| Other names | Windows Scripting Host |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Stable release |
5.812 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Automation technology |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | Windows Script Host overview |
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) (formerly named Windows Scripting Host) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 (Build 1111) and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97.[1] The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.[2][3][4]
It is language-independent in that it can make use of different Active Scripting language engines. By default, it interprets and runs plain-text JScript (.JS and .JSE files) and VBScript (.VBS and .VBE files).
Users can install different scripting engines to enable them to script in other languages, for instance PerlScript. The language independent filename extension WSF can also be used. The advantage of the Windows Script File (.WSF) is that it allows multiple scripts («jobs») as well as a combination of scripting languages within a single file.
WSH engines include various implementations for the Rexx, BASIC, Perl, Ruby, Tcl, PHP, JavaScript, Delphi, Python, XSLT, and other languages.
Windows Script Host is distributed and installed by default on Windows 98 and later versions of Windows. It is also installed if Internet Explorer 5 (or a later version) is installed. Beginning with Windows 2000, the Windows Script Host became available for use with user login scripts.
Usage[edit]
Windows Script Host may be used for a variety of purposes, including logon scripts, administration and general automation. Microsoft describes it as an administration tool.[5] WSH provides an environment for scripts to run – it invokes the appropriate script engine and provides a set of services and objects for the script to work with.[5] These scripts may be run in GUI mode (WScript.exe) or command line mode (CScript.exe), or from a COM object (wshom.ocx), offering flexibility to the user for interactive or non-interactive scripts.[6] Windows Management Instrumentation is also scriptable by this means.
The WSH, the engines, and related functionality are also listed as objects which can be accessed and scripted and queried by means of the VBA and Visual Studio object explorers and those for similar tools like the various script debuggers, e.g. Microsoft Script Debugger, and editors.
WSH implements an object model which exposes a set of Component Object Model (COM) interfaces.[7] So in addition to ASP, IIS, Internet Explorer, CScript and WScript, the WSH can be used to automate and communicate with any Windows application with COM and other exposed objects, such as using PerlScript to query Microsoft Access by various means including various ODBC engines and SQL, ooRexxScript to create what are in effect Rexx macros in Microsoft Excel, Quattro Pro, Microsoft Word, Lotus Notes and any of the like, the XLNT script to get environment variables and print them in a new TextPad document, and so on.
The VBA functionality of Microsoft Office, Open Office (as well as Python and other installable macro languages) and Corel WordPerfect Office is separate from WSH engines although Outlook 97 uses VBScript rather than VBA as its macro language.[8]
Python in the form of ActiveState PythonScript can be used to automate and query the data in SecureCRT, as with other languages with installed engines, e.g. PerlScript, ooRexxScript, PHPScript, RubyScript, LuaScript, XLNT and so on. One notable exception is Paint Shop Pro, which can be automated in Python by means of a macro interpreter within the PSP programme itself rather than using the PythonScript WSH engine or an external Python implementation such as Python interpreters supplied with Unix emulation and integration software suites or other standalone Python implementations et al.[9][10] as an intermediate and indeed can be programmed like this even in the absence of any third-party Python installation; the same goes for the Rexx-programmable terminal emulator Passport.[11] The SecureCRT terminal emulator, SecureFX FTP client, and related client and server programmes from Van Dyke are as of the current versions automated by means of the WSH so any language with an installed engine may be used; the software comes with VBScript, JScript, and PerlScript examples.
As of the most recent releases and going back a number of versions now, the programmability of 4NT / Take Command in the latest implementations (by means of «@REXX» and similar for Perl, Python, Tcl, Ruby, Lua, VBScript, JScript and the like and so on) generally uses the WSH engine.[12] The ZOC terminal emulator gets its ability to be programmed in Rexx by means of an external interpreter, one of which is supplied with the programme, and alternate Rexx interpreters can be specified in the configuration of the programme.[13][14] The MKS Toolkit provides PScript, a WSH engine in addition to the standard Perl interpreter perl.exe which comes with the package.
VBScript, JScript, and some third-party engines have the ability to create and execute scripts in an encoded format which prevents editing with a text editor; the file extensions for these encoded scripts is .vbe and .jse and others of that type.
Unless otherwise specified, any WSH scripting engine can be used with the various Windows server software packages to provide CGI scripting. The current versions of the default WSH engines and all or most of the third party engines have socket abilities as well; as a CGI script or otherwise, PerlScript is the choice of many programmers for this purpose and the VBScript and various Rexx-based engines are also rated as sufficiently powerful in connectivity and text-processing abilities to also be useful. This also goes for file access and processing—the earliest WSH engines for VBScript and JScript do not since the base language did not,[15] whilst PerlScript, ooRexxScript, and the others have this from the beginning.
WinWrap Basic, SaxBasic and others are similar to Visual Basic for Applications, These tools are used to add scripting and macro abilities to software being developed and can be found in earlier versions of Host Explorer for example. Many other languages can also be used in this fashion. Other languages used for scripting of programmes include Rexx, Tcl, Perl, Python, Ruby, and others which come with methods to control objects in the operating system and the spreadsheet and database programmes.[16] One exception is that the Zoc terminal emulator is controlled by a Rexx interpreter supplied with the package or another interpreter specified by the user; this is also the case with the Passport emulator.
VBScript is the macro language in Microsoft Outlook 97, whilst WordBasic is used for Word up to 6, Powerpoint and other tools. Excel to 5.0 uses Visual Basic 5.0. In Office 2000 forward, true Visual Basic for Applications 6.0 is used for all components. Other components use Visual Basic for Applications. OpenOffice uses Visual Basic, Python, and several others as macro languages and others can be added. LotusScript is very closely related to VBA and used for Lotus Notes and Lotus SmartSuite, which includes Lotus Word Pro (the current descendant of Ami Pro), Lotus Approach, Lotus FastSite, Lotus 1-2-3, &c, and pure VBA, licensed from Microsoft, is used in Corel products such as WordPerfect, Paradox, Quattro Pro &c.
Any scripting language installed under Windows can be accessed by external means of PerlScript, PythonScript, VBScript and the other engines available can be used to access databases (Lotus Notes, Microsoft Access, Oracle Database, Paradox) and spreadsheets (Microsoft Excel, Lotus 1-2-3, Quattro Pro) and other tools like word processors, terminal emulators, command shells and so on. This can be accomplished by means of the WSH, so any language can be used if there is an installed engine.
In recent versions of the Take Command enhanced command prompt and tools, the «script» command typed at the shell prompt will produce a list of the currently installed engines, one to a line and therefore CR-LF delimited.[17][18][19]
Examples[edit]
The first example is very simple; it shows some VBScript which uses the root WSH COM object «WScript» to display a message with an ‘OK’ button. Upon launching this script the CScript or WScript engine would be called and the runtime environment provided.
Content of a file hello0.vbs
WScript.Echo "Hello world" WScript.Quit
WSH programming can also use the JScript language.
Content of a file hello1.js
WSH.Echo("Hello world"); WSH.Quit();
Or, code can be mixed in one WSF file, such as VBScript and JScript, or any other:
Content of a file hello2.wsf
<job> <script language="VBScript"> MsgBox "hello world (from vb)" </script> <script language="JScript"> WSH.echo("hello world (from js)"); </script> </job>
Security concerns[edit]
Windows applications and processes may be automated using a script in Windows Script Host. Viruses and malware could be written to exploit this ability. Thus, some suggest disabling it for security reasons.[20] Alternatively, antivirus programs may offer features to control .vbs and other scripts which run in the WSH environment.
Since version 5.6 of WSH, scripts can be digitally signed programmatically using the Scripting.Signer object in a script itself, provided a valid certificate is present on the system. Alternatively, the signcode tool from the Platform SDK, which has been extended to support WSH filetypes, may be used at the command line.[21]
By using Software Restriction Policies introduced with Windows XP, a system may be configured to execute only those scripts which are stored in trusted locations, have a known MD5 hash, or have been digitally signed by a trusted publisher, thus preventing the execution of untrusted scripts.[22]
Available scripting engines[edit]
Note: By definition, all of these scripting engines can be utilised in CGI programming under Windows with any number of programmes and set up, meaning that the source code files for a script used on a server for CGI purposes could bear other file extensions such as .cgi and so on. The aforementioned ability of the Windows Script Host to run a script with multiple languages in it in files with a .wsh extension. Extended Html and XML also add to the additional possibilities when working with scripts for network use, as do Active Server Pages and so forth. Moreover, Windows shell scripts and scripts written in shells with enhanced capabilities like TCC, 4NT, etc. and Unix shells under interoperability software like the MKS Toolkit can have scripts embedded in them as well.
| Engine name | Scripting language implemented | Base language | File extensions | Availability | Produced by | Status | Initial release date | Encoded scripts | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBScript | Microsoft VBScript | Microsoft Visual Basic | .vbs | Installed by default | Microsoft | default install | 1999 | Yes, .vbe | Default windows host script |
| JScript | Microsoft JScript | ECMAScript | .js | Installed by default | Microsoft | default install | 1999 | Yes, .jse | Default java script host |
| WinWrap Basic | WinWrap Basic | Basic | .wwb | In the main WWB installation | Polar Engineering | Standard functionality of WWB; Utilises both .NET and COM | 2004 | Yes | |
| PerlScript | Perl | Perl 5 | .pls | with ActiveState Perl | ActiveState | Open source | 1999 | Reportedly yes | |
| PScript | Perl | Perl 5, CGI functionality | .p, .ps | with MKS Toolkit | MKS | Commercial | 2001 | ||
| XBScript | xBase Scripting Engine | xBase (Clipper) | .xbs, .prg | Clipper | with XBScript sofrware | Commercial | |||
| LotusScript WSH | LotusScript | Microsoft Visual Basic (q.v.) | .nsf | Third party download | Service Desk Plus | Freeware | 2001 | ||
| RexxScript | Rexx | Rexx | .rxs, .rx, .rex | With some Rexx implementations | Various | Freeware | 1998 | ||
| ooRexxScript | Open Object REXX | REXX | .rxs | with Open Object Rexx or free from some third parties | Open Object Rexx team | Open source | |||
| PythonScript | Python | Python | .pys | SourceForge & with ActivePython | The Pywin32 project | Open source | |||
| TclScript | Tcl/Tk | Tcl/Tk | .tcls | SourceForge | ActiveState or third party | Open source | |||
| ActivePHPScript | PHP | PHP | .phps | with PHP | PHP team | Open source | |||
| PHPScript | PHP | PHP | .phps | with PHP | PHP team | Open source | Earlier version of ActivePHPScript | ||
| RubyScript | Ruby | Ruby | .rbs | with Ruby distribution | Ruby team | Open source | Yes | ||
| XLNTScript | XLNT | DCL | .xcs | with XLNT | Advanced Systems Concepts, Inc. | Commercial | 1997 | An OpenVMS DCL-based multi-purpose scripting application for Windows | |
| LuaScript | Lua | Lua | .lua | with Lua | Lua organisation | Open Source | |||
| Object REXX engine | Object REXX | Rexx | .rex, .rxs | with IBM Object REXX | IBM | Commercial | 2002 | ||
| XML Engine | XML parsing | Extended HTML, XML | .xml | with many XML implementations | Elf Data | de facto Default install | 2000 | Macintosh too | |
| Kixtart WSH Engine | Kixtart | KixTart, MS-DOS, Windows 95. Windows NT shells | .kix | with KixStart | Microsoft Netherlands | Windows Resource Kits and other resources | 1996 | Download from Microsoft or elsewhere, aka KixStart32 | |
| NullScript | NullScript | Null language | .ns | with NullScript | NullScript Organisation | Windows Resource Kits and other resources | 1999 | ||
| ForthScript | Forth | Forth | .fth, others | Forth | DMOZ | Open Source | |||
| Haskell Script | Haskell | Haskell | *.hsk (provisional), others | free download | Open Source | ||||
| XSLT WSH Engine | XSLT | XSLT | .xslt | free download | Open Source | ||||
| CobolScript WSH Engine | Cobol | Cobol | .cbl. .cob, .cb | Fujitsu Cobol 3 — free for educational use | Commercialware from Fujitsu free with free compiler for educators &c | Proprietary | |||
| Delphi scripting engine | Delphi | Delphi, a Pascal variant | .dlp, .del, . | In some Delphi distributions or resource kits | Commercial | 2003 | |||
| DMDScript | DMDScript | D, a major incrementation of C | .dmd | DMD Distributions, download | Freeware | Available on Web | 2014 | DMD | |
| C# Script | C# | Microsoft C#.NET | .cs. .c#, others | Source code available | Open Source, active development underway | unclear | 2013 | ||
| Small C Scripting Engine | C | C (K&R, Ansi) | .c, others | Various locations, check Web | Freeware | 2009 | |||
| JavaScript WSH Engine | JavaScript/Java | Java & variants | .java, .j, jva, others | With many JavaScript implementations | Sun/Other Java Organisations | Freeware | |||
| Take Command WSH Engine | 4NT/Take Command | TCC, the current version of 4NT p | .btm, .cmd, bat, others | Check JP Software | JP Software | Proprietary | 2015 | Early development | |
| 92Script WSH Engine | TI-89/92+/Voyager 200 TI-Basic | Calculator TI-Basic | .92bs | Project Web/FTP site | Various independent programmers | Experimental, Open Source | 2014 | «possible» | Beta Q4 2015 for main engine; graphing functionality (92Script/Tk) then or later |
| 48Script WSH Engine | HP-48 Calculator family on-board programming language | HP 48 Programming Language, distant relative of Forth, Basic, Lisp | .48s | Project Web/FTP site | Various independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned | Status as of 2015-09-30. Language has Lisp, Basic, Forth, and other influences. |
| Fortran Script | Fortran | Fortran 77 | .for, .ftn. f77, f90, f95 | Various | Various | Experimental proof-of-concept, academic exercise, shareware, commercial, open source. | 2000 | ||
| PascalScript | Object Pascal | Pascal 7 | .pas, .ops, other | Object Pascal | RemObjects | Freeware | 2001 | Can also be used with Delphi directly | |
| Lisp WSH Engine | Lisp | Lisp | .lisp, .lsp | Various Lisp tools | AutoLisp and others | Freeware or Shareware | |||
| BESEN | ECMA-JavaScript | Java and Variants | .bes, .bsn, others | SourceForge | BESEN Organisation | Open Source | 2011 | ||
| ECMAScript WSH engines | Java and Variants | Various | Various | Various | Various | Experimental, Freeware, Open Source, Shareware, Proprietary, Commercialware | 2005 | There are numerous ECMAScript implementations but not all have WSH engines | |
| CFXScript WSH Engine | Casio CFX-9850 and fx Calculator series on-board programming language | Casio Calculator Programming Language, as ported to various operating systems as CFW | .cfxb | Project Web/FTP Sites | independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned[23] | Status as of 2015-09-30. Language has elements of Basic, Forth, Fortran, and others. |
| SharpCalcScript WSH Engine | Sharp graphing calculators on-board programming language | Sharp S-Basic as ported to windows as NeusSFortran | .scsb | Project Web/FTP Sites | independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned | Status as of 2015-09-30. Also subsumes the S-Basic language of Sharp’s Pocket Computers. |
There have been suggestions of creating engines for other languages, such as LotusScript, SaxBasic, BasicScript, KiXtart, awk, bash, csh and other Unix shells, 4NT, cmd.exe (the Windows NT shell), Windows PowerShell, DCL, C, C++, Fortran and others.[24]
The XLNT language[25] is based on DCL and provides a very large subset of the language along with additional commands and statements and the software can be used in three ways: the WSH engine (*.xcs), the console interpreter (*.xlnt) and as a server and client side CGI engine (*.xgi).[26]
When a server implementing CGI such as the Windows Internet Information Server, ports of Apache and others, all or most of the engines can be used; the most commonly used are VBScript, JScript, PythonScript, PerlScript, ActivePHPScript, and ooRexxScript. The MKS Toolkit PScript program also runs Perl. Command shells like cmd.exe, 4NT, ksh, and scripting languages with string processing and preferably socket functionality are also able to be used for CGI scripting; compiled languages like C++, Visual Basic, and Java can also be used like this. All Perl interpreters, ooRexx, PHP, and more recent versions of VBScript and JScript can use sockets for TCP/IP and usually UDP and other protocols for this.
Version history[edit]
| Windows version | Shipped with WSH version | Last redistributable version |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows NT 4.0 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows NT Server 4.0 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows CE 3.0 | 1.0 (optional install on installer disc) | 2.0 |
| Windows 98 | 1.0 | 5.6 |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | 1.0 | 5.6 |
| Windows 2000 | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.7 |
| Windows 2000 Server | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.7 |
| Windows 2000 SP3, SP4 and SP5 | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows Me | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.6 |
| Windows XP | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows XP SP3 | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2003 | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows Vista | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2008 | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows 7 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows 8 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2012 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows 10 | 5.812 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2016 | 5.812 | Not applicable |
The redistributable version of WSH version 5.6 can be installed on Windows 95/98/Me and Windows NT 4.0/2000. WSH 5.7 is downloadable for Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. Recently[when?], redistributable versions for older operating systems (Windows 9x and Windows NT 4.0) are no longer available from the Microsoft Download Center.
Since Windows XP Service Pack 3, release 5.7 is not needed as it is included, with newer revisions being included in newer versions of Windows since.
See also[edit]
- JScript .NET
References[edit]
- ^ ?MSDN, «Windows Scripting Host» and «VBScript»
- ^ MSDN April 2000 edition, «Windows Scripting Host»
- ^ The VBScript Bible (1999)
- ^ Windows 2000 Server Resource Kit (documentation
- ^ a b «What Is WSH?». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 7 January 2018. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ «Windows Script Host Basics». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ «Windows Script Host Object Model». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ MSDN «VBA»
- ^ User’s Manual, Paint Shop Pro 8
- ^ Paint Shop Pro 8 help, «Automation»
- ^ main help file, Passport for Windows
- ^ Take Command documentation 18.00 documentation hard copy and Help file
- ^ Zoc v 6.0 help
- ^ Zoc 5.0 printed manual
- ^ MSDN documentation
- ^ Windows Office 97 & 2000 Bibles (Wiley)
- ^ Take Command version 18.00 documentation
- ^ JP Software Take Command-4NT-4Dos-4OS/2 site, bulletin board
- ^ Take Command 18.00 help
- ^ «Norman — Antivirus & Security Software for Home & Business». AVG.com. Archived from the original on 21 February 2006. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ LLC), Tara Meyer (Aquent. «Providing a Secure eXPerience». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ Windows Script Host 5.6 Boasts Windows XP Integration, Security, New Object Model Archived 2008-02-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CasioCalc.com, msgs of 15.09.2016
- ^ «Notes/Domino 4 and 5 Forum : RE: Suggestion: Make LotusScript a script engine for Windows Scripting Host». Archived from the original on 2015-03-21. Retrieved 2015-03-12.
- ^ ASCI html help file
- ^ ASCI site
External links[edit]
- Windows Script Host
- Windows Script Host Reference on microsoft.com
| Other names | Windows Scripting Host |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Stable release |
5.812 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Automation technology |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | Windows Script Host overview |
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) (formerly named Windows Scripting Host) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 (Build 1111) and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97.[1] The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.[2][3][4]
It is language-independent in that it can make use of different Active Scripting language engines. By default, it interprets and runs plain-text JScript (.JS and .JSE files) and VBScript (.VBS and .VBE files).
Users can install different scripting engines to enable them to script in other languages, for instance PerlScript. The language independent filename extension WSF can also be used. The advantage of the Windows Script File (.WSF) is that it allows multiple scripts («jobs») as well as a combination of scripting languages within a single file.
WSH engines include various implementations for the Rexx, BASIC, Perl, Ruby, Tcl, PHP, JavaScript, Delphi, Python, XSLT, and other languages.
Windows Script Host is distributed and installed by default on Windows 98 and later versions of Windows. It is also installed if Internet Explorer 5 (or a later version) is installed. Beginning with Windows 2000, the Windows Script Host became available for use with user login scripts.
Usage[edit]
Windows Script Host may be used for a variety of purposes, including logon scripts, administration and general automation. Microsoft describes it as an administration tool.[5] WSH provides an environment for scripts to run – it invokes the appropriate script engine and provides a set of services and objects for the script to work with.[5] These scripts may be run in GUI mode (WScript.exe) or command line mode (CScript.exe), or from a COM object (wshom.ocx), offering flexibility to the user for interactive or non-interactive scripts.[6] Windows Management Instrumentation is also scriptable by this means.
The WSH, the engines, and related functionality are also listed as objects which can be accessed and scripted and queried by means of the VBA and Visual Studio object explorers and those for similar tools like the various script debuggers, e.g. Microsoft Script Debugger, and editors.
WSH implements an object model which exposes a set of Component Object Model (COM) interfaces.[7] So in addition to ASP, IIS, Internet Explorer, CScript and WScript, the WSH can be used to automate and communicate with any Windows application with COM and other exposed objects, such as using PerlScript to query Microsoft Access by various means including various ODBC engines and SQL, ooRexxScript to create what are in effect Rexx macros in Microsoft Excel, Quattro Pro, Microsoft Word, Lotus Notes and any of the like, the XLNT script to get environment variables and print them in a new TextPad document, and so on.
The VBA functionality of Microsoft Office, Open Office (as well as Python and other installable macro languages) and Corel WordPerfect Office is separate from WSH engines although Outlook 97 uses VBScript rather than VBA as its macro language.[8]
Python in the form of ActiveState PythonScript can be used to automate and query the data in SecureCRT, as with other languages with installed engines, e.g. PerlScript, ooRexxScript, PHPScript, RubyScript, LuaScript, XLNT and so on. One notable exception is Paint Shop Pro, which can be automated in Python by means of a macro interpreter within the PSP programme itself rather than using the PythonScript WSH engine or an external Python implementation such as Python interpreters supplied with Unix emulation and integration software suites or other standalone Python implementations et al.[9][10] as an intermediate and indeed can be programmed like this even in the absence of any third-party Python installation; the same goes for the Rexx-programmable terminal emulator Passport.[11] The SecureCRT terminal emulator, SecureFX FTP client, and related client and server programmes from Van Dyke are as of the current versions automated by means of the WSH so any language with an installed engine may be used; the software comes with VBScript, JScript, and PerlScript examples.
As of the most recent releases and going back a number of versions now, the programmability of 4NT / Take Command in the latest implementations (by means of «@REXX» and similar for Perl, Python, Tcl, Ruby, Lua, VBScript, JScript and the like and so on) generally uses the WSH engine.[12] The ZOC terminal emulator gets its ability to be programmed in Rexx by means of an external interpreter, one of which is supplied with the programme, and alternate Rexx interpreters can be specified in the configuration of the programme.[13][14] The MKS Toolkit provides PScript, a WSH engine in addition to the standard Perl interpreter perl.exe which comes with the package.
VBScript, JScript, and some third-party engines have the ability to create and execute scripts in an encoded format which prevents editing with a text editor; the file extensions for these encoded scripts is .vbe and .jse and others of that type.
Unless otherwise specified, any WSH scripting engine can be used with the various Windows server software packages to provide CGI scripting. The current versions of the default WSH engines and all or most of the third party engines have socket abilities as well; as a CGI script or otherwise, PerlScript is the choice of many programmers for this purpose and the VBScript and various Rexx-based engines are also rated as sufficiently powerful in connectivity and text-processing abilities to also be useful. This also goes for file access and processing—the earliest WSH engines for VBScript and JScript do not since the base language did not,[15] whilst PerlScript, ooRexxScript, and the others have this from the beginning.
WinWrap Basic, SaxBasic and others are similar to Visual Basic for Applications, These tools are used to add scripting and macro abilities to software being developed and can be found in earlier versions of Host Explorer for example. Many other languages can also be used in this fashion. Other languages used for scripting of programmes include Rexx, Tcl, Perl, Python, Ruby, and others which come with methods to control objects in the operating system and the spreadsheet and database programmes.[16] One exception is that the Zoc terminal emulator is controlled by a Rexx interpreter supplied with the package or another interpreter specified by the user; this is also the case with the Passport emulator.
VBScript is the macro language in Microsoft Outlook 97, whilst WordBasic is used for Word up to 6, Powerpoint and other tools. Excel to 5.0 uses Visual Basic 5.0. In Office 2000 forward, true Visual Basic for Applications 6.0 is used for all components. Other components use Visual Basic for Applications. OpenOffice uses Visual Basic, Python, and several others as macro languages and others can be added. LotusScript is very closely related to VBA and used for Lotus Notes and Lotus SmartSuite, which includes Lotus Word Pro (the current descendant of Ami Pro), Lotus Approach, Lotus FastSite, Lotus 1-2-3, &c, and pure VBA, licensed from Microsoft, is used in Corel products such as WordPerfect, Paradox, Quattro Pro &c.
Any scripting language installed under Windows can be accessed by external means of PerlScript, PythonScript, VBScript and the other engines available can be used to access databases (Lotus Notes, Microsoft Access, Oracle Database, Paradox) and spreadsheets (Microsoft Excel, Lotus 1-2-3, Quattro Pro) and other tools like word processors, terminal emulators, command shells and so on. This can be accomplished by means of the WSH, so any language can be used if there is an installed engine.
In recent versions of the Take Command enhanced command prompt and tools, the «script» command typed at the shell prompt will produce a list of the currently installed engines, one to a line and therefore CR-LF delimited.[17][18][19]
Examples[edit]
The first example is very simple; it shows some VBScript which uses the root WSH COM object «WScript» to display a message with an ‘OK’ button. Upon launching this script the CScript or WScript engine would be called and the runtime environment provided.
Content of a file hello0.vbs
WScript.Echo "Hello world" WScript.Quit
WSH programming can also use the JScript language.
Content of a file hello1.js
WSH.Echo("Hello world"); WSH.Quit();
Or, code can be mixed in one WSF file, such as VBScript and JScript, or any other:
Content of a file hello2.wsf
<job> <script language="VBScript"> MsgBox "hello world (from vb)" </script> <script language="JScript"> WSH.echo("hello world (from js)"); </script> </job>
Security concerns[edit]
Windows applications and processes may be automated using a script in Windows Script Host. Viruses and malware could be written to exploit this ability. Thus, some suggest disabling it for security reasons.[20] Alternatively, antivirus programs may offer features to control .vbs and other scripts which run in the WSH environment.
Since version 5.6 of WSH, scripts can be digitally signed programmatically using the Scripting.Signer object in a script itself, provided a valid certificate is present on the system. Alternatively, the signcode tool from the Platform SDK, which has been extended to support WSH filetypes, may be used at the command line.[21]
By using Software Restriction Policies introduced with Windows XP, a system may be configured to execute only those scripts which are stored in trusted locations, have a known MD5 hash, or have been digitally signed by a trusted publisher, thus preventing the execution of untrusted scripts.[22]
Available scripting engines[edit]
Note: By definition, all of these scripting engines can be utilised in CGI programming under Windows with any number of programmes and set up, meaning that the source code files for a script used on a server for CGI purposes could bear other file extensions such as .cgi and so on. The aforementioned ability of the Windows Script Host to run a script with multiple languages in it in files with a .wsh extension. Extended Html and XML also add to the additional possibilities when working with scripts for network use, as do Active Server Pages and so forth. Moreover, Windows shell scripts and scripts written in shells with enhanced capabilities like TCC, 4NT, etc. and Unix shells under interoperability software like the MKS Toolkit can have scripts embedded in them as well.
| Engine name | Scripting language implemented | Base language | File extensions | Availability | Produced by | Status | Initial release date | Encoded scripts | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBScript | Microsoft VBScript | Microsoft Visual Basic | .vbs | Installed by default | Microsoft | default install | 1999 | Yes, .vbe | Default windows host script |
| JScript | Microsoft JScript | ECMAScript | .js | Installed by default | Microsoft | default install | 1999 | Yes, .jse | Default java script host |
| WinWrap Basic | WinWrap Basic | Basic | .wwb | In the main WWB installation | Polar Engineering | Standard functionality of WWB; Utilises both .NET and COM | 2004 | Yes | |
| PerlScript | Perl | Perl 5 | .pls | with ActiveState Perl | ActiveState | Open source | 1999 | Reportedly yes | |
| PScript | Perl | Perl 5, CGI functionality | .p, .ps | with MKS Toolkit | MKS | Commercial | 2001 | ||
| XBScript | xBase Scripting Engine | xBase (Clipper) | .xbs, .prg | Clipper | with XBScript sofrware | Commercial | |||
| LotusScript WSH | LotusScript | Microsoft Visual Basic (q.v.) | .nsf | Third party download | Service Desk Plus | Freeware | 2001 | ||
| RexxScript | Rexx | Rexx | .rxs, .rx, .rex | With some Rexx implementations | Various | Freeware | 1998 | ||
| ooRexxScript | Open Object REXX | REXX | .rxs | with Open Object Rexx or free from some third parties | Open Object Rexx team | Open source | |||
| PythonScript | Python | Python | .pys | SourceForge & with ActivePython | The Pywin32 project | Open source | |||
| TclScript | Tcl/Tk | Tcl/Tk | .tcls | SourceForge | ActiveState or third party | Open source | |||
| ActivePHPScript | PHP | PHP | .phps | with PHP | PHP team | Open source | |||
| PHPScript | PHP | PHP | .phps | with PHP | PHP team | Open source | Earlier version of ActivePHPScript | ||
| RubyScript | Ruby | Ruby | .rbs | with Ruby distribution | Ruby team | Open source | Yes | ||
| XLNTScript | XLNT | DCL | .xcs | with XLNT | Advanced Systems Concepts, Inc. | Commercial | 1997 | An OpenVMS DCL-based multi-purpose scripting application for Windows | |
| LuaScript | Lua | Lua | .lua | with Lua | Lua organisation | Open Source | |||
| Object REXX engine | Object REXX | Rexx | .rex, .rxs | with IBM Object REXX | IBM | Commercial | 2002 | ||
| XML Engine | XML parsing | Extended HTML, XML | .xml | with many XML implementations | Elf Data | de facto Default install | 2000 | Macintosh too | |
| Kixtart WSH Engine | Kixtart | KixTart, MS-DOS, Windows 95. Windows NT shells | .kix | with KixStart | Microsoft Netherlands | Windows Resource Kits and other resources | 1996 | Download from Microsoft or elsewhere, aka KixStart32 | |
| NullScript | NullScript | Null language | .ns | with NullScript | NullScript Organisation | Windows Resource Kits and other resources | 1999 | ||
| ForthScript | Forth | Forth | .fth, others | Forth | DMOZ | Open Source | |||
| Haskell Script | Haskell | Haskell | *.hsk (provisional), others | free download | Open Source | ||||
| XSLT WSH Engine | XSLT | XSLT | .xslt | free download | Open Source | ||||
| CobolScript WSH Engine | Cobol | Cobol | .cbl. .cob, .cb | Fujitsu Cobol 3 — free for educational use | Commercialware from Fujitsu free with free compiler for educators &c | Proprietary | |||
| Delphi scripting engine | Delphi | Delphi, a Pascal variant | .dlp, .del, . | In some Delphi distributions or resource kits | Commercial | 2003 | |||
| DMDScript | DMDScript | D, a major incrementation of C | .dmd | DMD Distributions, download | Freeware | Available on Web | 2014 | DMD | |
| C# Script | C# | Microsoft C#.NET | .cs. .c#, others | Source code available | Open Source, active development underway | unclear | 2013 | ||
| Small C Scripting Engine | C | C (K&R, Ansi) | .c, others | Various locations, check Web | Freeware | 2009 | |||
| JavaScript WSH Engine | JavaScript/Java | Java & variants | .java, .j, jva, others | With many JavaScript implementations | Sun/Other Java Organisations | Freeware | |||
| Take Command WSH Engine | 4NT/Take Command | TCC, the current version of 4NT p | .btm, .cmd, bat, others | Check JP Software | JP Software | Proprietary | 2015 | Early development | |
| 92Script WSH Engine | TI-89/92+/Voyager 200 TI-Basic | Calculator TI-Basic | .92bs | Project Web/FTP site | Various independent programmers | Experimental, Open Source | 2014 | «possible» | Beta Q4 2015 for main engine; graphing functionality (92Script/Tk) then or later |
| 48Script WSH Engine | HP-48 Calculator family on-board programming language | HP 48 Programming Language, distant relative of Forth, Basic, Lisp | .48s | Project Web/FTP site | Various independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned | Status as of 2015-09-30. Language has Lisp, Basic, Forth, and other influences. |
| Fortran Script | Fortran | Fortran 77 | .for, .ftn. f77, f90, f95 | Various | Various | Experimental proof-of-concept, academic exercise, shareware, commercial, open source. | 2000 | ||
| PascalScript | Object Pascal | Pascal 7 | .pas, .ops, other | Object Pascal | RemObjects | Freeware | 2001 | Can also be used with Delphi directly | |
| Lisp WSH Engine | Lisp | Lisp | .lisp, .lsp | Various Lisp tools | AutoLisp and others | Freeware or Shareware | |||
| BESEN | ECMA-JavaScript | Java and Variants | .bes, .bsn, others | SourceForge | BESEN Organisation | Open Source | 2011 | ||
| ECMAScript WSH engines | Java and Variants | Various | Various | Various | Various | Experimental, Freeware, Open Source, Shareware, Proprietary, Commercialware | 2005 | There are numerous ECMAScript implementations but not all have WSH engines | |
| CFXScript WSH Engine | Casio CFX-9850 and fx Calculator series on-board programming language | Casio Calculator Programming Language, as ported to various operating systems as CFW | .cfxb | Project Web/FTP Sites | independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned[23] | Status as of 2015-09-30. Language has elements of Basic, Forth, Fortran, and others. |
| SharpCalcScript WSH Engine | Sharp graphing calculators on-board programming language | Sharp S-Basic as ported to windows as NeusSFortran | .scsb | Project Web/FTP Sites | independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned | Status as of 2015-09-30. Also subsumes the S-Basic language of Sharp’s Pocket Computers. |
There have been suggestions of creating engines for other languages, such as LotusScript, SaxBasic, BasicScript, KiXtart, awk, bash, csh and other Unix shells, 4NT, cmd.exe (the Windows NT shell), Windows PowerShell, DCL, C, C++, Fortran and others.[24]
The XLNT language[25] is based on DCL and provides a very large subset of the language along with additional commands and statements and the software can be used in three ways: the WSH engine (*.xcs), the console interpreter (*.xlnt) and as a server and client side CGI engine (*.xgi).[26]
When a server implementing CGI such as the Windows Internet Information Server, ports of Apache and others, all or most of the engines can be used; the most commonly used are VBScript, JScript, PythonScript, PerlScript, ActivePHPScript, and ooRexxScript. The MKS Toolkit PScript program also runs Perl. Command shells like cmd.exe, 4NT, ksh, and scripting languages with string processing and preferably socket functionality are also able to be used for CGI scripting; compiled languages like C++, Visual Basic, and Java can also be used like this. All Perl interpreters, ooRexx, PHP, and more recent versions of VBScript and JScript can use sockets for TCP/IP and usually UDP and other protocols for this.
Version history[edit]
| Windows version | Shipped with WSH version | Last redistributable version |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows NT 4.0 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows NT Server 4.0 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows CE 3.0 | 1.0 (optional install on installer disc) | 2.0 |
| Windows 98 | 1.0 | 5.6 |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | 1.0 | 5.6 |
| Windows 2000 | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.7 |
| Windows 2000 Server | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.7 |
| Windows 2000 SP3, SP4 and SP5 | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows Me | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.6 |
| Windows XP | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows XP SP3 | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2003 | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows Vista | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2008 | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows 7 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows 8 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2012 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows 10 | 5.812 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2016 | 5.812 | Not applicable |
The redistributable version of WSH version 5.6 can be installed on Windows 95/98/Me and Windows NT 4.0/2000. WSH 5.7 is downloadable for Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. Recently[when?], redistributable versions for older operating systems (Windows 9x and Windows NT 4.0) are no longer available from the Microsoft Download Center.
Since Windows XP Service Pack 3, release 5.7 is not needed as it is included, with newer revisions being included in newer versions of Windows since.
See also[edit]
- JScript .NET
References[edit]
- ^ ?MSDN, «Windows Scripting Host» and «VBScript»
- ^ MSDN April 2000 edition, «Windows Scripting Host»
- ^ The VBScript Bible (1999)
- ^ Windows 2000 Server Resource Kit (documentation
- ^ a b «What Is WSH?». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 7 January 2018. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ «Windows Script Host Basics». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ «Windows Script Host Object Model». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ MSDN «VBA»
- ^ User’s Manual, Paint Shop Pro 8
- ^ Paint Shop Pro 8 help, «Automation»
- ^ main help file, Passport for Windows
- ^ Take Command documentation 18.00 documentation hard copy and Help file
- ^ Zoc v 6.0 help
- ^ Zoc 5.0 printed manual
- ^ MSDN documentation
- ^ Windows Office 97 & 2000 Bibles (Wiley)
- ^ Take Command version 18.00 documentation
- ^ JP Software Take Command-4NT-4Dos-4OS/2 site, bulletin board
- ^ Take Command 18.00 help
- ^ «Norman — Antivirus & Security Software for Home & Business». AVG.com. Archived from the original on 21 February 2006. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ LLC), Tara Meyer (Aquent. «Providing a Secure eXPerience». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ Windows Script Host 5.6 Boasts Windows XP Integration, Security, New Object Model Archived 2008-02-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CasioCalc.com, msgs of 15.09.2016
- ^ «Notes/Domino 4 and 5 Forum : RE: Suggestion: Make LotusScript a script engine for Windows Scripting Host». Archived from the original on 2015-03-21. Retrieved 2015-03-12.
- ^ ASCI html help file
- ^ ASCI site
External links[edit]
- Windows Script Host
- Windows Script Host Reference on microsoft.com
| Other names | Windows Scripting Host |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
| Stable release |
5.812 |
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
| Type | Automation technology |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | Windows Script Host overview |
The Microsoft Windows Script Host (WSH) (formerly named Windows Scripting Host) is an automation technology for Microsoft Windows operating systems that provides scripting abilities comparable to batch files, but with a wider range of supported features. This tool was first provided on Windows 95 after Build 950a on the installation discs as an optional installation configurable and installable by means of the Control Panel, and then a standard component of Windows 98 (Build 1111) and subsequent and Windows NT 4.0 Build 1381 and by means of Service Pack 4. The WSH is also a means of automation for Internet Explorer via the installed WSH engines from IE Version 3.0 onwards; at this time VBScript became means of automation for Microsoft Outlook 97.[1] The WSH is also an optional install provided with a VBScript and JScript engine for Windows CE 3.0 and following and some third-party engines including Rexx and other forms of Basic are also available.[2][3][4]
It is language-independent in that it can make use of different Active Scripting language engines. By default, it interprets and runs plain-text JScript (.JS and .JSE files) and VBScript (.VBS and .VBE files).
Users can install different scripting engines to enable them to script in other languages, for instance PerlScript. The language independent filename extension WSF can also be used. The advantage of the Windows Script File (.WSF) is that it allows multiple scripts («jobs») as well as a combination of scripting languages within a single file.
WSH engines include various implementations for the Rexx, BASIC, Perl, Ruby, Tcl, PHP, JavaScript, Delphi, Python, XSLT, and other languages.
Windows Script Host is distributed and installed by default on Windows 98 and later versions of Windows. It is also installed if Internet Explorer 5 (or a later version) is installed. Beginning with Windows 2000, the Windows Script Host became available for use with user login scripts.
Usage[edit]
Windows Script Host may be used for a variety of purposes, including logon scripts, administration and general automation. Microsoft describes it as an administration tool.[5] WSH provides an environment for scripts to run – it invokes the appropriate script engine and provides a set of services and objects for the script to work with.[5] These scripts may be run in GUI mode (WScript.exe) or command line mode (CScript.exe), or from a COM object (wshom.ocx), offering flexibility to the user for interactive or non-interactive scripts.[6] Windows Management Instrumentation is also scriptable by this means.
The WSH, the engines, and related functionality are also listed as objects which can be accessed and scripted and queried by means of the VBA and Visual Studio object explorers and those for similar tools like the various script debuggers, e.g. Microsoft Script Debugger, and editors.
WSH implements an object model which exposes a set of Component Object Model (COM) interfaces.[7] So in addition to ASP, IIS, Internet Explorer, CScript and WScript, the WSH can be used to automate and communicate with any Windows application with COM and other exposed objects, such as using PerlScript to query Microsoft Access by various means including various ODBC engines and SQL, ooRexxScript to create what are in effect Rexx macros in Microsoft Excel, Quattro Pro, Microsoft Word, Lotus Notes and any of the like, the XLNT script to get environment variables and print them in a new TextPad document, and so on.
The VBA functionality of Microsoft Office, Open Office (as well as Python and other installable macro languages) and Corel WordPerfect Office is separate from WSH engines although Outlook 97 uses VBScript rather than VBA as its macro language.[8]
Python in the form of ActiveState PythonScript can be used to automate and query the data in SecureCRT, as with other languages with installed engines, e.g. PerlScript, ooRexxScript, PHPScript, RubyScript, LuaScript, XLNT and so on. One notable exception is Paint Shop Pro, which can be automated in Python by means of a macro interpreter within the PSP programme itself rather than using the PythonScript WSH engine or an external Python implementation such as Python interpreters supplied with Unix emulation and integration software suites or other standalone Python implementations et al.[9][10] as an intermediate and indeed can be programmed like this even in the absence of any third-party Python installation; the same goes for the Rexx-programmable terminal emulator Passport.[11] The SecureCRT terminal emulator, SecureFX FTP client, and related client and server programmes from Van Dyke are as of the current versions automated by means of the WSH so any language with an installed engine may be used; the software comes with VBScript, JScript, and PerlScript examples.
As of the most recent releases and going back a number of versions now, the programmability of 4NT / Take Command in the latest implementations (by means of «@REXX» and similar for Perl, Python, Tcl, Ruby, Lua, VBScript, JScript and the like and so on) generally uses the WSH engine.[12] The ZOC terminal emulator gets its ability to be programmed in Rexx by means of an external interpreter, one of which is supplied with the programme, and alternate Rexx interpreters can be specified in the configuration of the programme.[13][14] The MKS Toolkit provides PScript, a WSH engine in addition to the standard Perl interpreter perl.exe which comes with the package.
VBScript, JScript, and some third-party engines have the ability to create and execute scripts in an encoded format which prevents editing with a text editor; the file extensions for these encoded scripts is .vbe and .jse and others of that type.
Unless otherwise specified, any WSH scripting engine can be used with the various Windows server software packages to provide CGI scripting. The current versions of the default WSH engines and all or most of the third party engines have socket abilities as well; as a CGI script or otherwise, PerlScript is the choice of many programmers for this purpose and the VBScript and various Rexx-based engines are also rated as sufficiently powerful in connectivity and text-processing abilities to also be useful. This also goes for file access and processing—the earliest WSH engines for VBScript and JScript do not since the base language did not,[15] whilst PerlScript, ooRexxScript, and the others have this from the beginning.
WinWrap Basic, SaxBasic and others are similar to Visual Basic for Applications, These tools are used to add scripting and macro abilities to software being developed and can be found in earlier versions of Host Explorer for example. Many other languages can also be used in this fashion. Other languages used for scripting of programmes include Rexx, Tcl, Perl, Python, Ruby, and others which come with methods to control objects in the operating system and the spreadsheet and database programmes.[16] One exception is that the Zoc terminal emulator is controlled by a Rexx interpreter supplied with the package or another interpreter specified by the user; this is also the case with the Passport emulator.
VBScript is the macro language in Microsoft Outlook 97, whilst WordBasic is used for Word up to 6, Powerpoint and other tools. Excel to 5.0 uses Visual Basic 5.0. In Office 2000 forward, true Visual Basic for Applications 6.0 is used for all components. Other components use Visual Basic for Applications. OpenOffice uses Visual Basic, Python, and several others as macro languages and others can be added. LotusScript is very closely related to VBA and used for Lotus Notes and Lotus SmartSuite, which includes Lotus Word Pro (the current descendant of Ami Pro), Lotus Approach, Lotus FastSite, Lotus 1-2-3, &c, and pure VBA, licensed from Microsoft, is used in Corel products such as WordPerfect, Paradox, Quattro Pro &c.
Any scripting language installed under Windows can be accessed by external means of PerlScript, PythonScript, VBScript and the other engines available can be used to access databases (Lotus Notes, Microsoft Access, Oracle Database, Paradox) and spreadsheets (Microsoft Excel, Lotus 1-2-3, Quattro Pro) and other tools like word processors, terminal emulators, command shells and so on. This can be accomplished by means of the WSH, so any language can be used if there is an installed engine.
In recent versions of the Take Command enhanced command prompt and tools, the «script» command typed at the shell prompt will produce a list of the currently installed engines, one to a line and therefore CR-LF delimited.[17][18][19]
Examples[edit]
The first example is very simple; it shows some VBScript which uses the root WSH COM object «WScript» to display a message with an ‘OK’ button. Upon launching this script the CScript or WScript engine would be called and the runtime environment provided.
Content of a file hello0.vbs
WScript.Echo "Hello world" WScript.Quit
WSH programming can also use the JScript language.
Content of a file hello1.js
WSH.Echo("Hello world"); WSH.Quit();
Or, code can be mixed in one WSF file, such as VBScript and JScript, or any other:
Content of a file hello2.wsf
<job> <script language="VBScript"> MsgBox "hello world (from vb)" </script> <script language="JScript"> WSH.echo("hello world (from js)"); </script> </job>
Security concerns[edit]
Windows applications and processes may be automated using a script in Windows Script Host. Viruses and malware could be written to exploit this ability. Thus, some suggest disabling it for security reasons.[20] Alternatively, antivirus programs may offer features to control .vbs and other scripts which run in the WSH environment.
Since version 5.6 of WSH, scripts can be digitally signed programmatically using the Scripting.Signer object in a script itself, provided a valid certificate is present on the system. Alternatively, the signcode tool from the Platform SDK, which has been extended to support WSH filetypes, may be used at the command line.[21]
By using Software Restriction Policies introduced with Windows XP, a system may be configured to execute only those scripts which are stored in trusted locations, have a known MD5 hash, or have been digitally signed by a trusted publisher, thus preventing the execution of untrusted scripts.[22]
Available scripting engines[edit]
Note: By definition, all of these scripting engines can be utilised in CGI programming under Windows with any number of programmes and set up, meaning that the source code files for a script used on a server for CGI purposes could bear other file extensions such as .cgi and so on. The aforementioned ability of the Windows Script Host to run a script with multiple languages in it in files with a .wsh extension. Extended Html and XML also add to the additional possibilities when working with scripts for network use, as do Active Server Pages and so forth. Moreover, Windows shell scripts and scripts written in shells with enhanced capabilities like TCC, 4NT, etc. and Unix shells under interoperability software like the MKS Toolkit can have scripts embedded in them as well.
| Engine name | Scripting language implemented | Base language | File extensions | Availability | Produced by | Status | Initial release date | Encoded scripts | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VBScript | Microsoft VBScript | Microsoft Visual Basic | .vbs | Installed by default | Microsoft | default install | 1999 | Yes, .vbe | Default windows host script |
| JScript | Microsoft JScript | ECMAScript | .js | Installed by default | Microsoft | default install | 1999 | Yes, .jse | Default java script host |
| WinWrap Basic | WinWrap Basic | Basic | .wwb | In the main WWB installation | Polar Engineering | Standard functionality of WWB; Utilises both .NET and COM | 2004 | Yes | |
| PerlScript | Perl | Perl 5 | .pls | with ActiveState Perl | ActiveState | Open source | 1999 | Reportedly yes | |
| PScript | Perl | Perl 5, CGI functionality | .p, .ps | with MKS Toolkit | MKS | Commercial | 2001 | ||
| XBScript | xBase Scripting Engine | xBase (Clipper) | .xbs, .prg | Clipper | with XBScript sofrware | Commercial | |||
| LotusScript WSH | LotusScript | Microsoft Visual Basic (q.v.) | .nsf | Third party download | Service Desk Plus | Freeware | 2001 | ||
| RexxScript | Rexx | Rexx | .rxs, .rx, .rex | With some Rexx implementations | Various | Freeware | 1998 | ||
| ooRexxScript | Open Object REXX | REXX | .rxs | with Open Object Rexx or free from some third parties | Open Object Rexx team | Open source | |||
| PythonScript | Python | Python | .pys | SourceForge & with ActivePython | The Pywin32 project | Open source | |||
| TclScript | Tcl/Tk | Tcl/Tk | .tcls | SourceForge | ActiveState or third party | Open source | |||
| ActivePHPScript | PHP | PHP | .phps | with PHP | PHP team | Open source | |||
| PHPScript | PHP | PHP | .phps | with PHP | PHP team | Open source | Earlier version of ActivePHPScript | ||
| RubyScript | Ruby | Ruby | .rbs | with Ruby distribution | Ruby team | Open source | Yes | ||
| XLNTScript | XLNT | DCL | .xcs | with XLNT | Advanced Systems Concepts, Inc. | Commercial | 1997 | An OpenVMS DCL-based multi-purpose scripting application for Windows | |
| LuaScript | Lua | Lua | .lua | with Lua | Lua organisation | Open Source | |||
| Object REXX engine | Object REXX | Rexx | .rex, .rxs | with IBM Object REXX | IBM | Commercial | 2002 | ||
| XML Engine | XML parsing | Extended HTML, XML | .xml | with many XML implementations | Elf Data | de facto Default install | 2000 | Macintosh too | |
| Kixtart WSH Engine | Kixtart | KixTart, MS-DOS, Windows 95. Windows NT shells | .kix | with KixStart | Microsoft Netherlands | Windows Resource Kits and other resources | 1996 | Download from Microsoft or elsewhere, aka KixStart32 | |
| NullScript | NullScript | Null language | .ns | with NullScript | NullScript Organisation | Windows Resource Kits and other resources | 1999 | ||
| ForthScript | Forth | Forth | .fth, others | Forth | DMOZ | Open Source | |||
| Haskell Script | Haskell | Haskell | *.hsk (provisional), others | free download | Open Source | ||||
| XSLT WSH Engine | XSLT | XSLT | .xslt | free download | Open Source | ||||
| CobolScript WSH Engine | Cobol | Cobol | .cbl. .cob, .cb | Fujitsu Cobol 3 — free for educational use | Commercialware from Fujitsu free with free compiler for educators &c | Proprietary | |||
| Delphi scripting engine | Delphi | Delphi, a Pascal variant | .dlp, .del, . | In some Delphi distributions or resource kits | Commercial | 2003 | |||
| DMDScript | DMDScript | D, a major incrementation of C | .dmd | DMD Distributions, download | Freeware | Available on Web | 2014 | DMD | |
| C# Script | C# | Microsoft C#.NET | .cs. .c#, others | Source code available | Open Source, active development underway | unclear | 2013 | ||
| Small C Scripting Engine | C | C (K&R, Ansi) | .c, others | Various locations, check Web | Freeware | 2009 | |||
| JavaScript WSH Engine | JavaScript/Java | Java & variants | .java, .j, jva, others | With many JavaScript implementations | Sun/Other Java Organisations | Freeware | |||
| Take Command WSH Engine | 4NT/Take Command | TCC, the current version of 4NT p | .btm, .cmd, bat, others | Check JP Software | JP Software | Proprietary | 2015 | Early development | |
| 92Script WSH Engine | TI-89/92+/Voyager 200 TI-Basic | Calculator TI-Basic | .92bs | Project Web/FTP site | Various independent programmers | Experimental, Open Source | 2014 | «possible» | Beta Q4 2015 for main engine; graphing functionality (92Script/Tk) then or later |
| 48Script WSH Engine | HP-48 Calculator family on-board programming language | HP 48 Programming Language, distant relative of Forth, Basic, Lisp | .48s | Project Web/FTP site | Various independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned | Status as of 2015-09-30. Language has Lisp, Basic, Forth, and other influences. |
| Fortran Script | Fortran | Fortran 77 | .for, .ftn. f77, f90, f95 | Various | Various | Experimental proof-of-concept, academic exercise, shareware, commercial, open source. | 2000 | ||
| PascalScript | Object Pascal | Pascal 7 | .pas, .ops, other | Object Pascal | RemObjects | Freeware | 2001 | Can also be used with Delphi directly | |
| Lisp WSH Engine | Lisp | Lisp | .lisp, .lsp | Various Lisp tools | AutoLisp and others | Freeware or Shareware | |||
| BESEN | ECMA-JavaScript | Java and Variants | .bes, .bsn, others | SourceForge | BESEN Organisation | Open Source | 2011 | ||
| ECMAScript WSH engines | Java and Variants | Various | Various | Various | Various | Experimental, Freeware, Open Source, Shareware, Proprietary, Commercialware | 2005 | There are numerous ECMAScript implementations but not all have WSH engines | |
| CFXScript WSH Engine | Casio CFX-9850 and fx Calculator series on-board programming language | Casio Calculator Programming Language, as ported to various operating systems as CFW | .cfxb | Project Web/FTP Sites | independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned[23] | Status as of 2015-09-30. Language has elements of Basic, Forth, Fortran, and others. |
| SharpCalcScript WSH Engine | Sharp graphing calculators on-board programming language | Sharp S-Basic as ported to windows as NeusSFortran | .scsb | Project Web/FTP Sites | independent programmers | Experimental | 2015 | Planned | Status as of 2015-09-30. Also subsumes the S-Basic language of Sharp’s Pocket Computers. |
There have been suggestions of creating engines for other languages, such as LotusScript, SaxBasic, BasicScript, KiXtart, awk, bash, csh and other Unix shells, 4NT, cmd.exe (the Windows NT shell), Windows PowerShell, DCL, C, C++, Fortran and others.[24]
The XLNT language[25] is based on DCL and provides a very large subset of the language along with additional commands and statements and the software can be used in three ways: the WSH engine (*.xcs), the console interpreter (*.xlnt) and as a server and client side CGI engine (*.xgi).[26]
When a server implementing CGI such as the Windows Internet Information Server, ports of Apache and others, all or most of the engines can be used; the most commonly used are VBScript, JScript, PythonScript, PerlScript, ActivePHPScript, and ooRexxScript. The MKS Toolkit PScript program also runs Perl. Command shells like cmd.exe, 4NT, ksh, and scripting languages with string processing and preferably socket functionality are also able to be used for CGI scripting; compiled languages like C++, Visual Basic, and Java can also be used like this. All Perl interpreters, ooRexx, PHP, and more recent versions of VBScript and JScript can use sockets for TCP/IP and usually UDP and other protocols for this.
Version history[edit]
| Windows version | Shipped with WSH version | Last redistributable version |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 95 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows NT 4.0 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows NT Server 4.0 | None (separate redistributable) | 5.6 |
| Windows CE 3.0 | 1.0 (optional install on installer disc) | 2.0 |
| Windows 98 | 1.0 | 5.6 |
| Windows 98 Second Edition | 1.0 | 5.6 |
| Windows 2000 | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.7 |
| Windows 2000 Server | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.7 |
| Windows 2000 SP3, SP4 and SP5 | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows Me | 2.0 (also termed WSH 5.1) | 5.6 |
| Windows XP | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows XP SP3 | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2003 | 5.6 | 5.7 |
| Windows Vista | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2008 | 5.7 | Not applicable |
| Windows 7 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows 8 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2012 | 5.8 | Not applicable |
| Windows 10 | 5.812 | Not applicable |
| Windows Server 2016 | 5.812 | Not applicable |
The redistributable version of WSH version 5.6 can be installed on Windows 95/98/Me and Windows NT 4.0/2000. WSH 5.7 is downloadable for Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003. Recently[when?], redistributable versions for older operating systems (Windows 9x and Windows NT 4.0) are no longer available from the Microsoft Download Center.
Since Windows XP Service Pack 3, release 5.7 is not needed as it is included, with newer revisions being included in newer versions of Windows since.
See also[edit]
- JScript .NET
References[edit]
- ^ ?MSDN, «Windows Scripting Host» and «VBScript»
- ^ MSDN April 2000 edition, «Windows Scripting Host»
- ^ The VBScript Bible (1999)
- ^ Windows 2000 Server Resource Kit (documentation
- ^ a b «What Is WSH?». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 7 January 2018. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ «Windows Script Host Basics». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ «Windows Script Host Object Model». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ MSDN «VBA»
- ^ User’s Manual, Paint Shop Pro 8
- ^ Paint Shop Pro 8 help, «Automation»
- ^ main help file, Passport for Windows
- ^ Take Command documentation 18.00 documentation hard copy and Help file
- ^ Zoc v 6.0 help
- ^ Zoc 5.0 printed manual
- ^ MSDN documentation
- ^ Windows Office 97 & 2000 Bibles (Wiley)
- ^ Take Command version 18.00 documentation
- ^ JP Software Take Command-4NT-4Dos-4OS/2 site, bulletin board
- ^ Take Command 18.00 help
- ^ «Norman — Antivirus & Security Software for Home & Business». AVG.com. Archived from the original on 21 February 2006. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ LLC), Tara Meyer (Aquent. «Providing a Secure eXPerience». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on 10 November 2017. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ^ Windows Script Host 5.6 Boasts Windows XP Integration, Security, New Object Model Archived 2008-02-18 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ CasioCalc.com, msgs of 15.09.2016
- ^ «Notes/Domino 4 and 5 Forum : RE: Suggestion: Make LotusScript a script engine for Windows Scripting Host». Archived from the original on 2015-03-21. Retrieved 2015-03-12.
- ^ ASCI html help file
- ^ ASCI site
External links[edit]
- Windows Script Host
- Windows Script Host Reference on microsoft.com
Аннотация: Обсуждаются назначение и основные свойства сервера сценариев Windows Script Host (WSH). Описываются консольный и графический режимы работы сценариев WSH. Затрагиваются вопросы выбора языка для написания сценариев WSH
Сервер сценариев WSH. Языки сценариев VBScript и JScript
В двух предыдущих лекциях был рассмотрен язык командных файлов (язык командной оболочки), который в качестве инструмента для автоматизации работы поддерживается во всех версиях Windows. Однако с помощью командного интерпретатора cmd.exe трудно написать какую-либо сложную программу-сценарий (script): отсутствует полноценная интерактивность, нельзя напрямую работать с рабочим столом Windows и системным реестром и т. д.
Для исправления этой ситуации компанией Microsoft был разработан сервер сценариев Windows Script Host (WSH), с помощью которого можно выполнять сценарии, написанные, в принципе, на любом языке (при условии, что для этого языка установлен соответствующий модуль (scripting engine), поддерживающий технологию ActiveX Scripting). В качестве стандартных языков поддерживаются Visual Basic Script Edition (VBScript) и JScript.
Вообще говоря, принцип работы сценариев, поддерживаемых WSH, состоит в использовании объектов ActiveX, поэтому вначале мы очень кратко опишем возможности самой технологии ActiveX компании Microsoft.
Возможности технологии ActiveX
Напомним, что в Windows с самого начала для обеспечения обмена данными между приложениями была разработана технология связывания и внедрения объектов (Object Linking and Embedding, OLE). Вначале технология OLE использовалась для создания составных документов, а затем для решения более общей задачи — предоставления приложениями друг другу собственных функций (служб) и правильного использования этих функций. Технология, позволяющая одному приложению (клиенту автоматизации) вызывать функции другого приложения (сервера автоматизации) была названа OLE Automation. В основе OLE и OLE Automation лежит разработанная Microsoft базовая «компонентная» технология Component Object Model (COM). В общих словах, компонентное программное обеспечение — это способ разработки программ, при котором используются технологии создания программных модулей, подобные технологиям, применяемым для разработки аппаратных средств. Сложные элементные схемы собираются из стандартизированных микросхем, которые имеют четко определенные документированные функции. Разработчик может эффективно пользоваться такими микросхемами, не задумываясь об их внутренней структуре. В программных компонентах, написанных на каком-либо языке программирования, детали реализации используемых алгоритмов также скрыты внутри компонента (объекта), а на поверхности находятся общедоступные интерфейсы, которыми могут пользоваться и другие приложения, написанные на том же или другом языке.
В настоящее время термин OLE используется только по историческим причинам. Вместо него Microsoft с 1996 года использует новый термин — ActiveX, первоначально обозначавший WWW (World Wide Web) компоненты (объекты), созданные на базе технологии COM.
Технология ActiveX длительное время являлась ключевой в продуктах Microsoft. Наиболее полное воплощение она нашла в программах Microsoft Office, Internet Explorer, Internet Information Service (IIS). В эти продукты для управления соответствующими объектами автоматизации были встроены интерпретаторы специальных языков сценариев: VBScript (используется в Microsoft Office, Internet Explorer, IIS) и JScript (используется в Internet Explorer, IIS). Однако непосредственно в операционной системе, вне этих продуктов, выполнять сценарии, написанные на VBScript или JScript, было нельзя.
Сервер сценариев WSH является мощным инструментом, предоставляющим единый интерфейс (объектную модель) для специализированных языков (VBScript, JScript, PerlScript, REXX, TCL, Python и т. п.), которые, в свою очередь, позволяют использовать любые внешние объекты ActiveX. С помощью WSH сценарии могут быть выполнены непосредственно в операционной системе Windows, без встраивания в HTML-страницы.
Назначение и основные свойства WSH
WSH предъявляет минимальные требования к объему оперативной памяти, и является очень удобным инструментом для автоматизации повседневных задач пользователей и администраторов операционной системы Windows. Используя сценарии WSH, можно непосредственно работать с файловой системой компьютера, а также управлять работой других приложений (серверов автоматизации). При этом возможности сценариев ограничены только средствами, которые предоставляют доступные серверы автоматизации.
Перечислим только наиболее очевидные задачи, для автоматизации которых прекрасно подходят сценарии WSH.
- Организация резервного копирования на сетевой сервер файлов с локальной машины, которые отбираются по какому-либо критерию.
- Быстрое изменение конфигурации рабочего стола Windows в зависимости от задач, выполняемых пользователем.
- Автоматический запуск программ Microsoft Office, создание там сложных составных документов, распечатка этих документов и закрытие приложений.
- Управление работой приложений, не являющихся серверами автоматизации, с помощью посылки в эти приложения нажатий клавиш.
- Подключение и отключение сетевых ресурсов (дисков и принтеров).
- Создание сложных сценариев регистрации для пользователей.
- Выполнение задач администрирования локальной сети (например, добавление или удаление пользователей).
Создание и запуск простейших сценариев WSH
Простейший WSH-сценарий, написанный на языке JScript или VBScript — это обычный текстовый файл с расширением js или vbs соответственно, создать его можно в любом текстовом редакторе, способном сохранять документы в формате «Только текст».
Размер сценария может изменяться от одной до тысяч строк, предельный размер ограничивается лишь максимальным размером файла в соответствующей файловой системе.
В качестве первого примера создадим JScript-сценарий, выводящий на экран диалоговое окно с надписью «Привет!». Для этого достаточно c помощью, например, стандартного Блокнота Windows (notepad.exe) создать файл First.js, содержащий всего одну строку:
Тот же самый сценарий на языке VBScript, естественно, отличается синтаксисом и выглядит следующим образом:
Несмотря на то, что для работы этих двух сценариев достаточно всего одной строки, желательно сразу приучить себя к добавлению в начало файла информации о находящемся в нем сценарии: имя файла, используемый язык, краткое описание выполняемых действий. На языке JScript такая информация, оформленная в виде комментариев, может выглядеть следующим образом:
/*******************************************************************/ /* Имя: First.js */ /* Язык: JScript */ /* Описание: Вывод на экран приветствия */ /*******************************************************************/
На языке VBScript то же самое выглядит следующим образом:
'******************************************************************* ' Имя: First.vbs ' Язык: VBScript ' Описание: Вывод на экран приветствия '*******************************************************************
Для запуска сценариев WSH существует несколько способов.
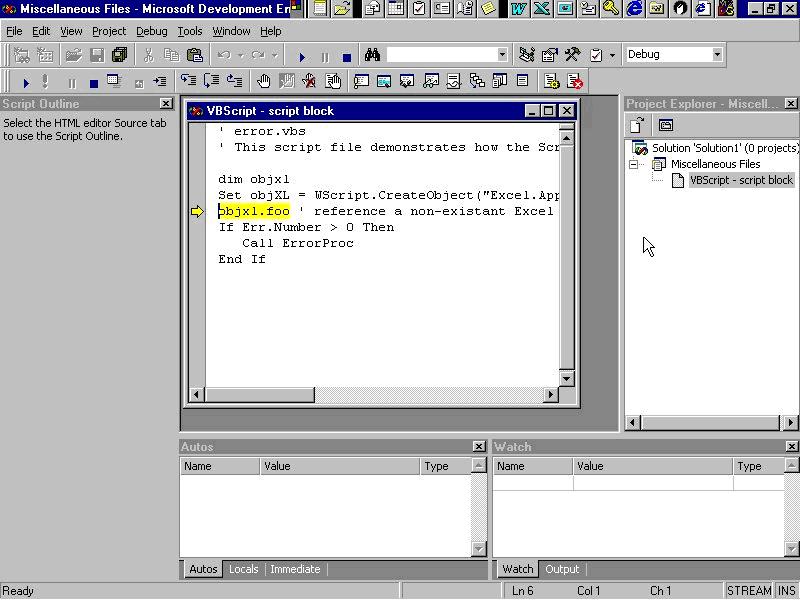
Запуск сценария из командной строки в консольном режиме
Можно выполнить сценарий из командной строки с помощью консольной версии WSH cscript.exe. Например, чтобы запустить сценарий, записанный в файле C:ScriptFirst.js, нужно загрузить командное окно и выполнить в нем команду
cscript C:ScriptFirst.js
В результате выполнения этого сценария в командное окно выведется строка «Привет!» (рис. 4.1)
Запуск сценария из командной строки в графическом режиме
Сценарий можно выполнить из командной строки с помощью (оконной) графической версии WSH wscript.exe. Для нашего примера в этом случае нужно выполнить команду
wscript C:ScriptFirst.js
Тогда в результате выполнения сценария на экране появится нужное нам диалоговое окно (рис. 4.2).
Таким образом, мы видим, что при запуске сценария в консольном режиме, вывод текстовой информации происходит в стандартный выходной поток (на экран), при запуске в графическом режиме — в диалоговое окно.
Всем привет, с вами автор блога scriptcoding.ru. В этой статье мы сделаем заключительный анализ сервера сценариев Windows Script Host и его возможностей.
На данном блоге собралось уже достаточно примеров скриптов и обучающих статей, что бы написать действительно качественный обзор по Windows Script Host, да, я такой, люблю публиковать материалы в обратном порядке… По ходу статьи я приведу примеры программного кода для Windows Script Host (коротко — WSH), а пока немного лирического предисловия.
Операционная система изначально создавалась как платформа для программистов, это теперь, мы привыкли, что Windows – это красочный интерфейс пригодный для посиделок в социальных сетях, разговорах по скайпу и игре в компьютерные игры. Но как бы там не было, ОС это как не как программа, а любую программу нужно отлаживать и исправлять в ней ошибки. Это теперь мы привыкли, что есть мышка, а ведь когда то все делали ручками – все команды вводили вручную, и если программисту это не в дикость, то рядовому пользователю такая картина покажется дикостью… Но, хотя времена уже не те, Windows по прежнему позволяет решать административные вопросы без сторонних приложений…
Содержание
- Windows Script Host — вначале была командная строка…
- И был день, и была ночь, и пришел Windows Script Host
- «Привет Мир», или пишем первые примеры по Windows Script Host…
Windows Script Host — вначале была командная строка…
Да, да, черный экран и взгляд в неизвестность… До появления Windows Script Host и PowerShell, командная строка являлась практический единственным средством для решения внештатных задач. Помню в детстве, мне частенько приходилось бегать с загрузочными дискетами и даже держать их в тайнике целыми стопками. Ну, а старый добрый Doom!!! Не знаю как теперь, но он у меня он работал только под управлением командной строки. Помню, в школе на уроках информатики нам приходилось изучать базовые команды CMD, типа, переход по каталогам и дискам, создание папок и файлов и так далее. Даже в нынешнее время приходится использовать базовые утилиты командной оболочки, взять тот же ping или ipconfig, когда я приходил к клиентам, у которых не работал интернет, эти утилиты шли в бой всегда..
Но, времена идут, и продвинутому пользователю хочется чего-то больше…
И был день, и была ночь, и пришел Windows Script Host
В простом варианте, сервер сценариев Windows Script Host – это программа, точнее две: wscript.exe (позволяет запускать сценарии в оконном интерфейсе) и cscript.exe (запуск скриптов в режиме командной строки). Так как Windows Script Host не требует установки и входит в состав практически всех версий Windows, то можно сразу приступать к программированию. У пользователя есть выбор, писать программный код на языке VBScript (файлы с расширением .vbs) или JScript (файлы с расширением .js). Те, кто самые ленивые, могут открыть текстовый блокнот и сразу приступить к делу, но лучше использовать редактор Notepad++. Я даже написал несколько статей по данному редактору, например — «Редактор Notepad++ — Знакомство«.
Оба языка программирования vbscript и jscript являются разработкой компании Майкрософт, их код частично может выполняться в теле интернет страницы, хотя, более эффективней они используются как прикладные сценарии.
Некоторые преимущества сценариев Windows Script Host по сравнению с рядовыми файлами командной оболочки:
- Расширяемость возможностей за счет подключения внешних объектов. Объекты – это файлы (библиотеки) с набором различных функций для выполнения определенных задач: создание графического интерфейса (WindowSystemObject), работа со ссылками на сайте (Chilkat.Spider) или работа с протоколом HTTP (Компоненты для создания HTTP запроса), однако, Windows Script Host предоставляет и собственные объекты, например, работа с файловой системой (FileSystemObject), или взаимодействие с системой (WScript.Shell).
- Взаимодействие с Windows Management Instrumentation (Инструментарий управления Windows). WMI содержит практически неограниченные возможность для администрирования системы, с его помощью можно получить доступ практически к каждому элементу (как оборудование, так и системная информация).
- Универсальность использования. Нет необходимости устанавливать программные пакеты по несколько сотен мегабайт, вы можете написать сценарий и потом запустить его на другом компьютере, да и компиляция отсутствует, что позволяет в любой момент изменить программный код.
«Привет Мир», или пишем первые примеры по Windows Script Host…
Пожалуй, я не буду нарушать традицию…
Вывод сообщения «Привет Мир» на языке Jscript:
WScript.Echo("Привет Мир");
Вывод сообщения «Привет Мир» на языке VBscript:
Как видим все довольно просто, но… хочется чего-то большего, поэтому приведу вам пример сценариев Windows Script Host, которые будут выводить список имен пользователей системы и их SID (уникальный идентификатор, который назначается каждой учетной записи):
Программный код на языке VBSCRIPT:
'-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------' Примеры программного кода для сервера Windows Script Host' Список имен пользователей и их SID' windows_script_host_UserSID.vbs'------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ' включаем проверку переменныхOptionExplicit dim objWMIService, colItems, objItem, list list = "Имя пользователя и его SID" & vbCrLf & vbCrLf' получаем доступ к WMISet objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:.rootcimv2")' получаем доступ к классу WMI - Win32_UserAccountSet colItems = objWMIService.ExecQuery("SELECT * FROM Win32_UserAccount") ' начинаем перебор значенийForEach objItem In colItems list = list &"Имя" & vbTab & vbTab & objItem.Name & vbCrLf list = list &"Значение SID" & vbTab & objItem.SID & vbCrLf & vbCrLfNext ShowInNotepad(list) 'Процедура создания временного файла с даннымиSub ShowInNotepad(StrToFile)dim FSO, TempPath, TxtFileSet FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")TempPath = CreateObject("WScript.Shell").ExpandEnvironmentStrings("%TEMP%") & "" & FSO.GetTempNameSet TxtFile = FSO.CreateTextFile(TempPath)TxtFile.WriteLine(StrToFile)TxtFile.CloseCreateObject("WScript.Shell").Run "wordpad.exe " & TempPathEndSub
Программный код на языке JSCRIPT:
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------// Примеры программного кода для сервера Windows Script Host// Список имен пользователей и их SID// windows_script_host_UserSID.js//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- var objWMIService1, colItems1, objItem1, list1; list1 ="Имя пользователя и его SIDnn";// получаем доступ к WMIobjWMIService1 = GetObject("winmgmts:.rootcimv2");// получаем доступ к классу WMI - Win32_UserAccountcolItems1 =new Enumerator(objWMIService1.ExecQuery("SELECT * FROM Win32_UserAccount")); // начинаем перебор значенийfor(;!colItems1.atEnd(); colItems1.moveNext()){ objItem1 = colItems1.item(); list1 +="Имяtt"+ objItem1.Name+"n"; list1 +="Значение SIDt"+ objItem1.SID+"nn";} ShowInNotepad(list1) //Функцияя создания временного файла с даннымиfunction ShowInNotepad(StrToFile){var FSO, TempPath, TxtFile; with(WScript){ FSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject"); TempPath = CreateObject("WScript.Shell").ExpandEnvironmentStrings("%TEMP%")+""+ FSO.GetTempName(); TxtFile = FSO.CreateTextFile(TempPath); TxtFile.WriteLine(StrToFile); TxtFile.Close(); CreateObject("WScript.Shell").Run("wordpad.exe "+ TempPath);}}
Как видим, не все так сложно, как бы казалось, кстати, данный пример я взял из книги Windows Script Host – новичок, там я собрал 132 примера сценариев на обоих языках. Я стараюсь всегда приводить программный код как на языке VBScript так и на языке Jscript, что бы можно было провести сравнительный анализ.
Хорошо, теперь придерживаясь этикета, давайте разберем программный код примеров.
Логика работы идентична, вначале происходит объявление переменных (ключевые слова dim и var). Видим, что имена переменных практически одинаковые, смотрите «Урок 2 по JScript — типы данных и переменные» и «Урок 2 по VBScript: Переменные«. Обратите внимание, что в отличии от прикладных языков программирования, в скриптах Windows Script Host не нужно указывать тип данных.
Переменная list будех хранить основную информацию относительно имени и значении SID. Мы присваиваем переменной сначала информативную фразу и добавляем дважды перевод строки (n и vbCrLf). Далее с помощью функции CreateObject происходит подключение внешних классов WMI, которые и позволят выполнить поставленную задачу.
Далее нам надо обработать все найденные идентификаторы. Для этих целей мы применили цикл FOR и FOR EACH – смотрите статьи «Урок 6 по VBScript: Циклы for…next и for each…next» и «Урок 9 по JScript — оператор цикла for«. Все найденные результат будут записываться в переменную. Обратите внимание, что для объедения строк мы использовали Windows Script Host операторы «&» и «+».
В самом конце происходит вызов пользовательской процедуры (функции) ShowInNotepad, принципы создания пользовательских процедур и функций смотрите в статье «Урок 3 по JScript — создание пользовательских функций JS«. В результате, будет открыто приложение WordPad.exe, в котором будут содержаться имена идентификаторов и их значений.
Сегодня поговорим об очень полезном компоненте операционной системы Windows — это Windows Script Host, если быть конкретней, то о языке Jscript, на котором можно писать эти самые WSH скрипты.
Начнем мы с небольшой теории, так как мы еще не затрагивали Windows Script Host.
Содержание
- Что такое Windows Script Host?
- Возможности Windows Script Host
- Примеры написания WSH скриптов
- Выводим сообщение на JScript
- Работа с Excel на JScript
- Работа с текстовым файлом и Excel на JScript
Что такое Windows Script Host?
Windows Script Host – сервер выполнения сценариев (скриптов) на таких языках как VBScript и JScript. WSH разработан компанией Microsoft и он является компонентом операционной системы Windows начиная с Windows 98.
Первоначально для администрирования использовались только bat-файлы, но их возможности ограничены (хотя также очень полезны!), поэтому компания Microsoft предложила такой вариант WSH. Возможности WSH-скриптов уже гораздо больше, ведь данные скрипты уже создаются на полноценных языках, таких как VBScript и JScript.
Именно о JScript мы сегодня и поговорим.
Но о VBScript мы тоже скажем пару слов.
VBScript – это скриптовой язык программирования, созданный компанией Microsoft для разработки скриптов в операционной системе Windows. Другими словами, это один из языков, которые может интерпретировать Windows Script Host. И из названия ясно, что VBScript основан на языке Visual Basic, поэтому тем, кто знаком с Visual Basic будет просто писать WSH-скрипты на этом языке программирования.
JScript – скриптовой язык программирования, с помощью которого можно создавать (писать) скрипты, которые будут интерпретироваться компонентом Windows Script Host.
С первого взгляда JScript во многом похож на JavaScript (ECMAScript), это и естественно, так как синтаксис, некоторый объекты, методы, свойства аналогичны JavaScript. Но это все же не JavaScript, а именно JScript. JavaScript (ECMAScript) ориентирован на объекты браузера, а JScript уже на компоненты операционной системы Windows. Но как мы сказали, они похожи, поэтому те, кто владеют языком программирования JavaScript с легкостью перейдут на JScript.
Возможности Windows Script Host
А теперь давайте поговорим о том, зачем нам нужно писать эти самые WSH-скрипты, т.е. об их возможностях и преимуществах:
- Возможность взаимодействия с файловой системой (файлы, каталоги), системным реестром, ресурсами локальной сети;
- Взаимодействие с такими продуктами как Microsoft Word, Excel и другими программами. Т.е. например, мы можем создавать excel файлы или конвертировать другие форматы в excel файлы;
- Взаимодействие с ActiveX-технологиями, например: ActiveX Data Object (ADO) — доступ к базам данных разных форматов, Active Directory Service Interface (ADSI) — работа со службами каталогов Active Directory;
- Наличие полноценного языка программирования, с помощью которого можно реализовывать сложные алгоритмы, которые например нельзя реализовать с помощью bat файлов.
Скрипты на JScript имеют расширение .js такое же, как и на JavaScript за исключением того, что эти скрипты обрабатывает не браузер, а Windows Script Host.
На JScript возможно даже реализация графического интерфейса через объект браузера (internet explorer), согласитесь это уже полноценная программа.
Перейдем к практике, так как у нас сегодня статья по основам, мы рассмотрим простые примеры написание скриптов на JScript.

Примечание! Для того чтобы попробовать примеры ниже скопируйте код любого примера в текстовый файл и сохраните с расширением .js, например, test.js.
Выводим сообщение на JScript
В WSH имеется специальный объект, на основе которого мы уже можем в дальнейшем создавать другие объекты, настраивать взаимодействие с программами, файлами и другими компонентами операционной системы.
Этим объектом является WScript. Пример его использования на Jscript:
var WshShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell");
Тем самым мы создали объект, с помощью которого мы можем получить доступ к компонентам Windows.
Например, вывести сообщение:
//Выводим сообщение
WshShell.Popup( "Моя первая программа на JScript");
//Завершаем работу с объектом
WScript.Quit();
Работа с Excel на JScript
Теперь давайте создадим другой объект, например, Excel файл:
// создаем объект для работы с Excel
var Excel = WScript.CreateObject("Excel.Application");
// добавляем книгу в Excel
Excel.WorkBooks.Add;
//добавляем в первую ячейку нужный текст
Excel.Cells(1,1).Value ="Мой текст для вставки в Excel";
// делаем активным наш Excel документ
Excel.Visible = true;
Как Вы понимаете, мы имеем доступ ко всем свойствам в Excel, другими словами, мы можем изменить внешний вид, задать формат ячеек и многое другое. Для примера давайте поэкспериментируем с некоторыми свойствами:
//создаем объект для работы с Excel
var Excel = WScript.CreateObject("Excel.Application");
//добавляем книгу в Excel
Excel.WorkBooks.Add;
//выделяем нужный нам диапазон
Excel.Range("A1:C1").Select;
//объединяем ячейки в нашем диапазоне
Excel.Selection.MergeCells = true;
//добавляем нужный текст
Excel.Selection.Value ="Мой текст для вставки в Excel";
//делаем наш текст жирным
Excel.Selection.Font.Bold = true;
//изменяем в 4 ячейке формат данных на числовой с двумя знаками после запятой
Excel.Cells(1, 4).NumberFormat = "00.00"
//вставляем в 4 ячейку нашу цифру
Excel.Cells(1, 4).Value = 1234;
//выровняем по центру наше значение
Excel.Cells(1, 4).HorizontalAlignment = 3;
//делаем активным наш Excel документ
Excel.Visible = true;
Работа с текстовым файлом и Excel на JScript
Я думаю с Excel все понятно, теперь давайте прочитаем какие-нибудь данные из текстового файла и запишем их в нашу Excel таблицу, для закрепления наших знаний.
Для того чтобы настроить взаимодействие с файловой системой, необходимо создать объект FileSystemObject, который работает с файлами и каталогами. Вот пример небольшого скрипта, который считывает данные из текстового файла построчно и записывает их в Excel документ, причем мы все строки пронумеруем и зададим ширину столба для данных в Excel:
Пример текстового файла:
Первая строка Вторая строка Третья строка
Пример скрипта:
//создаем объект FileSystemObject
var FileSysObj = WScript.CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject");
//объявляем нужные нам переменные
var nRow = 1, num=1;
var txt = '';
//открываем файл my.txt в той же папке, параметр 1 для чтения файла
var myText = FileSysObj.OpenTextFile('my.txt', 1 );
//как и раньше создаем объект для работы с Excel
var Excel = WScript.CreateObject("Excel.Application");
//добавляем книгу в Excel
Excel.WorkBooks.Add;
//циклом считываем строки из файла, пока они не закончатся
// и записываем их в наш Excel документ
while (!myText.AtEndOfStream) {
//считываем строку
txt = myText.ReadLine();
//нумеруем наши строки в Excel
Excel.Cells(nRow, 1).Value = num;
//выставляем ширину вторго столбца
Excel.Columns(2).ColumnWidth = 15;
//записываем данные в ячейку
Excel.Cells(nRow, 2).Value = txt;
//увеличиваем переменные на 1
nRow++;
num++;
}
//закрываем файл
myText.Close();
//делаем активным наш Excel документ
Excel.Visible = true;
//выходим из скрипта
WScript.Quit();
Как всегда весь код я прокомментировал, поэтому неясностей возникнуть не должно.
Я думаю для начала этого вполне достаточно, в дальнейшем мы будем разбирать задачи посложней, ведь при помощи Jscript в WSH можно очень много чего сделать, гораздо больше, чем с помощью простых bat файлов. До встречи!
R0emember batch files? They were simple, easy to program, and very productive since many tasks could be automated.
Windows still allows batch files, but batch files don’t allow any control over the Windows shell and Windows environment. By introducing the Windows Scripting Host, Microsoft has introduced a script and COM based engine that can access the Windows Shell, the computer’s environment and network settings using simple VBScript or JScript code. In addition you can even access any COM component, including your own. This column will introduce you to the basics of how the scripting host works and how you can incorporate its features into your Visual FoxPro Applications.
What you need to get started
The Windows Scripting Host ships with Windows 2000 and Windows 98, and is also available as part of the NT Option Pack when installed on Windows NT 4.0. Older Windows NT and 95 can download the Windows Scripting Host files from the Microsoft Website at: http://msdn.microsoft.com/scripting/. In addition to the core scripting engine, a series of whitepapers, code samples, and technical articles can be downloaded as well.
What is the Windows Scripting Host (WSH)?
The Windows Scripting Host is a language independent scripting engine. Scripting languages such as VBScript and JScript can be used to drive many processes. The same language that is used in client-side scripts in Internet Explorer (IE) or server-side scripts in Internet Information Server (IIS) can now be hosted by the Windows Operating System itself.
Prior to the release of the WSH, the only scripting language that existed for Windows was MS-DOS batch files. Although powerful, batch files lacked the control over the Windows Operating System that is truly required. The WSH provides this capability.
Scripting Files
Unlike scripting in Active Server Pages, where the language can be specified with tags, the same is not true for script files used by the Windows Scripting Host. Instead, the WSH relies on the file extension to determine which language to use. If the script file ends in VBS, VBScript is used. If the script file ends in JS, JScript is used.
The following files are simple hello world examples the point out the differences between VBScript and JScript:
VBSscript:
'hello world.vbs
Dim WSHShell
Set WSHShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
WSHShell.Popup "Hello World"
JScript:
// hello world.js
var WSHShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell");
WSHShell.Popup("Hello World")
The following is a more complex example that uses scripting to open and control Microsoft Excel:
'This VBScript File opens Excel and creates a workbook
Dim objXL,oWorkbook
Set objXL = WScript.CreateObject("Excel.Application")
objXL.Visible = TRUE
Set oWorkbook = objXL.WorkBooks.Add
With objXL
.Cells(1,1) = oWorkbook.Sheets.Count
End With
Running these script files is a very simple task. In Explorer, you can click the right mouse key over the file, and select Open. Alternatively, you can double-click the item in Explorer as well. Yet another alternative is to use the Run Method of the Windows Scripting Shell Object. This technique will be illustrated when the Shell Object is discussed in more detail. Furthermore, you can execute these script files directly from your applications using the ShellExecute() API simply by specifying the filename.
A quick word about debugging and handling errors
No programming environment is complete with a full-featured debugging environment and the Windows Scripting Host is no exception. As far as error handling is concerned, VBScript does not have a global error handler. Instead, errors need to be handled on an in-line basis. The following code demonstrates how to deal with errors on an in-line basis:
On Error Resume Next
dim objxl
Set objXL = WScript.CreateObject("Excel.Application")
objxl.foo ' reference a non-existent Excel Method
If Err.Number > 0 Then
Call ErrorProc
End If
Sub ErrorProc
msgbox err.description
End Sub
If no error trapping exists, you will be prompted with a dialog asking if you wish to debug the application. Figure 1 illustrates how the code will appear in the script debugger.
Figure 1 — The Microsoft Script Debugger uses the same IDE as Visual InterDev and Visual J++ 6.0
The scripting host objects
There are two primary objects contained within the Windows Scripting Host. The following code illustrates how these objects can be created:
WSHshell = CreateObject("Wscript.Shell")
WSHNetwork = CreateObject("Wscript.Network")
Both the shell and network objects are hosted by the wshom.ocx ActiveX Control.
Complete documentation for the WSHShell and WSHNetwork Objects can be found by navigating to the following URLS:
For the WSHShell Object:
http://www.microsoft.com/iis/support/iishelp/iis/htm/asp/wsho7t84.htm
For the WSHNetwork Object:
http://www.microsoft.com/iis/support/iishelp/iis/htm/asp/wsho20qc.htm
Wscript Methods
CreateObject (strProgid [,strPrefix])
This method creates an instance of an automation server. This article began with an example of using the Shell Object to create an instance of Microsoft Excel. The ability also exists to create instances of your own COM Components as well. The first parameter specifies the ProgID of the automation server instance you wish to create.
oMyObject = Wscript.Createobject("MyObject.MyClass")
The second parameter relates to instances where the new object supports an event model. For example, if the object you create has an event called MyEvent, you can write a handler for the event. The only requirement is that a procedure prefix must be specified:
oMyObject = Wscript.Createobject("MyObject.MyClass","eventhandler_")
Sub eventhandler_myevent()
'Your custom event code goes here...
End Sub
ConnectObject (strObjName,strPrefix)
The ConnectObject method allows developers to hook into the event model for objects that have already been created. To illustrate, an object called oMyObject already exists. The oMyObject object has an event called myevent.
oMyObject = Wscript.Createobject("MyObject.MyClass")
Wscript.ConnectObject oMyObject, "eventhandler_"
Sub eventhandler_myevent()
'Your custom event code goes here...
End Sub
DisconnectObject (ObjID)
The DisconnectObject method allows for the uncoupling of an object instance and an event handler. It is important to note that once the event handler is uncoupled, the object instance remains in tact.
Wscript.DisconnectObject(oMyObject)
Echo(...argN)
The Echo Method provides a host independent mechanism for dialoging the user. Within the Windows GUI, where Wscript.EXE is used, the Echo Method is manifested as a Messagebox:
Wscript.Echo "Cool"
script files can also be run from the command prompt. If the previous example was contained in a file called FOO.VBS, the following code would display the word Cool on the command line:
C:Temp>cScript foo.vbs
Microsoft (R) Windows Script Host Version 5.1 for Windows
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation 1996-1999. All rights reserved.
Cool
Sleep
The Sleep Method suspends program execution for a specified period of time. The following example suspends execution for 2 seconds before continuing:
Wscript.Sleep 2000
Shell Object Properties and Methods
Environment: This property provides access to environment collection. Information such as number of processors, paths, OS, etc can be determined from this collection.
oEnv = wshshell.environment
For Each x In oEnv
?oEnv
Next x
The following is a partial listing of some typical environmental variables:
NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORSOSPROCESSOR_ARCHITECTUREPROCESSOR_IDENTIFIERWINDIR
So, to find out the number of processors:
Numprocessors = oEnv.Item("NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS")
Like most collections, if you want to find out how many members are contained in the collection, you can refer to the Count Property:
Numitems = oEnv.Count
To be compliant with the Java Language, collections in the Windows Scripting Host also support the Length Property, which provides the same functionality as the Count Property:
Numitems = oEnv.Length
SpecialFolders: This property provides access to the collection of Windows Shell Folders. The following is a listing of folders:
AllUsersDesktopAllUsersStartMenuAllUsersProgramsAllUsersStartupDesktopFavoritesFontsMyDocumentsNetHoodPrintHoodProgramsRecentSendToStartMenuStartupTemplates
To find the actual path of the desktop folder, issue this line of code:
DesktopPath = WSHShell.SpecialFolders("Desktop")
CreateShortcut (strPathname)
This method creates and returns a shortcut object. The following block of code illustrates how to create a desktop shortcut:
*/ Read desktop path using WshSpecialFolders object
DesktopPath = WSHShell.SpecialFolders("Desktop")
*/ Create a shortcut object on the desktop
MyShortcut = ;
WSHShell.CreateShortcut(DesktopPath + "Shortcut to MyFile.lnk")
*/ Set shortcut object properties and save it
FileName = GetFile()
If !Empty(FileName)
FileDir = JustPath(FileName)
With MyShortcut
.TargetPath = Filename
.WorkingDirectory = FileDir
.Save
EndWith
Endif
The CreateShortcut Method returns a WSHShortcut Object. This object is only exposed through the CreateShortcut Method. The WSHShortcut object has the following properties:
Arguments— Parameters to a shortcut object.Description— A description of a shortcut object.Hotkey— The hot key of a shortcut object.IconLocation— The icon location of a shortcut object.TargetPath— The target path of a shortcut object.WindowStyle— The window style of a shortcut object.WorkingDirectory— The working directory of a shortcut object.
The WSHShortcut Object only has one method, Save(), which saves the shortcut object to the file system.
ExpandEnvironmentSettings (*strString)*
This method expands a process environment variable and returns the result. A typical environment variable is WINDIR. The following code illustrates how this method works:
Fullpath = WSHShell.ExpandEnvironmentStrings("%windir%notepad.exe, 0")
Popup (strText, [natSecondsToWait], [strTitle], [natType])
This method displays the Window MessageBox. Unlike the existing MessageBox Function, the Popup method accepts an optional argument to clear the dialog after a specified amount of time. The following line of code illustrates how the Popup Method works:
WSHShell.Popup("Message",1,"Title",64)
RegDelete(strName)
RegRead(strName)
RegWrite(strName, anyValue, [strType] )
The Windows Scripting Host Shell Object provides three methods for working with the Windows Registry. With these methods, entries can be created, written, read, and deleted. If you attempt to write to a key that does not exist, the key will be created. The following code illustrates how these three methods work:
To create a new key:
WSHshell.RegWrite("HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftVisualFoxPro6.0DesktopJVP",'Default Value')
Then, to modify the value:
WSHshell.RegWrite("HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftVisualFoxPro6.0DesktopJVP",'New Value')
Next, to just read a value from a key:
WSHshell.RegRead("HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftVisualFoxPro6.0DesktopJVP")
Finally, to delete a key:
WSHshell.RegDelete("HKCUSoftwareMicrosoftVisualFoxPro6.0DesktopJVP")
Run(strCommand, [intWindowStyle], [blnWaitOnReturn])
The Run Method creates a new process that executes a specified command with a specified window style. In addition to being able to specify the command and the window style, a third parameter can be used to determine if script execution should pause until the new process has terminated.
Applications windows can be started in several states. The following outlines the various options available:
SW_HIDE= 0SW_MINIMIZE= 6SW_RESTORE= 9SW_SHOW= 5SW_SHOWMAXIMIZED= 3SW_SHOWMINIMIZED= 2SW_SHOWMINNOACTIVE= 7SW_SHOWNA= 8SW_SHOWNOACTIVATE= 4SW_SHOWNORMAL= 1
The following code starts Notepad with a normal window:
WSHshell.Run("notepad",1)
This code starts Notepad with a maximized window. In addition, the user must close Notepad before control will return to Visual FoxPro:
WSHshell.Run("notepad",3,.T.)
Fully qualified paths can be used to denote a file to execute. The following code starts Visio:
WSHshell.Run("D:VISIOVISIO32.EXE")
Also, script files can be executed with the Run Method as well:
WSHshell.Run("hello world.vbs")
WSHshell.Run("hello world.js")
Network Object Properties and Methods
ComputerName: This property denotes the name of the computer.
ComputerName = WSHNetwork.ComputerName
UserDomain: This property denotes the domain to which the user belongs.
DomainName = WSHNetwork.UserDomain
UserName: This property denotes the ID of the currently logged-in user.
UserName = WSHNetwork.UserName
AddPrinterConnection(strLocalName, strRemoteName, [bUpdateProfile], [strUser], [strPassword] )
This method maps a network printer to a local resource.
WSHNetwork.AddPrinterConnection("LPT1","\serverprinter_share",.T.,"UserID","Password")
Of special interest here is the third parameter, bUpdateProfile. If this parameter is set to .T., the user profile for the local machine is updated to restore the printer mapping the next time the user logs onto the machine and network.
EnumNetworkDrives
This method returns a collection of drive mappings. The following code loops through the collection of network drive mappings:
oDrives = WSHNetwork.EnumDriveMappings
item = -1
For Each x In oDrives
item = item + 1
If Mod(item,2) = 0
?"Drive Letter: ",x
Else
?"Network Resource: ",x
Endif
Next x
Like other collections, the drive mapping collection supports both the Count and Length Properties, as well as the Item() Method.
EnumPrinterConnections
This method works just like the EnumNetworkDrives, with the exception that the collection returned represents printers, not drive mappings:
item = -1
For Each x In oPrinters
item = item + 1
If Mod(item,2) = 0
?"Printer Name: ",x
Else
?"Network Resource: ",x
Endif
Next x
MapNetworkDrive( strLocalName, strRemoteName, [bUpdateProfile], [strUser], [strPassword] )
This method works just like the AddPrinterConnection Method, with the exception that a local drive to a network resource is created:
WSHNetwork.MapNetworkDrive("z:","\serverserver_share",.T.,"User","Password")
RemoveNetworkDrive(strName, [bForce], [bUpdateProfile] )
This method removes a specified network drive mapping. Optionally, you can force the removal even if the resource is being used. An optional third parameter specifies if the user profile should be updated:
WSHNetwork.RemoveNetworkDrive("z:",.T.,.T.)
Or
WSHNetwork.RemoveNetworkDrive("\serverserver_share",.T.,.T.)
RemovePrinterConnection( strName, [bForce], [bUpdateProfile] )
This method works just like the RemoveNetworkDrive method, with the exception that a printer resource is being removed:
WSHNetwork.RemovePrinerConnection("LPT1",.T.,.T.)
Or
WSHNetwork.RemovePrinterConnection("\serverprinter_share",.T.,.T.)
SetDefaultPrinter(strName)
This method sets the default printer:
WSHNetwork.SetDefaultPrinter("\serverprinter_share")
Summary
The ability to work with the Windows Registry, create desktop shortcuts, map and view network resources, all required you to know how to use extensive Windows API Functions, or a 3rd party DLL. The Windows Scripting Host provides a simple and elegant set of objects with simple interfaces that allow you to accomplish many of these tasks. Perhaps your application requires special Registry Entries. Perhaps you have been tasked with developing a utility that modifies the default printer or dynamically maps network resources. All of these tasks can easily be accomplished with the Windows Scripting Host.
The good news is that the Windows Scripting Host is part of the Operating System beginning with Windows 98 and Windows 2000. For older systems you need to make sure WSH is installed on any client workstation that uses your application. One approach to this problem is to add a method to your application class that tests to see if the Windows Scripting Host is installed. If it is not, prompt the user through the process of both downloading and installing WSH.
The Windows Scripting Host is yet another valuable tool to add to your toolbox!