типа выбивания кегль, ударов молотком по платформе или бросания мячиков в лунки доступны любым посетителям.
Помимо этого, на территории Луга Терезы на время праздника появляется очень много палаток. В каждой из них можно найти что-то по душе: сувениры, пряники, предметы национальной одежды, дудки и другие интересные вещички. Однако, стоит отметить, что цены в таких палатках завышены. Например, магнит с изображением Музея BMW на фестивале продают за 3 евро, в то время как в городе можно купить аналогичный презент за 1,2 евро.
Особенности
Оказаться на территории Луга Терезы может любой желающий, а вот побывать внутри самих павильонов, где и разгорается основное веселье, могут только счастливчики. На территории, где проводят Октоберфест расположено около пяти павильонов, каждый из которых рассчитан на определенное количество человек, например, оказаться в самом вместительном из них может только 12,000 посетителей.

Учитывая, что ежедневно на праздник приходит больше полумиллиона человек, а в первый и последний дни около миллиона, побывать в павильонах всем просто не представляется возможным. Люди занимают километровую очередь ночью, ночуют на территории Луга Терезы, вымаливают охранников пропустить их в павильоны, в общем, делают все для того, чтобы попасть на этот пивной праздник.
Мне повезло, я оказалась внутри одного из павильонов благодаря своим знакомым, которые уже не первый раз посещали это мероприятие и были морально готовы отстоять в очереди несколько часов.
Примечательно, что Октоберфест — это тот праздник, где все равны. Ведь даже если у тебя есть лишняя пара сотен евро, ты все равно не получишь никакой привилегии и будешь вынужден ждать своей очереди, но дождешься ли ты? Вопрос твоей выдержки и самообладания. Многие просто не выдерживали и уходили из своей очереди, при этом, кто-то был непрочь поторговать своим местом, однако, такое предпринимательство быстро пресекалось охранниками.

Итак, что ждет тех, кому все-таки удалось оказаться в павильоне?
Первое, что мне бросилось в глаза, — это невероятный гул, а так же довольно простенький дизайн и посредственный интерьер: деревянные полы, небольшие столы и скамейки, кстати, тоже из дерева.

На каждом из столиков лежит меню, которое поделено на два раздела: пиво и закуски. Что касается пива, то оно подается исключительно в объеме 0,5 литра. По сравнению с ценами в магазинах стоимость пива на фестивале немного завышена, а вот кушанья, в принципе, стоят столько же, сколько и в обычных кафе.
Лично мне хватило одной кружки, которая, по моим ощущениям, никак не отличалась от пива, что продается в бутылках. Еще к особенностям можно отнести то, что официанты обслуживают посетителей очень быстро, за каждым столиком закреплено по два работника, которые принимают, приносят заказ и рассчитывают гостей.
Многие из посетителей дают официантам чаевые, обычно это 10% от заказа. Поскольку цены мне показались довольно приемлемыми, я решила тоже отблагодарить девушку, которая нас обслуживала. Кстати, как оказалось, если вы рассчитайтесь сразу и дадите официанту чаевые, то можете рассчитывать на некий комплимент от того, кто вас обслуживает, в виде пары чесночных гренок или двойной порции соуса. Довольно приятный бонус, не правда ли?
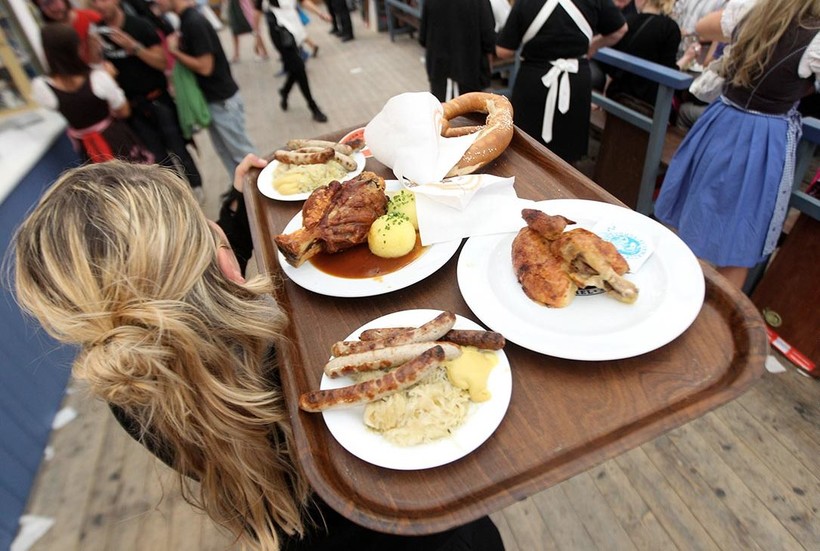

Если вас не пустили в один из павильонов, то не стоит расстраиваться — праздник не обойдет вас стороной. На улице так же можно найти множество небольших торговых палаток, которые пестрят большим количеством пива. Конечно, в основном, это пиво в бутылках. Но, по-моим ощущениям, пиво в павильоне было похоже на бутылочное, так что это обстоятельство вряд ли испортит впечатления от праздника. К тому же на Лугу Терезы продается множество уличной еды: колбаски, сосиски, фаст-фуд и даже первые блюда. В общем, голодными вы точно не уйдете.
Цены
Пиво
Стоимость пива, что продается на территории Октоберфеста в 1,5-2 раза дороже, чем хмельной напиток, который вы бы могли купить в любом мюнхенском кафе. Однако, цены все же не являются запредельными, да и раз в год, баварцы и гости города считают, что могут себе позволить качественной выпивки от известных пивоварен. Итак, цена за одну кружку пива варьируется от 4,5 до 7€. Такое разнообразие цен обусловлено сортом пива, а так же производителем. Кстати, стоит отметить личное наблюдение, в павильонах, где вместительной посетителей меньше, пиво всегда на 1-2€ дешевле.

Закуски
Закуски на Октоберфесте можно негласно поделить на два вида: уличные и павильонные. Примечательно, что и там, и там, в принципе, подается одна и та же еда. Например, супы на кости, тушенная капуста и овощи на гриле, а так же излюбленные кушанья — чесночные колбаски, соленные крендельки, сосиски.
Если говорить о ценах на крытой территории, то первые блюда обойдутся посетителю в 6-8€, вторые — 5,5-9€, что касается мелких закусок (чесночные гренки, сосиски), то цена на них не превышает 2-3€.
Еда из палаток на улице будет стоит на 0,5-1€ дешевле. Поэтому, если вы хотите немного сэкономить, то занимайте очередь за кушаньями именно на уличных гастрономических точках.
Кстати, заходить в павильоны со своей едой никто не запрещал).
Сувениры
Любая сувенирная продукция, а так же памятные презенты Октоберфеста, на мой взгляд, самая большая и бесполезная затрата. Магниты, брелки, кружки и тарелки с изображением Луга Терезы — неоправданно дорогое удовольствие.
Все это стоит действительно огромных денег. Если за пределами Октоберфеста на всю эту атрибутику турист может потратить максимум 1,5-2€, то тут только за одну вещичку придется выложить 3€, самая дорогая цена — 5€.
Я искренне считаю, что если вы хотите приобрести что-то, что напоминало бы вам о этом приключении, то лучше сделайте это в самом Мюнхене, за пределами пивного фестиваля, так, вы сэкономите и деньги и время, ведь очередь на Октоберфесте огромная даже за сувенирами.
На заметку
- Не старайтесь выносить бокалы, в которые вам наливают пиво. Удивительно, но многие действительно пытаются это сделать. Однако, на выходе стоят охранники, которые заставляют вас показывать все сумки. Если они все же обнаружат бокал, то он отправится в огромный бак, который предназначен для таких ситуаций. По своему наблюдению хочу сказать, что охранники прощают такие шалости только в том случае, если вы признаетесь и сдадите бокал в урну. Иначе вас ждет долгое разбирательство. Кстати, выходя из павильона я заметила несколько таких урн, которые были с горкой наполнены стеклянными кружками для пива.
- Постарайтесь идти на Октоберфест в компании знакомых. Если же вы решили отправиться туда в одиночку, не советую задерживаться там, когда начинает темнеть. В такое время уровень преступности возрастает, да и сами немцы забывают о нормах приличия и частенько начинают навязывать свое общество одиноким девушкам.
- Не берите с собой много денег. Октоберфест — один большой соблазн, который пестрит возможностями. А на следующее утро вы несколько раз пожалейте, что позволили себе купить несколько пряников и ненужных магнитов, цены на которые на Лугу Терезы просто зашкаливают. Держите в кармане 20 евро — это просто идеальная сумма для одного дня на Октоберфесте.
Окто́берфест (Октябрьские народные гуляния, нем. Oktoberfest) — фольклорный фестиваль, ежегодно проводимый в Мюнхене (Германия), крупнейший в мире фестиваль пива. Ivbg.ru расскажет об истории праздника и интересных фактах.
Октоберфест организуется и проводится администрацией Мюнхена. К участию в этом фестивале допускаются только мюнхенские пивоваренные компании, которые варят для него специальное октоберфестовское пиво(нем. Oktoberfestbier) с содержанием алкоголя 5,8—6,3 %, которое в другое время года обычно называют мартовским или венским.
На празднике имеется множество аттракционов — от традиционных каруселей, на которых можно покататься вот уже более восьмидесяти лет, до сверхсовременных конструкций вроде «американских горок».

История праздника
Праздник имеет длинную историю проведения. С 1872 года он начинается уже в сентябре. Первым днём традиционно является суббота, из-за чего продолжительность может сильно варьироваться (в среднем 16 дней). Праздник заканчивается в первое воскресенье октября. Если же оно приходится на 1 или 2 октября, то праздник продлевается до 3 октября.
Впервые Октоберфест состоялся 12 октября 1810 года в честь свадьбы кронпринца Людвига (в будущем король Людвиг I) и принцессы Терезы Саксонской-Хильдбургхаузской (её именем назван луг, где проходит праздник). В честь свадьбы 17 октября также были устроены скачки. По этой причине в разных источниках называется разная дата первого Октоберфеста (12 и 17 октября).
Изначально праздник организовывался и проводился частным образом. В 1819 году организация и управление праздником были отданы в руки городского совета Мюнхена. Было решено, что Октоберфест будет проводиться каждый год без исключения.
В 1872 году Октоберфест был впервые перенесён на конец сентября — начало октября, так как в это время погода в Мюнхене более комфортная, чем в середине октября. В 1904 было принято окончательное решение о переносе праздника на конец сентября, однако последнее воскресенье праздника должно было быть в октябре. Эта традиция сохранилась и до наших дней.
В 1881 году открылась первая жарильня курочек, а в 1892 году пиво впервые стали подавать в привычных сейчас стеклянных кружках. Примерно в то же время палатки, в которых продавалось пиво, приняли тот вид, который они имеют сейчас.
В 1910 году Октоберфест отпраздновал столетие. По этому поводу было продано 1,2 млн литров пива. В 1913 году была установлена самая большая в истории праздника палатка на 12 000 мест.
С 1914 по 1918 год Октоберфест не проводился из-за Первой мировой войны. В 1919 и 1920 году Октоберфест был переименован в «Осенний праздник» (нем. Herbstfest).
В 1936—1938 годах баварские бело-голубые флаги, украшавшие праздник, заменялись на нацистские флаги со свастикой.
С 1939 по 1945 год Октоберфест не проводился из-за Второй мировой войны.
С 1946 по 1948 год снова праздновался лишь «Осенний праздник». Был запрещён розлив настоящего «октоберфестовского пива» — посетителям приходилось довольствоваться разрешённым слабоалкогольным (< 2 %) пивом.
С 1950 года существует традиция начинать праздник двенадцатью выстрелами в небо из пушки, а также откупориванием первой бочки праздничного пива обер-бургомистром Мюнхена с характерным восклицанием «O’zapft is!».
С 1960 года начинается приток иностранных туристов на Октоберфест.
В 1980 году в результате теракта у главного входа на Октоберфест погибло 13 и было ранено более 200 посетителей. Тем не менее, этот террористический акт не привёл к отмене праздника.
Террористические акты 11 сентября 2001 года не привели к отмене Октоберфеста, хотя такая возможность всерьёз обсуждалась организаторами. В знак солидарности с жертвами террористических актов организаторы отказались от церемоний выезда хозяев пивных палаток и откупоривания первой бочки. Также был отменён праздничный фейерверк.
Интересные факты
- Ежегодно Октоберфест посещают около 6 миллионов посетителей, которые выпивают около 6 миллионов литров пива и съедают 500 000 жареных кур.
- На Октоберфесте работает 12 000 человек.
- Праздник предлагает 100 000 сидячих мест для посетителей.
- Право принимать участие в празднике имеют шесть пивоварен — Spaten (Шпа́тэн), Augustiner (Аугусти́нэр), Paulaner(Паула́нэр), Hacker-Pschorr (Хаккэр-Пшо́рр), Hofbräuhaus (Хо́фбройхауз), Löwenbräu (Лёвэнброй), которые в 2004 году продали 5,5 миллионов литров пива (6,1 в 2003 году).
- Оборот праздника в 2006 году составил 449 миллионов евро.
- На проживание в отелях и проезд в общественном транспорте гости праздника потратили в 2006 году более 500 миллионов евро.
- Цена литра пива, как правило, каждый год возрастает. Так, в 2007 году она составляла от 7,30 до 7,90 евро, а в 2008 году от 7,80 до 8,30 евро.
- В 2007 году была зарегистрирована 351 карманная кража — на 99 меньше, чем в 2006 году.
- Громкость музыки в палатках до 18 часов не должна превышать 85 децибел.
- Для снабжения праздника электроэнергией используются 18 трансформаторов и 43 километра электрокабеля.
- Потребление энергии составляет примерно 3 миллиона киловатт-часов, что соответствует примерно 13 % ежедневного потребления электроэнергии Мюнхеном.
- Пивная палатка потребляет около 400 киловатт-часов, большие аттракционы — около 300.
- Для обеспечения палаток газом была проложена четырёхкилометровая сеть газовых труб.
- 200 тысяч кубометров газа потребляются кухнями и ещё 20 тысяч уходит на отопление пивных садов, расположенных на открытом воздухе.
- Объём продаваемого пива в кружке не должен отличаться от 1 литра более чем на десятую часть. За соблюдением этого правила следит специальное общество «Verein gegen betrügerisches Einschenken».
- Для посетителей открыты 830 туалетов, оборудованных обычными унитазами, и уриналы, общей длиной 750 метров. Для инвалидов доступны 17 специально оборудованных туалетов.

















































